Auto Body Repair Painting
advertisement
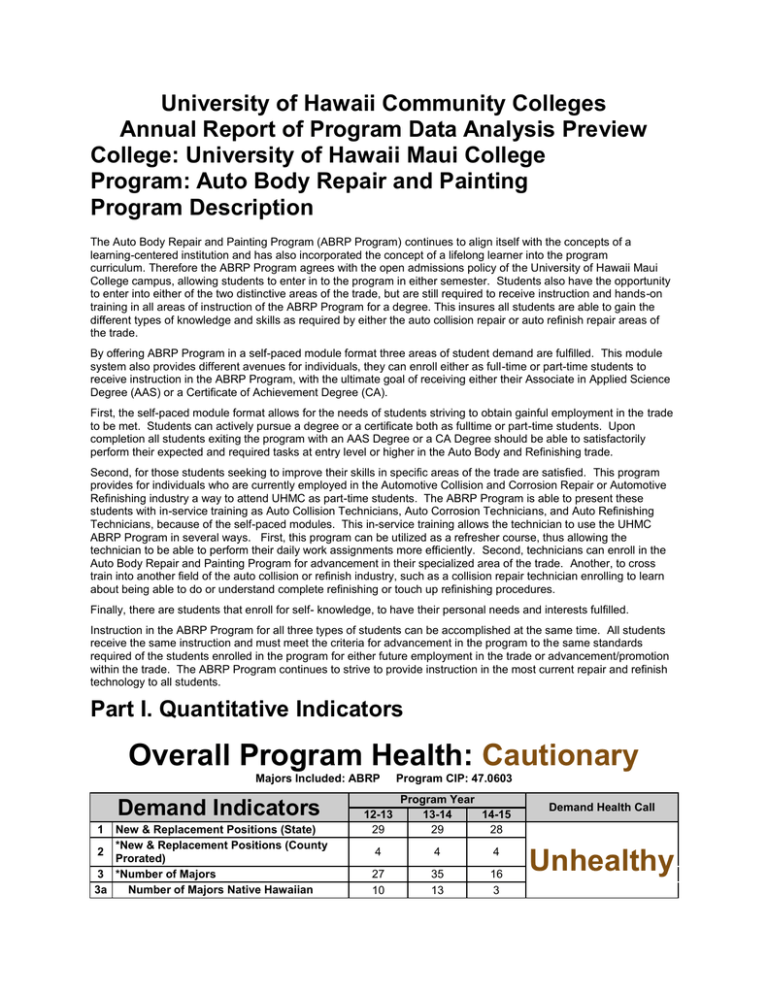
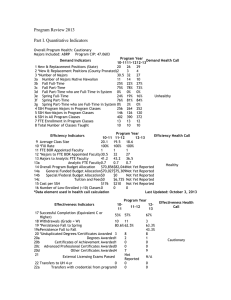
University of Hawaii Community Colleges Annual Report of Program Data Analysis Preview College: University of Hawaii Maui College Program: Auto Body Repair and Painting Program Description The Auto Body Repair and Painting Program (ABRP Program) continues to align itself with the concepts of a learning-centered institution and has also incorporated the concept of a lifelong learner into the program curriculum. Therefore the ABRP Program agrees with the open admissions policy of the University of Hawaii Maui College campus, allowing students to enter in to the program in either semester. Students also have the opportunity to enter into either of the two distinctive areas of the trade, but are still required to receive instruction and hands-on training in all areas of instruction of the ABRP Program for a degree. This insures all students are able to gain the different types of knowledge and skills as required by either the auto collision repair or auto refinish repair areas of the trade. By offering ABRP Program in a self-paced module format three areas of student demand are fulfilled. This module system also provides different avenues for individuals, they can enroll either as full-time or part-time students to receive instruction in the ABRP Program, with the ultimate goal of receiving either their Associate in Applied Science Degree (AAS) or a Certificate of Achievement Degree (CA). First, the self-paced module format allows for the needs of students striving to obtain gainful employment in the trade to be met. Students can actively pursue a degree or a certificate both as fulltime or part-time students. Upon completion all students exiting the program with an AAS Degree or a CA Degree should be able to satisfactorily perform their expected and required tasks at entry level or higher in the Auto Body and Refinishing trade. Second, for those students seeking to improve their skills in specific areas of the trade are satisfied. This program provides for individuals who are currently employed in the Automotive Collision and Corrosion Repair or Automotive Refinishing industry a way to attend UHMC as part-time students. The ABRP Program is able to present these students with in-service training as Auto Collision Technicians, Auto Corrosion Technicians, and Auto Refinishing Technicians, because of the self-paced modules. This in-service training allows the technician to use the UHMC ABRP Program in several ways. First, this program can be utilized as a refresher course, thus allowing the technician to be able to perform their daily work assignments more efficiently. Second, technicians can enroll in the Auto Body Repair and Painting Program for advancement in their specialized area of the trade. Another, to cross train into another field of the auto collision or refinish industry, such as a collision repair technician enrolling to learn about being able to do or understand complete refinishing or touch up refinishing procedures. Finally, there are students that enroll for self- knowledge, to have their personal needs and interests fulfilled. Instruction in the ABRP Program for all three types of students can be accomplished at the same time. All students receive the same instruction and must meet the criteria for advancement in the program to the same standards required of the students enrolled in the program for either future employment in the trade or advancement/promotion within the trade. The ABRP Program continues to strive to provide instruction in the most current repair and refinish technology to all students. Part I. Quantitative Indicators Overall Program Health: Cautionary Majors Included: ABRP Demand Indicators 1 New & Replacement Positions (State) *New & Replacement Positions (County 2 Prorated) 3 *Number of Majors 3a Number of Majors Native Hawaiian 12-13 29 Program CIP: 47.0603 Program Year 13-14 14-15 29 28 4 4 4 27 10 35 13 16 3 Demand Health Call Unhealthy 3b 3c 3d 3e 3f 3g 4 5 6 7 8 Fall Full-Time Fall Part-Time Fall Part-Time who are Full-Time in System Spring Full-Time Spring Part-Time Spring Part-Time who are Full-Time in System SSH Program Majors in Program Classes SSH Non-Majors in Program Classes SSH in All Program Classes FTE Enrollment in Program Classes Total Number of Classes Taught Efficiency Indicators 9 Average Class Size 10 *Fill Rate 11 FTE BOR Appointed Faculty *Majors