Ch 1 - Opto Terms
advertisement

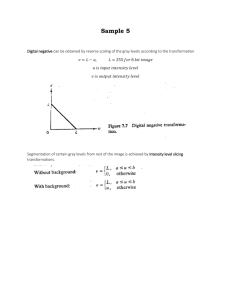
Optoelectronics Chapter 1 Terminology EM Spectrum Terms • Photometry – visible light – Flux (Power) is in Lumens (lm) – Subscript is “v” for visible light • Radiometry – non-visible light – Flux (Power) is in Watts (W) – Subscript is “e” for radiant energy Particle or Wave? • Light – Particles – Proposed by Newton in 1666 • Tiny particles called corpuscles – Waves – Proposed by Huygens during same time – Electromagnetic waves • Proposed by Maxwell in 1860 – Surfaces emit electrons when exposed to light • Proposed by Hertz in 1887 – Quanta – small packets of energy • Max Planck in 1900 – Light has both Particle and Wave characteristics • Photons E=hf Where h = Planck’s constant = 6.63 x 10-34 f = frequency in Hertz – Einstein proposed equation in 1905 – Energy from light is directly proportional to frequency • Speed of Light C = f λ = 3.0 x 108 m/s Radiometric and Photometric Terms • Eyes and Ears are not linear. – Logrithmic – Sound intensity measured in Decibels (dBs) – LED can saturate eye’s retinal response in low light – Eye detects certain frequencies much better • Green at 555 nm CIE Curve • Intensity • Solid Angle • Ten Diameter Rule – Distance, d, must be 10 times the diameter of the source – Reduces errors of greater than 10% due to distance Photometer • Photometer – Device to measure visible light parameters • Flux • Intensity • Incidance amount of light brightness Intensity Measurements • To measure Intensity of an LED by Two Point Method – If distance from LED is not defined • Make intensity measurement at two different distances. • Only need to know distance between the two measurements. • Photometer reads Ev1 and Ev2 Standards • Color Temperature – Tungsten lamp • Used to measure light parameters • Different colors at different temperatures – NIST – National Bureau of Standards • NIST has the primary standard • NIST gives out secondary standards to use in labs