Carolinas Healthcare Grand Rounds - Afternoon Session

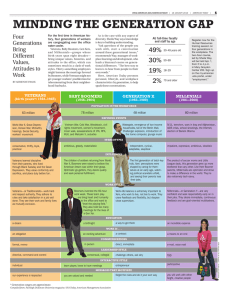
Generations in the Workforce
WHAT SETS THEM APART
What You Remember
Reveals Your Age….
Do you remember when smoking wasn’t hazardous to your health?
The Veterans (oldest generation still working) How They Learn
New is not necessarily better
Not innovative with new ideas
Like structure, schedules and procedures
Brain processes new ideas into old mental framework
Some refuse to work with technology (too overwhelming a learning curve, others jump in)
Want clear expectations and guidelines
Must memorize the basics
School Experiences for
Hard work
Veterans
Respected their elders
Children were to be seen & not heard
Felt an obligation to make the grade
Performance based on individual ability
Little feedback unless negative
More intrinsic reward for good performance
Learned from history (other’s experiences)
Small class size, one curriculum for all
No special ed (students no where in sight)
Virtually never tested with standardized tests – less comparison to others
Did you ever use one of these???
The Veteran’s First Computer
Changes in the Workforce
Veterans have experienced the most change in their lifetime. They have had to adapt to:
Computers
Communication channels changing
World getting smaller
Keeping up with rapid increases in information
Move from content to process
Marketing to Veterans
Faith in the government and national institutions
Want quality but believe standard options are fine (not luxury)
Loyal customers that follow the rules
How Boomers Learn
Want things to fit into the “big picture”
Want recognition for how well they have done
Team oriented, work well in groups
Like to explore and analyze, look at different views
Follow instructions well
Good with content
Boomer’s Educational
Experiences
Overwhelmed the school system starting in
1950, large class sizes
Ability grouped (red birds and blue birds)
Question authority but respect position
See life as an adventure (and school)
Emphasis on team work (cohort education)
Boomer’s Educational
Experiences
Need silence to concentrate
Were told “you are lucky to be here, others are standing in line to get in.”
Want to feel valued
No special ed students in school but honors courses in a few subjects
Rarely tested and not for school performance (PSAT, SAT)
Remember these……
Boomer’s First Computer
Marketing to Boomers
Are individualistic so they like
“customized and custom-made products”
Want to look successful (lots of stuff)
Seek self-improvement
Products/services that help them reach a balanced life (work/home)
Like technology but see the problems that come with it
How Gen Xers Learn
Task oriented – like to learn new skills
Speed is important
Self-paced learning, independent learning
Want to have fun while they learn
Informal learning environments are best
Hate group work
Want feedback from teacher/boss
Gen X Educational
Experiences
Learned to rely on self
Distrust authority
Seek challenging environment
(career education emphasis)
Want feedback on progress
Want to do things their way – like no rules and freedom on assignments
Gen X Educational
Experiences
Had special education classrooms in school but separated
Had honors programs
Funding cut to education
Testing “mania” began with them
First daycare centers arose with them
Many latch-key kids
Remember these…..
Gen X’s First Computer
Was this your first video game?
Was this your first calculator and cell phone?
Marketing to Xers
Can spot a phony
Peer to peer referral
Like technology
Like products and services with options
Millennial School
Experiences
Many private schools, charter schools, magnet schools – all to meet the needs of the individual child –many, many choices
School uniforms, child safety, high performance standards, character education, cooperative learning and community service
Millennial School Experiences
Goal oriented – outcome based education
(what’s in it for me)
School is a means to an end – one must endure until the next level
Interactive, participatory and engaging – are consulted by adults
Everything 24/7 and available electronically
No “grunt work” - must do “meaningful work”, participate in decisions
International flavor, celebrate diversity, different is okay
Millennial School Experiences
Motivated by working with bright, motivated and moral people
Student makes judgments about truth and believability of what is taught
Classroom mainstreamed – multiple levels based on ability and interest
Constantly tested and compared to peers
(learned to take tests so now of little use for college admissions)
Feel pressure for high achievement
How Millennials Learn
Try it their way – always looking for better, faster way of doing things
Prefer graphics before text, reading of excerpts
Like small and fast processing technology – best when networked
Want instant gratification and frequent rewards
(spot)
How Millennials Learn
Focus on skill development – not memorization of what they perceive they don’t need to know
Productivity is key – not attendance – so make it worthwhile or they won’t come
Have different critical thinking skills based on their high tech world not thought processing
(need help here)
Rely on teacher to facilitate learning
Group think and interaction
This is what millennials grew up with?