to FTE BOR Appointed 12 Faculty 13 Majors to Analytic FTE Faculty 13a Analytic FTE Faculty 27% 73% 24% 76% 28% 72% 0% 0% 0% 16% 84% 16% 84% 36% 64% 0% 0% 0% 252 120 372 12 10 330 64 394 13 10 24 0 24 1 4 12-13 18.6 100% 1 Program Year 13-14 14-15 19.7 3 100% 37.5% 1 1 27 35 16 36.5 0.7 47.3 0.7 14 Overall Program Budget Allocation $93,902 $82,833 14a General Funded Budget Allocation $78,796 $80,904 14b Special/Federal Budget Allocation $0 $0 14c Tuition and Fees $15,106 $1,929 $252 $210 54 0.3 Not Yet Reported Not Yet Reported Not Yet Reported Not Yet Reported Not Yet Reported 0 0 15 Cost per SSH Number of Low-Enrolled (<10) Classes *Data element used in health call calculation 16 Effectiveness Indicators 17 18 19 19a 20 20a 20b 20c 20d 21 Successful Completion (Equivalent C or Higher) Withdrawals (Grade = W) *Persistence Fall to Spring Persistence Fall to Fall *Unduplicated Degrees/Certificates Awarded Degrees Awarded Certificates of Achievement Awarded Advanced Professional Certificates Awarded Other Certificates Awarded External Licensing Exams Passed Efficiency Health Call Cautionary 4 Last Updated: October 7, 2015 Program Year 12-13 13-14 14-15 67% 60% 83% 3 63.3% 44.8% 11 65.7% 21.6% 0 55.5% 35.2% 8 6 3 1 0 1 0 2 1 0 0 0 9 Not 8 Not 1 N/A Effectiveness Health Call Cautionary 22 Transfers to UH 4-yr Transfers with credential from 22a program Transfers without credential from 22b program Reported 0 Reported 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Distance Education: Completely On-line Classes 23 24 25 26 27 Number of Distance Education Classes Taught Enrollments Distance Education Classes Fill Rate Successful Completion (Equivalent C or Higher) Withdrawals (Grade = W) Persistence (Fall to Spring Not Limited to 28 Distance Education) Perkins IV Core Indicators 2013-2014 29 30 31 32 33 34 1P1 Technical Skills Attainment 2P1 Completion 3P1 Student Retention or Transfer 4P1 Student Placement 5P1 Nontraditional Participation 5P2 Nontraditional Completion Performance Funding Program Year 12-13 13-14 14-15 0 N/A N/A N/A N/A 0 N/A N/A N/A N/A 0 N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A Goal Actual Met 91.00 47.00 75.21 68.92 17.50 16.00 93.33 13.33 40.91 100.00 10.26 16.67 Met Not Met Not Met Met Not Met Met 12-13 1 Program Year 13-14 1 14-15 35 Number of Degrees and Certificates 3 Number of Degrees and Certificates Native 36 0 0 2 Hawaiian 37 Number of Degrees and Certificates STEM Not STEM Not STEM Not STEM 38 Number of Pell Recipients 19 22 13 39 Number of Transfers to UH 4-yr 0 0 0 *Data element used in health call calculation Last Updated: October 7, 2015 Glossary | Health Call Scoring Rubric Part II. Analysis of the Program Demand Indicator: Historically, the number of available positions listed for the County of Maui by the Hawaii State Department of Labor, which also includes the island Molokai and Lanai, has always appeared low in the demand indicator section. I believe that this count reflects only the journeyman positions in trade for auto collision and refinish technicians and not for entry level positions. The auto collision repair and refinishing facilities here in the island of Maui is always contacting the ABRP Program seeking to employ our students as apprentice collision/corrosion repair and refinish technicians, as well as related vocations seeking to employ our students with entry level knowledge in the auto body and refinish trade. Efficiency Indicator: Since repair to the building was not completed as promised by the contractor, classes were cancelled for the Fall Semester of 2014. Though the building was not completed for the Spring Semester of 2015, three students were enrolled to insure their being able to graduate. Though the program was been able to maintain its enrollments, the number of majors has not a strong point for the program. By offering the curriculum in a self-paced format, the program is able to fulfill the specific needs of individual students to receive instruction on specific skills. It is these students enrolled as part-time for only one or two ABRP classes that choose to not declare themselves as majors, as they feel that they will be committed to complete the general education (math, science, English…) part of the program. Effectiveness Indicator: Many of the students do not complete the ABRP program, because as students they are offered employment not only in an auto body and refinish shop, but at other related businesses, such as a glass repair