NZQA registered unit standard 20715 version 2 Page 1 of 5
advertisement
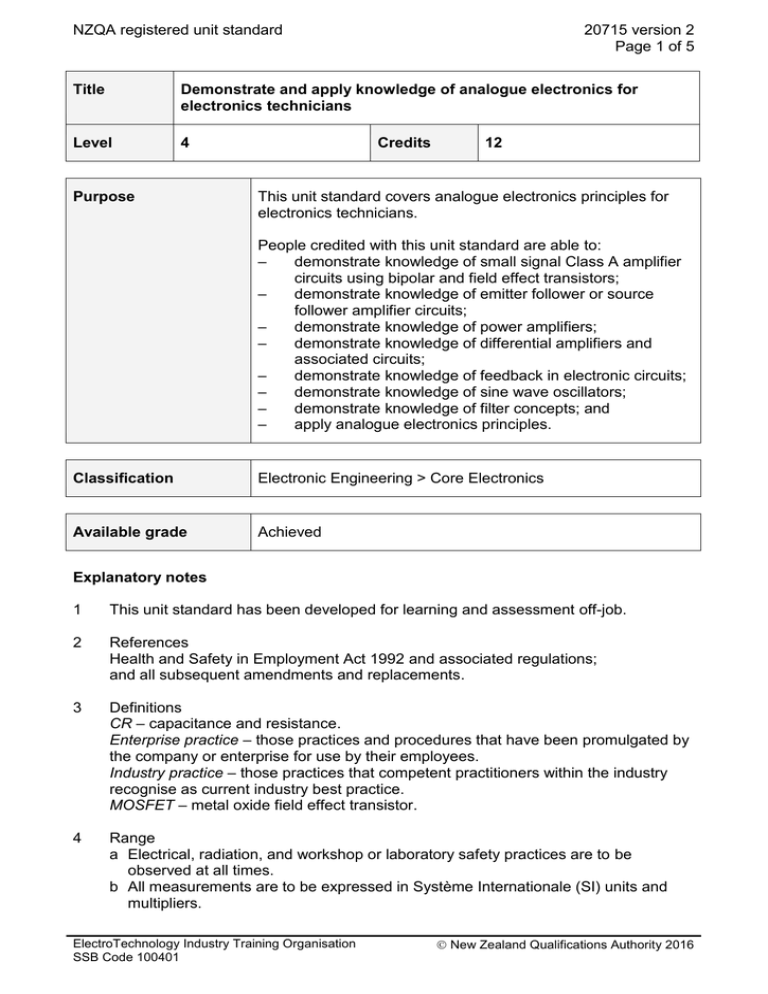
NZQA registered unit standard 20715 version 2 Page 1 of 5 Title Demonstrate and apply knowledge of analogue electronics for electronics technicians Level 4 Purpose Credits 12 This unit standard covers analogue electronics principles for electronics technicians. People credited with this unit standard are able to: – demonstrate knowledge of small signal Class A amplifier circuits using bipolar and field effect transistors; – demonstrate knowledge of emitter follower or source follower amplifier circuits; – demonstrate knowledge of power amplifiers; – demonstrate knowledge of differential amplifiers and associated circuits; – demonstrate knowledge of feedback in electronic circuits; – demonstrate knowledge of sine wave oscillators; – demonstrate knowledge of filter concepts; and – apply analogue electronics principles. Classification Electronic Engineering > Core Electronics Available grade Achieved Explanatory notes 1 This unit standard has been developed for learning and assessment off-job. 2 References Health and Safety in Employment Act 1992 and associated regulations; and all subsequent amendments and replacements. 3 Definitions CR – capacitance and resistance. Enterprise practice – those practices and procedures that have been promulgated by the company or enterprise for use by their employees. Industry practice – those practices that competent practitioners within the industry recognise as current industry best practice. MOSFET – metal oxide field effect transistor. 4 Range a Electrical, radiation, and workshop or laboratory safety practices are to be observed at all times. b All measurements are to be expressed in Système Internationale (SI) units and multipliers. ElectroTechnology Industry Training Organisation SSB Code 100401 New Zealand Qualifications Authority 2016 NZQA registered unit standard 20715 version 2 Page 2 of 5 c Candidates are expected to have memorised and to be able to use the following formula: AOL ACL . 1 . AOL d Use of non-programmable calculators is permitted during assessments. e All activities and evidence presented for all outcomes and evidence requirements in this unit standard must be in accordance with legislation, policies, procedures, ethical codes, Standards, applicable site and enterprise practice, and industry practice; and, where appropriate, manufacturers’ instructions, specifications, and data sheets. Outcomes and evidence requirements Outcome 1 Demonstrate knowledge of small signal Class A amplifier circuits using bipolar and field effect transistors. Evidence requirements 1.1 Resistor values are calculated to select an operating point for linear operation in Class A. Range 1.2 common emitter 4 resistor biasing, common source MOSFET biasing. Small signal parameters for amplifier circuits are determined by calculation. Range circuits – common emitter, common source; parameters – input and output impedance, voltage gain, current gain, power gain. 1.3 Capacitive and transformer coupling between amplifier stages are explained, with reference to circuit sketches and frequency effects. 1.4 The effect on gain and frequency response of the emitter or source by-pass capacitor is explained. Outcome 2 Demonstrate knowledge of emitter follower or source follower amplifier circuits. Evidence requirements 2.1 Basic amplifier circuit is sketched. 2.2 Advantages and disadvantages compared to common emitter or common source circuits are stated. 2.3 Voltage gain and input and output impedances are calculated. ElectroTechnology Industry Training Organisation SSB Code 100401 New Zealand Qualifications Authority 2016 NZQA registered unit standard 20715 version 2 Page 3 of 5 Outcome 3 Demonstrate knowledge of power amplifiers. Range Classes A, B (push-pull and complementary pair), AB, C, D. Evidence requirements 3.1 Amplifier class is determined by inspection of given circuit diagrams. 3.2 Given circuit diagrams, the classes of amplifiers and the circuit operation of each is explained with reference to load line and operating point, and sketches of input and output waveforms are drawn. 3.3 Features of each class of amplifier are identified and compared. Outcome 4 Demonstrate knowledge of differential amplifiers and associated circuits. Evidence requirements 4.1 The characteristic features of differential amplifiers are identified. 