Their Idea of Computer
Technology
What Do Businesses and Colleges/
Universities Need to Know about
Today’s College Students and
Graduates
Here Come the Girls
Boys Issues in K-12
For Every 100 Girls Who….
Number of Boys
Enroll in Kindergarten 116
Enroll in Ninth Grade
Enroll in Twelfth Grade
Are Suspended from K-12
Are Expelled from K-12
Diagnosed with Learning Disability 276
Enroll in the gifted and talented program
94
101
98
250
335
The Boys Project. http://www.boysproject.net/statistics.html
Boys and Their Educational
Choices
For Every 100 Girls Who….
Number of Boys
Graduate from High School
Enroll in College
Earn an Associates Degree
Earn a Bachelors Degree
Earn a Masters Degree
Earn a Doctorate
73
62
92
96
77
67
The Boys Project. http://www.boysproject.net/statistics.html
First Time Freshman Enrollments by Gender –
50 Years (numbers in thousands)
1600
1400 )
(54.8%
1200
(45.2%)
1000
800
600
400
200
0
19
55
19
60
19
65
19
70
19
75
19
80
Males
Females
19
85
19
90
19
95
20
00
20
04
College Graduation Projections (numbers in thousands) (61% of degrees will go to women)
1050
950
850
750
650
550
450
350
250
20
05
-6
Assoc. Degree Male
Assoc. Degree Female
Bach. Degree Male
Bach. Degree Female
(62.6%)
(37.4%)
(60%)
(40%)
20
06
-7
20
07
-8
20
08
-9
20
09
-1
0
20
10
-1
1
20
11
-1
2
20
12
-1
3
20
13
-1
4
At Your Tables
Discuss:
When you were an undergraduate student and had a paper assigned in a class, what was your process for preparing for and writing the paper?
Where did your reference material come from?
How long did it take?
Would it be done differently today?
When you were in medical school, what was the process you were taught to diagnose and treat a condition?
What reference materials did you have?
How is it done now?
Ambitions
Source: Industry Week, March, 1998.
Most popular college majors:
• Medicine • Engineering
•
Education/teaching •
Law and politics
•
Business and marketing
•
Computer science
Most sought after qualities in careers:
•
•
Responsibility
Independence
•
Idealistic and committed coworkers
•
Creativity
•
•
Most common job trends :
Multi-taskers
• Seek security & benefits
Stay with company that offers a challenge
Difference in Values
They have witnessed their baby boomer parents coming home from stressed jobs, exhausted, falling asleep at the dinner table; and don’t want that for themselves.
They are a generation who is interested in a life with value and meaning – they do not aspire to what the “boomers” aspire to – they want something different.
True Multi-taskers
Millennials have lived programmed lives and are already quite capable of learning several jobs simultaneously and performing them admirably.
Millennials will change careers many times (retool/recycling skills).
To retain them, smart employers will encourage Millennials to try out different careers within the same company.
Salary Expectations of
Millennials
Realistically, what do you expect your starting salary will be when you begin working?
Millennials
$15-20K 7.7%
$21-30K 29.3%
$31-40K 27.0%
$41-50K
$50K+
15.9%
7.0%
Approximately
65% felt they would earn
$40K or less
Not sure 12.5%
Future Odds
How likely is it that someday you will:
• Work for yourself/own business?
• Have lifestyle you grew up with?
% Indicating Somewhat or Very Likely
64.3%
93.4%
How important will a two-income household be in reaching your lifestyle goals?
• Somewhat to very Important
• Not Important
%
77.4%
22.6%
Quality of Life?