facility, new auto parts stores and outlets, recycled auto parts facilities, or an automotive paint supply store. The UHMC ABRP Program has always been able to fulfill the requests of not only the auto collision and refinish industry, but also other related businesses in Maui County. Unfortunately, many students then decide not to continue on and obtain a degree from the ABRP Program. Perkins Core Indicator: Three students were enrolled for the Spring Semester 2015 and two students only needed two or three ABRP program classes to graduate from the program with their AAS Degree. According to the Quantitative Indicators the UHMC ABRP program had successfully met its goals in three areas, 1P1 Technical Skills Attainment, 4P1 Student Placement, and 5P2 Nontraditional Completion. There were no students enrolled for the fall 2014 semester, so there would be no gauge for 2 P1 Completion and 3P1 Student Retention or Transfer count into the Spring Semester 2015. Also, there were no students that qualified for the 5P1Nontraditional Participation. Part III. Action Plan Retention of students has always been of concern for the ABRP Program. Many of the ABRP Program students are often employed not only at a body and refinish shop, but also find employment at a related businesses, such as a glass repair facility, auto parts retail outlets, recycled auto parts facilities, or an automotive paint supply store before they even reach the second year of the ABRP Program. Retention often leads to a student graduating from this program. Due to health issues of the instructor for the ABRP Program in the 2009-10 year the college hired a lecturer to help with of students. At this time it became obvious the student retention increased as more students returned the following semester. And with increased enrollments in the 2010-11 year, the college again hired a lecturer for two class sessions to help with the over load of students. The lecturer assists with the students in the laboratory, while the instructor handled the classroom portion. I believe that by having two instructors, one in the laboratory and one in the classroom is what produced an increase in the persistence rate for returning students. This was in part because both instructors were able to provide more one-on-one support needed, instead of one instructor being stretched thin with up to 20 beginning and advanced students, with each student doing a different task or assignment in either the laboratory or classroom. Having one instructor teaching and evaluating the students while they are actively participating in laboratory exercises while the other instructor help students with their classroom activities, with both instructors grading each student practical and written assignments. An alternative would be to have one instructor for the first year students and another for the second year students. I believe either system will work, but the latter being a better choice as each instructor then can spend more time with his specific group of students. Particularly, for the first year students that require much more guidance and encouragement to remain in and to complete the program. This could possibly be the step to place the program in the right direction in dealing with the issue of student retention as well as dealing with the high enrollments the ABRP Program has encountered these past years. Creating an APT Position would also be of great assistance to the program and the instructor. The APT position would be of an assistant to the program instructor, making sure the students are doing their tasks or projects in a safe manner while in the laboratory. The APT position is not an instructional position, but more of a supervisory position. Another idea for program enhancement that has been tossed about with members of the ABRP Advisory Committee members is to incorporate more computer skills related assignments. Employing IICAR computer instruction for auto body repair and refinishing. Another major project for the ABRP Program is having the capabilities to allow students to be able to take their test and quizzes on line, using campus resources such as Laulima. Part IV. Resource Implications As noted in previous program reviews, there is anticipation in the refinishing trade here in the State of Hawaii of new EPA mandates for automotive refinishing in the state. Also in anticipation of enforcement of these new Volatile Organic Compound (VOC) limits, the refinishing industry is