Electrochemical reduction of CO to CO using graphene oxide/carbon nanotube
advertisement

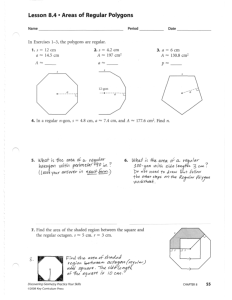
Electrochemical reduction of CO2 to CO using graphene oxide/carbon nanotube electrode in ionic liquid/acetonitrile system ZHU QingGong, MA Jun, KANG XinChen, SUN XiaoFu, HU JiaYin, YANG GuanYing & HAN BuXing * Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Sciences, Key Laboratory of Colloid and Interface and Thermodynamics, Institute of Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100190, P.R. China E-mail: hanbx@iccas.ac.cn 1. As the transient current is controlled by a diffusion process of the redox system of Fe(CN)63-/4- at GO/MWCNT-CP, Chronoamperometry is applied to study the various catalytic and kinetic effects of the hybrid ratio. Fig. S1 shows that as the amount of MWCNT gradually increased in the hybrid, the transient current starts to increase from 10% and reach its maximum at 50%. However, it decreases consequently from 60% and upwards. Thus, the hybrid ratio GO/MWCNT (1:1) was selected for kinetic study. 3.0 1:5 2:5 3:5 4:5 1:1 5:4 5:3 5:2 2.5 I (mA) 2.0 1.5 1.0 0.5 0.0 0.0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 t (s) Figure S1. Chronoamperograms of GO/MWCNT-CP with various ratio of MWCNT to GO. The applied potential steps were 0.0 V and 0.5 V vs Ag/AgCl, respectively. Table S1 Detail of analysis GC column on product distribution of various electrodes in BmimBF4 (90 wt%)/MeCN at applied potential of -2.2 V vs Ag/Ag+. Vol. %/cm2 H2 Vol. %/cm2 CO Vol. %/cm2 CH4 GO/MWCNT-CP 0.020 0.119 0.001 CP 0.039 0.085 0.000 Au 0.018 0.074 0.001 Ag 0.008 0.059 0.005 Electrodes