NZQA registered unit standard 20448 version 2 Page 1 of 6
advertisement

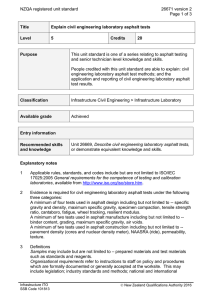
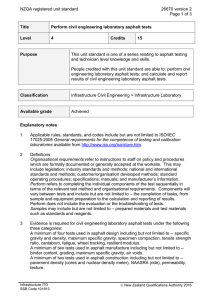
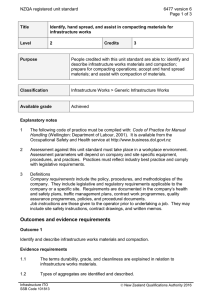
NZQA registered unit standard 20448 version 2 Page 1 of 6 Title Operate a self-propelled roller for asphalt surfacing Level 3 Credits 10 Purpose People credited with this unit standard are able to: demonstrate knowledge of asphalt paving compaction equipment and asphalt paving compaction; identify, control, and monitor health and safety hazards and adverse effects on the environment of asphalt compaction operations; perform operator servicing and maintenance on a self-propelled roller; prepare for rolling asphalt surfacings; control a self-propelled roller on asphalt construction sites; compact asphalt pavement surfacings; and move a self-propelled roller from site to site. Classification Pavement Surfacing > Asphalt Surfacing Available grade Achieved Entry information Critical health and safety prerequisites Unit 16702, Demonstrate knowledge and skills for driving on a road for endorsement R (rollers), or demonstrate equivalent knowledge and skills. Explanatory notes 1 The following legislation and requirements apply to this unit standard, and must be complied with: Health and Safety in Employment Act 1992; Traffic Regulations 1976; Operator Safety Manual for Earthmoving Machinery, Infrastructure ITO, available at http://www.infrastructureito.org.nz; New Zealand Transport Agency specifications, available at http://www.nzta.govt.nz/resources/; NZTA P9: Specification for Construction of Asphaltic Concrete Paving; NZTA P9P (Auckland): Specification for Construction of Asphaltic Concrete Paving; NZTA P11: Specification for Open Graded Porous Asphalt; Company procedures; Local authority requirements. Any legislation or other requirements superseding any of the above will apply, pending the review of this unit standard. 2 Personal protective equipment must be used throughout operations in accordance with company procedures. Infrastructure ITO SSB Code 101813 New Zealand Qualifications Authority 2016 NZQA registered unit standard 20448 version 2 Page 2 of 6 3 When working on the road, candidates must hold a current full driver licence of the appropriate class for the gross vehicle mass of the vehicle to be used for assessment and, where required by legislation, the appropriate licence endorsement for the vehicle being driven. 4 Assessment against this unit standard must be based on evidence from a workplace context. 5 Evidence is required of both static and vibrating compaction. 6 Definitions Company procedures refers to all documented policies, procedures and methodologies of the candidate’s employer at the time of training including but not limited to those relating to health, safety, environment, quality, and operations. Job requirements take account of site conditions to meet contract specifications, and accord with procedures and work instructions written in quality manuals. OGPA means Open Graded Porous Asphalt. SMA means stone mastic asphalt. Walk round means to walk around a machine or equipment inspecting it, and its environment, for hazards and removing hazards that may impair operation. Outcomes and evidence requirements Outcome 1 Demonstrate knowledge of asphalt paving compaction equipment. Evidence requirements 1.1 Static and vibrating self-propelled rollers are compared in terms of their use on asphalt pavements. Range static – three-wheeled steel, multi wheel pneumatic-tyred, tandem steel; vibrating – single drum (walk behind), tandem drum (both vibrating), combination tandem drum (one vibrating and one static), combination tandem (vibrating drum and pneumatic tyre). 1.2 Effects of rollers on asphalt surfacings are described in terms of static weight, impact force, and frequency and amplitude of vibration. 1.3 Ballast is described in terms of its effect on compaction. 1.4 Equipment is described in terms of its use for rolling. Range 1.5 rolling – breakdown, secondary, finishing or ‘ironing out’. Equipment is described in terms of its suitability for different site conditions. Range Infrastructure ITO SSB Code 101813 slope, pavement shape, physical site constraints, access, clearances, obstructions. New Zealand Qualifications Authority 2016 NZQA registered unit standard 1.6 Equipment is described in terms of limitations on use of rollers. Range 1.7 dead load, live load, vibration hazards. Equipment is described in terms of suitability for specified mix types and layers. Range 1.8 20448 version 2 Page 3 of 6 mix types – dense-graded, open-graded, SMA; layers – levelling, high fatigue base, structural, wearing. Equipment is described in terms of maintenance requirements. Range water system, scraper operation, cleaning rollers, cleaning tyres, tyre pressure, tyre wear, oil leaks, fuel leaks. Outcome 2 Demonstrate knowledge of asphalt paving compaction. Evidence requirements 2.1 Rolling operation is described in terms of roller type, sequence, pattern, and number of passes required to meet job requirements. Range 2.2 Compaction is described in terms of influence of climate, mat, and roller type. Range 2.3 sequence – initial and/or breakdown, secondary and/or principal, final and/or finish. climate – road temperature, ambient temperature, wind conditions; mat – thickness, temperature. Compaction is described in terms of methods for achieving uniformity at joints and edges. Range joints – transverse, longitudinal, hot, cold. 2.4 Compaction is described in terms of avoiding mat pickup, deformation, overrolling, and cracking. 