moving to water based refinishing products. For the ABRP Program, this requires the refinishing equipment employed in the application of refinishing materials to be upgraded and/or replaced within the next three or four years. Continue to explore and obtain funding for an additional faculty member or a full-time lecturer, or an APT position. As stated in previously, one instructor to provide instruction and supervision in the laboratory, while the other instructor is in the classroom working with students, or one instructor for the first year students and one for the second year students. Even an APT position would enhance a student’s experience while participating in the UHMC ABRP Program. Any of the three options is workable to enhance student retention and improve completion/graduation rates. Program Student Learning Outcomes For the 2014-2015 program year, some or all of the following P-SLOs were reviewed by the program: Assessed this year? 1 Yes Program Student Learning Outcomes Program Learning Outcomes 1. Explain and describe both personal and public health and safety issues as it pertains to the products used in the auto collision repair and auto refinishing industry. Describe in general the effect of these products have on themselves, co-workers and the environment. Demonstrate proper personal and public safety precautions to be utilized when using these products. Will be able to identify hazardous products and describe the proper methods of disposal for different types of hazardous waste. 2. Describe and demonstrate proper and safe usage as pertaining to the hand and power tools and equipment needed to complete the required tasks for auto body sheet metal repair for the return both exterior and interior sheet metal of a vehicle to a like new condition. 3. Employ required math and reading skills to be able to complete vehicle repairs as described from a work order and also written specifications when using vehicle service information or a vehicle dimensioning manual, obtained either as a hard copy or on line. Be able to communicate both written and verbally with fellow employees and other shop personnel. 4. Demonstrate the proper MIG and resistance spot welding skills required to achieve a weld that is equal to factory specifications for a given type of repair, in a safe manner. Be able to identify and correct MIG and resistance spot welds that are not compliant with factory recommendations for acceptable repairs. 5. Display the appropriate refinishing skills required to achieve a vehicle topcoat (finish) that is equal to factory refinishing specifications. Describe the health and safety issues surrounding the use and disposal of refinishing and related materials. Be able to identify and correct paint imperfections in the topcoat to meet factory recommendations for an acceptable finish. Also, describe and demonstrate proper and safe usage as pertaining to the hand and power tools and refinishing tools and equipment employed when refinishing a vehicle, both touch-up repair and complete vehicle refinishing. 6. Present to the prospective employer the required skills for entry-level employability in the auto body repair and refinishing trade, along with proper work attitude and ethics. Will also exhibit responsibility and professionalism upon seeking employment in the auto body repair and refinishing trade. A) Evidence of Industry Validation Currently, the UHCC ABRP Program Coordinating Council is in discussion about various topics of concern to the programs state wide and the topic of industry validation is being discussed. Here in the Maui county level there is no official industry validation of the UHMC ABRP Program as the UHMC ABRP Advisory Committee had not officially met for several years, however there is always an ongoing informal discussion with the ABRP Advisory Committee members as well as shop owners and employees from industry when problems or concerns arise concerning the UHMC ABRP Program Advisory Committee Meeting(s) _0_, How many? _0_ Did Advisory Committee discuss CASLO/PLO? Yes__ No _X_ Coop Ed Placements _0_ Fund raising activities/events _0_ Service Learning _0_ Provide program services that support campus and/or community _YES_ Outreach to public schools _NO_ Partner with other colleges, states and/or countries _NO_ Partner with businesses and organizations _YES_ Other Inter Industry Conference on Collision Repair (IICAR) B) Expected Level Achievement All students are required to complete a