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Rank order of items that contribute to a good quality of life
(% ranking item in top 3 on a scale of 1-8)
Having a secure future for my family
Time to enjoy family/children
Having family/children
Having a great job
Having good friends
Having plenty of money
Having plenty of free time
%
70.2%
69.9%
65.0%
54.7%
50.7%
38.6%
38.1%
Your Generation in the Future
Someday your generation will be raising kids, running corporations and occupying high political office. When that day comes, which areas of American life will be better, the same or worse than today because of your generation?
3=better
2=same
1=worse
Will be better, the same or worse than today because of your generation?
3=better
2=same
1=worse
• Technology
• Race Relations
• Economy
• Schools
• Arts/Culture mean
2.90
2.47
2.23
2.09
2.21
Will be better, the same or worse than today because of your generation?
3=better
2=same
1=worse
• Foreign Affairs
• Government
• Family Life
• Religion
• Crime/Public Order mean
2.13
2.02
2.01
1.93
1.79
Importance of Career
Components
Millennials felt the following career elements would be very important:
Respected on the Job
Opportunity for Professional Development
Ability to Have an Impact on the World
Importance of Career
Components
Items thought to be somewhat important:
Access to Information and Expression of Personal Opinion
Having High Job Prestige
Working with Inspiring Colleagues
Geographic Location of Job
Receive Guidance and Direction from Supervisor
Participating in Company Decisions
Independence/Professional Autonomy
Using Creativity on the Job
Lots of Responsibility
Flexible Work Hours
Dress Code Appropriate to Work Environment
Importance of Job Benefits
Benefits thought to be very important
Health Insurance
Salary Growth
Plans like 401K
Life Insurance
Bonuses
Employer-paid Retirement
Benefits thought to be unimportant
Stock Options
Profit Sharing
Jobs in Lifetime
How many jobs millennials thought they would hold in their lifetime?
1-3
4-6
7-10
35.7%
41.5%
16.5%
Over 10 6.2%
64% expect to have 4 or more jobs
Reasons US Workers Change
Jobs
In 2006, 21% of US workers made voluntary job changes for the following reasons:
Growth and earnings potential (30%)
Time and flexibility (23%)
Financial compensation (22%)
Culture and work environment (22%)
Benefits (12%)
Supervisor relationship (10%)
Travel and development (9%)
Management climate (9%) Benefit News
Changing Workforce
Workers are demanding the ability to balance their work and personal responsibilities.
Workers are not afraid of changing jobs.
The idea that the best way to grow financially and otherwise is to stay with one employer has been eroding to the point of extinction.
Younger workers and those earning $15,000 or less were the most likely to change jobs.
The cost of turnovers range from $7,000 for hourly employees to $30,000 for mid-level managers and
$80,000 for technical or senior level management
(Center for Workforce Learning).
Charlotte Biz, March 2007
What can managers do?
1. Mentor their employees
• About how the organization runs, what makes people of different generations work well together. Teach people skills not just medical processes.
Great leaders can motivate all people by balancing processes and people’s needs for the good of the organization
Messages that Motivate
Veterans
Your experience is respected here
What has and hasn’t worked in the past is relevant
Perseverance is valued
Boomers
You are important to our success
Your contribution is unique and important
We need you
Messages that Motivate
Gen Xers
Do it your way
There aren’t a lot of rules here
We’re not very corporate
Millennials
You will work with other bright, creative people
You can help turn this organization around
You can be a hero here
We value independent workers
Your boss will help you succeed
2. Communicate with employees
• Encourage them to develop trust with others and empower people to do their jobs. Ask for input rather than telling them what to do.
Open communication reduces resistance.
3. Value their values
• Want work-life balance. They value family and friends and want to work their eight hour day and go home. Older workers think long hours show your loyalty and productivity.
Younger workers often get things done faster. They value efficiency and effectiveness and doing things faster.
4. Focus on Retention
• People leave for several reasons: older workers retire but younger workers often leave feeling unvalued.
• Have strategies to retain both groups.
• Older generations like monetary rewards, younger generations like time off work.
Questions (if we have time)
What are the greatest challenges you face with the multiple generations in your area?
What strengths do the younger generations have that you did not at their age?
Has anyone discovered “a great truth” in working with the younger generations that you can share with us?