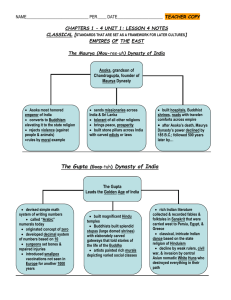
Classical Power Point
advertisement

Chapters 1-4 Unit I Lesson 4 Notes: Classical Empires of the East The Maurya (Mou-ree-uh) Dynasty of India Asoka, grandson of Chandragupta, founder of Maurya Dynasty • Asoka most honored emperor of India • converts to Buddhism elevating it to the state religion • rejects violence (against people & animals) • rules by moral example • sends missionaries across India & Sri Lanka • tolerant of all other religions • brings peace, prosperity • built stone pillars across India with carved edicts or laws • built hospitals, Buddhist shrines, roads, with travelercomforts across empire • after Asoka’s Maurya Dynasty’s power declined by 185 B.C.; followed 500 years later by… The Gupta (Goop-tuh) Dynasty of India The Gupta Leads the Golden Age of India • devised simple math system of writing numbers • called “Arabic” numerals today • originated concept of zero • developed decimal system of numbers based on 10 • surgeons set bones & repaired injuries • introduced smallpox vaccinations not seen in Europe for another 1000 years • built magnificent Hindu temples • Buddhists built splendid stupas (large domed shrines) with elaborately carved gateways that told stories of the life of the Buddha • artists painted rich murals depicting varied social classes • rich Indian literature collected & recorded fables & folktales in Sanskrit that were carried west to Persia, Egypt, & Greece • classical, intricate Indian dance based on the state religion of Hinduism • decline by weak rulers, civil war, & invasion by central Asian nomadic White Huns who destroyed everything in their path CLASSICAL CHINA PHILOSOPHIES Confucianism: • philosophy to ensure social order, good government, & harmony supported by 5 key relationships among people with proper behavior based on filial piety "Never impose on others what you would not choose for yourself." Legalism: • philosophy emphasizing strict laws & harsh punishments • autocratic rule “wielding it like lightning or like thunder” • official policy of the Qin emperor [to follow] Han Feizi - 280 B.C. – 233 B.C. Daoism: • philosophy that encouraged harmony with nature rejecting conflict & strife • the best kind of government is one that governs least Buddhism: • originally from India • emphasized personal salvation by appealing to followers with its promise of escape from suffering through prayer, good works, & devotion DYNASTIC EMPIRES OF CHINA Zhou (Jo) Dynasty 1100 B.C. – 260 B.C. • justified its rule by the Mandate of Heaven Qin (Chin) Dynasty 221 B.C. – 210 B.C. • unified China • ushered in China’s classical era • built the Great Wall to protect itself from invaders • practiced Legalism Han (Hahn) Dynasty 200 B.C. – A.D. 200 • kept China unified for 400 years • established trade along the Silk Road supporting a cultural diffusion of ideas and customs • introduced Buddhism to China