capstone class prior to proceeding into the next major segment of the ABRP Program. They are all expected to complete a “live” project in the laboratory to meet minimal or entry level industry standards. One example is a student in the basic auto body repair must complete a project employing the skills and knowledge they acquired their previous basic auto body modules, such as corrosion repair. Another example is the student is required refinish a complete vehicle to industry standards and more importantly, the vehicles owner expectations and satisfaction. Instrument used for assessment (check all that apply) (IV-B): Work Sample _X_ Portfolio__ Project _X_ Exam _X_ Writing Sample __ Other__ Please explain_________________________________________________ C) Courses Assessed During the academic year Fall 2014-Spring 2015 semesters all the ABRP modules were reviewed for the 5 Year Course Outline Review. Also, I revised the program curriculum to incorporate implementing the new 6th Edition of the Auto Body Repair Technology textbook and Student Technicians Workbook into the UHMC Auto Body Repair and Painting Program self-paced modules . D) Assessment Strategy/Instrument Though the ABRP Advisory Committee has not officially met for a while, I always pursue the advice of the members of the ABRP Advisory Committee and also from individuals in the auto body trades to review and help me with any modifications to curriculum or laboratory projects to comply with industry expectations before it is presented to the students. Also; with the UHMC ABRP Program’s association with IICAR, I employ their curriculum materials and expectations of student outcomes. And students are also gauged by the collision repair standards set by IICAR while completing their “shop projects” in the laboratory. This is in part due to the association of NATEF, the sanctioning body for ASE Certification of technicians employed in the auto collision and refinish trade and their use the IICAR standards as part of their certification process. E) Results of Program Assessment Because the UHMC ABRP Program was shut down for the 2014-2015 Academic year due to a complete building repair and renovation, the only projects that could be accomplished was incorporating the new 6th Edition Auto Body Repair Technology text and the Student Technician’s Manual to Accompany work 6 th Edition Auto Body Repair Technology into the ABRP Program curriculum. Also the revision of the student’s quizzes and final exams were also reviewed and revised. F) Other Comments The ABRP Program has desired the addition of another instructor, as the program has been over enrolled for many years and the school has had to hire a lecturer every semester to cover the additional students. If it is not feasible to add another full-time instructor, then having an APT person to insure students in the laboratory are working safely and to provide limited assistance to the students as they work on their laboratory projects. The APT will not provide instruction to the student, just guidance as they are working on their “live jobs” in the laboratory. This will eliminate having students standing around waiting for the one instructor to help them in either the laboratory or classroom. Only the program instructor will provide the actual instruction and final approval of the student’s completed projects. G) Next Steps Due to the ABRP Program being placed into a hibernation status because of building renovations for the 2014-2015 academic year, I spent my time reviewing each set of module instructions and the program’s quizzes and tests to insure cohesiveness with the 6th Edition of the Auto Body Repair Technology text book and the Student Technicians Manual to Accompany 6th Edition of the Auto Body Repair Technology. Once the laboratory and classroom are completely done, I can then put everything in its place and have the classroom and laboratory up and running 100% for the students enrolled in the program without compromising their learning experience. Then we will be able to host IICACR seminars again, I can proceed with revision of the program modules to include the latest updated IICAR curriculum, materials, classroom props and training aids. Also; as it was mentioned earlier, the introduction of environmentally safer refinishing materials, as mandated by the Environment Protection Agency, will have to be included in the curriculum and laboratory exercises for the future students in the very near future.