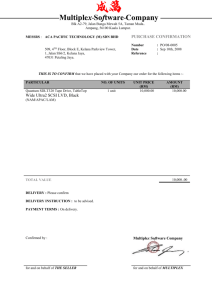
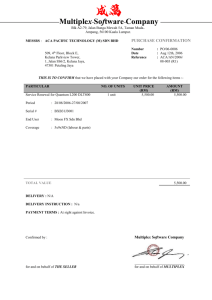
AUTOMOTIVE ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS Demonstrate knowledge of automotive multiplex and databus applications, and
advertisement

21090 28-Jun-16 1 of 4 AUTOMOTIVE ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS Demonstrate knowledge of automotive multiplex and databus applications, and diagnose faults level: 5 credit: 6 planned review date: December 2008 sub-field: Motor Industry purpose: People credited with this unit standard are able to identify and distinguish automotive multiplex and databus applications, and diagnose faults in multiplex wiring systems. entry information: Open. accreditation option: Evaluation of documentation and visit by NZQA and industry. moderation option: A centrally established and directed national moderation system has been set up by the NZ Motor Industry Training Organisation. special notes: 1 The following legislation must be consulted and followed where applicable: Consumer Guarantees Act 1993; Fair Trading Act 1986; Health and Safety in Employment Act 1992. 2 Reference to company policy means that the standard must comply with any policies, procedures, and requirements of the company involved, and the ethical codes of relevant professional management organisations. 3 The practical skills of this unit standard can be assessed in the workplace or in simulated workplace conditions off-job. For the purpose of off-job assessment the term customer means the training provider. New Zealand Qualifications Authority 2016 21090 28-Jun-16 2 of 4 AUTOMOTIVE ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS Demonstrate knowledge of automotive multiplex and databus applications, and diagnose faults Elements and Performance Criteria element 1 Identify and distinguish automotive multiplex and databus applications. performance criteria 1.1 The description distinguishes differences between multiplex wiring and conventional wiring according to the manufacturers’ specifications. Range: 1.2 The explanation shows a typical operational sequence for a multiplex circuit. Range: 1.3 may include but is not limited to – weight reduction, easier assembly, simplicity, greater reliability, simpler fault diagnosis and repair, cost savings, design flexibility. The description identifies approaches manufacturers use for multiplexing electrical systems consistent with the manufacturers’ specifications. Range: 1.5 may include but is not limited to – turning on a lamp. The description identifies features of multiplex wiring according to the manufacturers’ specifications. Range: 1.4 includes but is not limited to – replacing partly or completely by a single common bus, power and control signals, high power IC (integrated circuit) devices, electronic switching. includes but is not limited to – each load has its own interface connected to the multiplex bus, loads are grouped together and share a common electronics module. Multiplex component functions are described according to the manufacturers’ specifications. Range: components may include but are not limited to – control module, input/output module, display module, data link cable. element 2 New Zealand Qualifications Authority 2016 21090 28-Jun-16 3 of 4 AUTOMOTIVE ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS Demonstrate knowledge of automotive multiplex and databus applications, and diagnose faults Diagnose faults in multiplex wiring systems. performance criteria 2.1 Safe working practices are observed throughout the task. Range: personal safety, safety of others, safe operation of test equipment, vehicle and machine safety, preventing damage to circuits and components. 2.2 Suitable equipment is selected and used to enable testing to be carried out. 2.3 Test points are identified according to the vehicle manufacturers’ specifications. 2.4 The self-test codes are activated, read, and interpreted, with reference to the manufacturers’ literature, and any faulty circuit is identified. 2.5 Faults are isolated according to test procedure findings. Range: 2.6 any slave module, data link connection. The cause of the fault is determined according to the manufacturers’ specifications. Comments on this unit standard Please contact the NZ Motor Industry Training Organisation jlane@mito.org.nz if you wish to suggest changes to the content of this unit standard. Please Note Providers must be accredited by the Qualifications Authority or a delegated interinstitutional body before they can register credits from assessment against unit standards or deliver courses of study leading to that assessment. Industry Training Organisations must be accredited by the Qualifications Authority before they can register credits from assessment against unit standards. Accredited providers and Industry Training Organisations assessing against unit standards must engage with the moderation system that applies to those standards. New Zealand Qualifications Authority 2016 21090 28-Jun-16 4 of 4 AUTOMOTIVE ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS Demonstrate knowledge of automotive multiplex and databus applications, and diagnose faults Accreditation requirements and an outline of the moderation system that applies to this standard are outlined in the Accreditation and Moderation Action Plan (AMAP). The AMAP also includes useful information about special requirements for providers wishing to develop education and training programmes, such as minimum qualifications for tutors and assessors, and special resource requirements. This unit standard is covered by AMAP 0014 which can be accessed at http://www.nzqa.govt.nz/site/framework/search.html. New Zealand Qualifications Authority 2016