NZQA unit standard 20556 version 4
advertisement

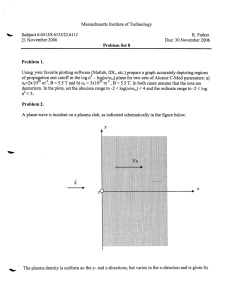
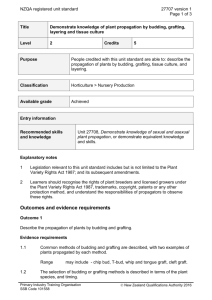
NZQA Expiring unit standard 20556 version 4 Page 1 of 5 Title Demonstrate knowledge of plant propagation Level 2 Credits 10 Purpose People credited with this unit standard are able to: explain the differences between sexual and asexual plant propagation; describe the propagation of plants from seed; describe the propagation of plants from division; describe the propagation of plants by cuttings; describe the propagation of plants by budding and grafting; describe the propagation of plants by tissue culture; describe propagation of plants by layering; and outline plant breeder’s rights. Classification Horticulture > Nursery Production Available grade Achieved Explanatory notes None. Outcomes and evidence requirements Outcome 1 Explain the differences between sexual and asexual plant propagation. Evidence requirements 1.1 Sexual and asexual propagation are defined. 1.2 Sexual and asexual propagation are compared in terms of their advantages and disadvantages for plant propagators. Range three advantages and three disadvantages for each method. Outcome 2 Describe the propagation of plants from seed. Evidence requirements 2.1 Seed sources and the storage of seed to maintain viability are described. 2.2 Conditions required for seed germination are described. New Zealand Horticulture Industry Training Organisation SSB Code 101558 New Zealand Qualifications Authority 2016 NZQA Expiring unit standard Range 20556 version 4 Page 2 of 5 seed treatments, germination requirements, seed viability. 2.3 Seed raising media, containers for seed raising, and soil conditions for fieldsown seed are described. 2.4 Seed sowing in containers and in the field is described. Range two methods for each. 2.5 The maintenance of conditions for seed germination and seedling establishment in containers and in the field is described. 2.6 Plants grown from seed are named, and the reasons for growing them from seed are stated. Range ten plants named, two reasons for each. Outcome 3 Describe the propagation of plants from division. Evidence requirements 3.1 Common types of divisions are described, and two examples of plants grown by each method are listed. Range crowns, rhizomes, tubers, bulbs, corms, runners. 3.2 Division timing and the selection of suitable parent plant material are described in general terms. 3.3 The establishment and after care of divided plant material are described. 3.4 Two reasons for growing plants from division are stated. Outcome 4 Describe the propagation of plants by cuttings. Evidence requirements 4.1 Common types of cuttings are described, with two examples of plants propagated by each method. Range stem cuttings, leaf cuttings, root cuttings, hardwood cuttings, semihardwood cuttings, soft wood cuttings. 4.2 The selection of suitable cutting material is described in terms of plant type and timing. 4.3 The selection of suitable propagation media and containers, and suitable soils for setting cuttings in the field, is described. New Zealand Horticulture Industry Training Organisation SSB Code 101558 New Zealand Qualifications Authority 2016 NZQA Expiring unit standard 4.4 20556 version 4 Page 3 of 5 Suitable environments for cutting propagation are described. Range greenhouse or protected environments, in the field. 4.5 The care of cuttings until rooted is described. 4.6 Two reasons for propagating plants from cuttings are stated. Outcome 5 Describe the propagation of plants by budding and grafting. Evidence requirements 5.1 Common methods of budding and grafting are described, with two examples of plants propagated by each method. Range may include chip bud, T bud, whip and tongue graft, cleft graft. 5.2 The selection of budding or grafting methods is described in terms of the plant species, and timing. 5.3 The selection of scion material and rootstocks and their compatibility is described in terms of the plants to be propagated. 5.4 The aftercare of budded and grafted plants is described. 5.5 Two reasons for growing plants by budding and grafting are stated. Outcome 6 Describe the propagation of plants by tissue culture. Evidence requirements 6.1 Common tissue culture methods are described in general terms, with two examples of plants propagated by each method. Range may include meristem culture, embryo culture. 6.2 The selection of the plant parts, the culture medium, and timing, are described in terms of the plants to be propagated and the culture method used. 6.3 The culture process is described. Range 6.4 may include hygiene, parent material, dissection, culture, deflasking, hardening off. Two reasons for propagating plants by tissue culture are stated. New Zealand Horticulture Industry Training Organisation SSB Code 101558 New Zealand Qualifications Authority 2016 NZQA Expiring unit standard 20556 version 4 Page 4 of 5 Outcome 7 Describe propagation of plants by layering. Evidence requirements 7.1 Common methods of plant layering are described with one example of plants propagated by each method. Range simple layering, mound layering, tip layering, air layering. 7.2 The layering method selection is described in terms of plant species propagated and timing. 7.3 The establishment and after care of layered material are described. 7.4 Two reasons for propagating plants by layering are stated. Outcome 8 Outline plant breeder’s rights. Evidence requirements 8.1 The forms of protection available and the rights of plant breeders and licensed growers are outlined in general terms. Range may include Plant Variety Rights, trademarks, copyright, patents. Replacement information This unit standard has been replaced by unit standard and 27707 and unit standard 27708. This unit standard replaced unit standard 814 and unit standard 12404. This unit standard is expiring. Assessment against the standard must take place by the last date for assessment set out below. Status information and last date for assessment for superseded versions Process Version Date Last Date for Assessment Registration 1 23 February 2004 31 December 2014 Revision 2 24 February 2006 31 December 2014 Review 3 19 April 2012 31 December 2014 Reinstatement 4 17 September 2015 31 December 2019 New Zealand Horticulture Industry Training Organisation SSB Code 101558 New Zealand Qualifications Authority 2016 NZQA Expiring unit standard 20556 version 4 Page 5 of 5 Consent and Moderation Requirements (CMR) reference 0032 This CMR can be accessed at http://www.nzqa.govt.nz/framework/search/index.do. Please note Providers must be granted consent to assess against standards (accredited) by NZQA, before they can report credits from assessment against unit standards or deliver courses of study leading to that assessment. Industry Training Organisations must be granted consent to assess against standards by NZQA before they can register credits from assessment against unit standards. Providers and Industry Training Organisations, which have been granted consent and which are assessing against unit standards must engage with the moderation system that applies to those standards. Requirements for consent to assess and an outline of the moderation system that applies to this standard are outlined in the Consent and Moderation Requirements (CMR). The CMR also includes useful information about special requirements for organisations wishing to develop education and training programmes, such as minimum qualifications for tutors and assessors, and special resource requirements. New Zealand Horticulture Industry Training Organisation SSB Code 101558 New Zealand Qualifications Authority 2016