Physics 321 Hour 11 Simple and Damped Harmonic Oscillators
advertisement

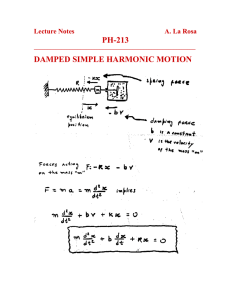
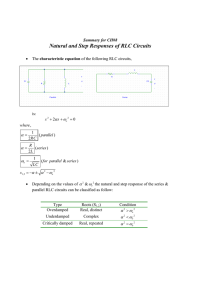
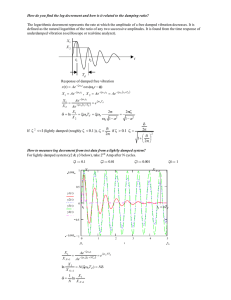
Physics 321 Hour 11 Simple and Damped Harmonic Oscillators Bottom Line • Equation for a damped oscillator: 𝑚𝑥 = −𝑘𝑥 − 𝑏𝑥 𝑥 = −𝜔02 𝑥 − 2𝛽 𝑥 • Damping regimes: • Underdamped: 𝛽 < 𝜔0 • Critically damped: 𝛽 = 𝜔0 • Overdamped: 𝛽 > 𝜔0 Exam #1 Reminders (Spring 2015) See Review #1, Sample Test #1, Example Problem Review is Wednesday 5/13 Test is available Thurs. 5/14 – Monday 5/18 Average time will be about 1 hr 15 min Simple Harmonic Oscillator 1) What is the equation of motion? 2) Where is your origin? 3) What is the frequency of oscillation? 4) What are the three ways you can write the general solution? 5) How many constants do you have to fix to get a specific solution? 6) How do you find those constants? x Mass on a Massless Spring 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) Find U and T 𝑇+𝑈 =0 Equilibrium Equation of motion ω, T Energy plot y Example VertSpringUWell.nb A Shallow Frictionless Bowl 1) Assume 𝑧 ≈ 0, 𝑧 = 𝛼𝑟 2 2) Find U and T 3) 𝑇 + 𝑈 = 0 4) 𝐹 = −𝛻𝑈 = 𝑚𝑟 5) ω, T y x z Another Bowl 1) Assume 𝑧 ≈ 0, 𝑧 = 𝛼𝑥 2 + 𝛽𝑦 2 2) Find U 3) 𝐹 = −𝛻𝑈 = 𝑚𝑟 4) Two frequencies y x z Example Lissajous.nb Damped Oscillator The equation: 𝑚𝑥 = −𝑘𝑥 − 𝑏𝑥 𝑘 − 𝑥 𝑚 A little rearranging: 𝑥 = 𝑥 = −𝜔02 𝑥 − 2𝛽 𝑥 − 𝑏 𝑥 𝑚 A trial solution: 𝑥(𝑡) = 𝑒 𝑟𝑡 𝑟 2 𝑥 𝑡 = − 𝜔02 𝑥 𝑡 − 2𝛽𝑟𝑥 𝑡 𝑟 2 + 𝜔02 + 2𝛽𝑟 = 0 𝑟 = −𝛽 ± 𝛽 2 − 𝜔02 Three Regimes • Underdamped: 𝛽 < 𝜔0 • Critically damped: 𝛽 = 𝜔0 • Overdamped: 𝛽 > 𝜔0 Underdamped 𝛽 < 𝜔0 , 𝑟 = −𝛽 ± 𝛽 2 − 𝜔02 𝑟 = −𝛽 ± 𝑖 𝜔02 − 𝛽 2 Solution: 𝑥 𝑡 = 𝐴𝑒 or −𝛽𝑡 +𝑖 𝜔02 −𝛽 2 𝑡 𝑒 + 𝐵𝑒 −𝛽𝑡 −𝑖 𝜔02 −𝛽 2 𝑡 𝑒 𝑥 𝑡 = 𝐴𝑒 −𝛽𝑡 sin( 𝜔02 − 𝛽 2 𝑡) + 𝐵𝑒 −𝛽𝑡 cos( 𝜔02 − 𝛽 2 𝑡) Note: ω = 𝜔02 − 𝛽 2 Overdamped 𝑟 = −𝛽 ± 𝛽 2 − 𝜔02 𝛽 > 𝜔0 , Solution: 𝑥 𝑡 = 𝐴𝑒 −𝛽𝑡 + 𝛽2 −𝜔02 𝑡 𝑒 + 𝐵𝑒 −𝛽𝑡 − 𝛽2 −𝜔02 𝑡 𝑒 Critically Damped 𝛽 = 𝜔0 , 𝑟 = −𝛽 ± 𝛽 2 − 𝜔02 𝑟 = −𝛽 Solution: 𝑥 𝑡 = 𝐴𝑒 −𝛽𝑡 + 𝐵𝑡𝑒 −𝛽𝑡 Example DampOsc5_4.nb