Qualification details New Zealand Certificate in Teaching Individuals with Specific Learning
advertisement

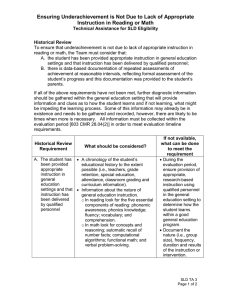
Qualification details Title New Zealand Certificate in Teaching Individuals with Specific Learning Disabilities (Level 5) Version 1 Qualification type Certificate Level 5 Credits 60 070199 Education > Teacher Education > Teacher Education not elsewhere classified Qualification developer NZQA Qualifications Services on behalf of and in collaboration with the sector. Next review 31 December 2020 Approval date January 2016 Strategic purpose statement This qualification is for Specific Learning Disabilities (SLD)related professionals, including teachers and educators, to enable them to help students with SLD to achieve their potential and engage in life-long learning. Graduates will work independently and be able to offer guidance to other SLD professionals. Outcome Statement NZSCED Graduate profile Graduates of this qualification will be able to: - recognise a wide range of SLD indicators in individuals - develop individualised intervention plans for individuals with SLD using related assessment data - support those who work with individuals with SLD - refer individuals with SLD to other service providers when appropriate - apply appropriate educational programmes for individuals with SLD - evaluate the effectiveness of interventions, make improvements, and adapt into practice Education pathway Graduates of this qualification may pathway into qualifications in allied disciplines. Employment pathway Graduates of this qualification will have the skills and knowledge to volunteer or gain employment: - in education settings as teachers or educators with SLD expertise - in the community as specialist SLD teachers or educators Qualification Reference 2760 © New Zealand Qualifications Authority 2015 This qualification will also have wider application, including in the Page 1 of 4 justice and mental health sectors. Qualification specifications Qualification award Awarding bodies for this qualification will be any education organisation accredited under section 250 of the Education Act 1989 to deliver a programme leading to the qualification. The certificate will display the NZQF logo and the name and logo of the awarding body. Evidence requirements for assuring consistency Standard evidence for programme providers may include: - assessment information leading to the achievement of the graduate outcomes - a portfolio of candidate work relating to the qualification and the annual review focus requirements - graduate and/or stakeholder/end-user feedback on outcome achievement - tertiary education organisation (TEO) moderation outcomes which may include moderation/benchmarks across common programmes. Minimum standard of achievement and standards for grade endorsements Achieved. Other requirements for the qualification (including regulatory body or legislative requirements) None. General conditions for the programme leading to the qualification General conditions for programme ‐ ‐ Qualification Reference 2760 © New Zealand Qualifications Authority 2015 Outcomes should be integrated across programme design in a way that makes it clear outcomes are mutually supportive and not entirely discrete. In a programme, assessment of all outcomes should be integrated so each assessment task provides evidence of at least two outcomes in ways that demonstrate their interdependence. ‐ Practicum must be carried out in an authentic teaching context. Authentic refers to a wide variety of possible cultural and educational contexts. It involves instructional techniques that connect what candidates learn to the world beyond the classroom and enables the application of the learning in that world. ‐ During practicum, candidates may be working with learners 18 years and under. In this case, practical experience will require a safety check to comply with the requirements of the Vulnerable Children Act 2014. For more information on the Vulnerable Children Act 2014, safety checking regulations Page 2 of 4 ‐ ‐ ‐ and guidelines see http://childrensactionplan.govt.nz. Providers need to ensure candidates have access to actual learners for practical components or assessments. Specific learning disabilities (SLD) include disabilities such as dyslexia. Programmes must include a range of pedagogical principles. These principles include those informed by Te Tiriti o Waitangi, to ensure that the indigenous status of Tangata Whenua and the role of Tangata Tiriti are understood. The principles also include those informed by Aotearoa New Zealand’s Pacific location and multicultural environment. Programmes delivered outside Aotearoa New Zealand must include cultural practices in relation to the given contexts in which graduates will practice. Glossary ‐ ‐ Candidate is the person who is enrolled in a programme leading to this qualification. Learner is the person who, in turn, is taught by the candidate. Conditions relating to the Graduate profile Qualification outcomes Conditions 1 Recognising a wide range of indicators includes applying knowledge of definition and core understanding of SLD including: - general overview of theories of SLD including causes and effects - differentiating between specific learning disabilities, general learning disabilities, and other neurodevelopmental disorders - sub-groups of SLD and overlap between sub-groups Recognise a wide range of SLD indicators in individuals. Credits 15 Recognising a wide range of indicators covers applying knowledge of characteristics of SLD, including: - genetic pre-disposition - individual learner characteristics including their particular SLD profile - societal impact on learner and society’s response to learners with SLD - impacts of the structure of language on presentation of disabilities - evolution of indicators for different age groups 2 Develop individualised intervention plans for individuals with SLD using related assessment data. Credits 5 Qualification Reference 2760 © New Zealand Qualifications Authority 2015 Developing individualised intervention plans includes applying knowledge of: - effect of particular SLDs on development of life skills - effects of SLD on literacy and numeracy acquisition - interpreting assessment reports to create individual teaching plans Page 3 of 4 - 3 Support those who work with individuals with SLD. Credits 5 4 Refer individuals with SLD to other service providers when appropriate. Credits 5 5 Apply appropriate educational programmes for individuals with SLD. Credits 15 determining and utilising learners’ strengths to maximise learning Providing support includes: - professional relationships with colleagues and learners - recognising a wide range of appropriate interventions for the individual and situation - recognising difficulties individual learners could encounter in their setting and providing appropriate advice - advocating for the learner - finding ways to encourage and contribute to professional development of those working with individuals with SLD Considerations when referring individuals include: - existing or developing factors that influence the learning and/or well-being of the learner - availability of support services for SLDs and when further referral is necessary Applying appropriate educational programmes include: - a variety of plans, methods, and programmes to deal with particular SLDs - observing learners, analysing learner response and adapting accordingly to ensure learner success and motivation - the use of repetition and revision in accordance with learners’ needs Programmes for individuals with SLD should be evidence-based and demonstrate meaningful, logical progression. They may be multi-sensory. 6 Evaluate the effectiveness of interventions, make improvements, and adapt into practice. Credits 15 Evaluation includes: - reviewing overall programme according to learner responses and progress - ongoing reflective practice to inform the planning, delivery and evaluation of programmes Interventions should reflect integration of the candidate’s accumulated knowledge. Qualification Reference 2760 © New Zealand Qualifications Authority 2015 Page 4 of 4