2.5 Compaction is described in terms of methods for achieving specified shape, density, and uniformity of mat. Outcome 3 Identify, control, and monitor health and safety hazards and adverse effects on the environment of asphalt compaction operations. Evidence requirements 3.1 Health hazards are identified and the procedures and equipment for controlling them are explained in accordance with company procedures and legislation. Infrastructure ITO SSB Code 101813 New Zealand Qualifications Authority 2016 NZQA registered unit standard 20448 version 2 Page 4 of 6 3.2 Safety hazards are identified and the procedures and equipment for controlling them are explained in accordance with company procedures and legislation. 3.3 Adverse effects on the environment are identified and the procedures and equipment for controlling them are explained in accordance with company procedures and legislation. 3.4 Health and safety hazards are monitored in accordance with company procedures and legislation. 3.5 Adverse effects on the environment are monitored in accordance with company procedures and legislation. Outcome 4 Perform operator servicing and maintenance on a self-propelled roller. Evidence requirements 4.1 Machinery is checked according to operator servicing requirements and minor adjustments are made in accordance with manufacturer’s instructions. Range 4.2 Where routine servicing indicates that it is required, specialist maintenance is reported to specialist mechanic or supervisor in accordance with company procedures. Range 4.3 includes but is not limited to – fuel, lubricants, water levels, hydraulic fluid level, cleanliness, machine controls and gauges. may include but is not limited to – tyres, batteries, fuel lines, coolants, hydraulic pressure. Routine servicing and maintenance are documented in accordance with company procedures. Outcome 5 Prepare for rolling asphalt surfacings. Evidence requirements 5.1 Job requirements are confirmed in accordance with company procedures and contract and site requirements. 5.2 Prestart safety and equipment checks are carried out in accordance with manufacturer’s instructions and company procedures. Range Infrastructure ITO SSB Code 101813 includes – walk round, safety equipment, cleanliness, leaks, fuel, oil, water; may include but is not limited to – scrapers, water sprayers, tyre pressure, hydraulic hoses. New Zealand Qualifications Authority 2016 NZQA registered unit standard 5.3 Startup checks and procedures are followed in accordance with manufacturer’s instructions and company procedures. Range 5.4 20448 version 2 Page 5 of 6 includes but is not limited to – vibrator amplitude and frequency, governor on engine. Machine is manoeuvred into position in accordance with company procedures and job requirements. Outcome 6 Control a self-propelled roller on asphalt construction sites. Evidence requirements 6.1 Roller is manoeuvred safely in accordance with the Operator Safety Manual for Earthmoving Machinery and site safety requirements. 6.2 Roller is controlled on slopes in accordance with manufacturer’s instructions and the Operator Safety Manual for Earthmoving Machinery. 6.3 Roller is manoeuvred with smoothness of movement and machine stability. 6.4 Rollers are controlled to avoid damage to services, people, plant, roadside furniture, kerb, pavement edge, or adjacent structures. 6.5 Vibration of vibrating rollers is monitored and controlled to avoid damage to pavement, surfacing, or adjacent structures. 6.6 Shutdown procedures are followed in accordance with manufacturer’s instructions. Outcome 7 Compact asphalt pavement surfacings. Evidence requirements 7.1 Rolling pattern, sequence, and number of passes is carried out in accordance with job requirements. 7.2 Roller operations are carried out without crushing aggregate, mat pickup, deformation, over-rolling, and cracking. 7.3 Rolling uniformity of compaction and shape including at longitudinal and transverse joints is achieved. 7.4 Compaction of surfacing adjacent to structures is carried out without damage to machine or structures. Infrastructure ITO SSB Code 101813 New Zealand Qualifications Authority 2016 NZQA registered unit standard 20448 version 2 Page 6 of 6 Outcome 8 Move a self-propelled roller from site to site. Evidence requirements 8.1 Roller is driven on road in accordance with Traffic Regulations 1976 and local authority requirements. 8.2 Roller is loaded onto, parked on, and unloaded from transporter in accordance with manufacturer’s and transporter operator’s instructions. excludes – permits, securing, transporting. Range Planned review date 31 December 2016 Status information and last date for assessment for superseded versions Process Version Date Last Date for Assessment Registration 1 27 October 2005 31 December 2013 Review 2 15 March 2012 N/A Consent and Moderation Requirements (CMR) reference 0101 This CMR can be accessed at http://www.nzqa.govt.nz/framework/search/index.do. Please note Providers must be granted consent to assess against standards (accredited) by NZQA, before they can report credits from assessment against unit standards or deliver courses of study leading to that assessment. Industry Training Organisations must be granted consent to assess against standards by NZQA before they can register credits from assessment against unit standards. Providers and Industry Training Organisations, which have been granted consent and which are assessing against unit standards must engage with the moderation system that applies to those standards. Requirements for consent to assess and an outline of the moderation system that applies to this standard are outlined in the Consent and Moderation Requirements (CMR). The CMR also includes useful information about special requirements for organisations wishing to develop education and training programmes, such as minimum qualifications for tutors and assessors, and special resource requirements. Comments on this unit standard Please contact Infrastructure ITO askus@infratrain.co.nz if you wish to suggest changes to the content of this unit standard. Infrastructure ITO SSB Code 101813 New Zealand Qualifications Authority 2016