4.2 The circuit operation of a discrete component differential amplifier is explained with reference to differential gain, common mode rejection, and the purpose of each component. 4.3 The characteristics and operation of constant current source and current mirror circuits are explained, and the reasons for their use in conjunction with differential amplifiers are stated. Outcome 5 Demonstrate knowledge of feedback in electronic circuits. Evidence requirements 5.1 The concept and purpose of negative and positive feedback are explained. 5.2 The terms open loop, closed loop, feedback fraction, and loop gain are AOL explained, and the feedback formula ACL is described and applied. 1 . AOL 5.3 Methods of applying negative feedback are described using block diagrams, and are identified in operational amplifier circuits. Range methods – voltage series, current series, voltage shunt, current shunt; circuits – voltage shunt inverting op-amp circuit, voltage series non-inverting op-amp circuit. ElectroTechnology Industry Training Organisation SSB Code 100401 New Zealand Qualifications Authority 2016 NZQA registered unit standard 5.4 The effect of negative feedback on amplifier parameters is explained. Range 5.5 20715 version 2 Page 4 of 5 parameters – gain, bandwidth, input and output impedance, distortion. The need for stability in an amplifier is explained, and the conditions for stability are stated. Outcome 6 Demonstrate knowledge of sine wave oscillators. Range oscillators may include – Hartley, Colpitts, Pierce, CR phase shift, variable capacitance tuned, Wien bridge. Evidence of two oscillators is required. Evidence requirements 6.1 The type of oscillator and the frequency determining components are identified by inspection of a given circuit diagram. Outcome 7 Demonstrate knowledge of filter concepts. Evidence requirements 7.1 Filter types are identified and their Bode plots sketched. Range 7.2 Cut-off frequencies are calculated for simple filters. Range 7.3 filter types – band pass, band stop, low pass, high pass. two calculations. Given a circuit diagram, the operation of a simple passive bass and treble tone control circuit is explained and the component block identified. Range component blocks – treble boost, treble cut, bass boost, bass cut. Outcome 8 Apply analogue electronics principles. Range application must relate to the preceding outcomes and may include but is not limited to – circuit construction, experiment, fault finding, or project. Evidence requirements 8.1 The application demonstrates use of instruments, tests, and experimental procedure. ElectroTechnology Industry Training Organisation SSB Code 100401 New Zealand Qualifications Authority 2016 NZQA registered unit standard 20715 version 2 Page 5 of 5 8.2 The application demonstrates analysis of measurements and observations. 8.3 Purpose, method, observations, measurements, and conclusions are recorded in accordance with a given format. Planned review date 31 December 2016 Status information and last date for assessment for superseded versions Process Version Date Last Date for Assessment Registration 1 26 July 2004 31 December 2012 Review 2 21 July 2011 N/A Consent and Moderation Requirements (CMR) reference 0003 This CMR can be accessed at http://www.nzqa.govt.nz/framework/search/index.do. Please note Providers must be granted consent to assess against standards (accredited) by NZQA, before they can report credits from assessment against unit standards or deliver courses of study leading to that assessment. Industry Training Organisations must be granted consent to assess against standards by NZQA before they can register credits from assessment against unit standards. Providers and Industry Training Organisations, which have been granted consent and which are assessing against unit standards must engage with the moderation system that applies to those standards. Requirements for consent to assess and an outline of the moderation system that applies to this standard are outlined in the Consent and Moderation Requirements (CMRs). The CMR also includes useful information about special requirements for organisations wishing to develop education and training programmes, such as minimum qualifications for tutors and assessors, and special resource requirements. Comments on this unit standard Please contact the ElectroTechnology Industry Training Organisation reviewcomments@etito.co.nz if you wish to suggest changes to the content of this unit standard. ElectroTechnology Industry Training Organisation SSB Code 100401 New Zealand Qualifications Authority 2016