Ch. 5.ppt
advertisement

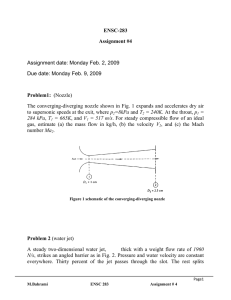
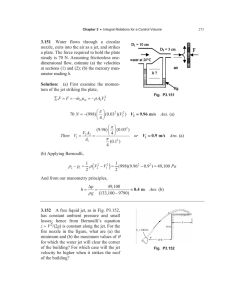
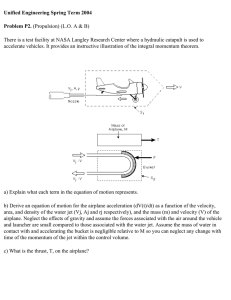
Chapter 5. About mechanism of origin and evolution of the coherent structures in the laminar and turbulent round jet The results of researches presented in presentation are published in the following main articles: 1. Kozlov G.V., Litvinenko Yu.A., Grek G.R., Sorokin A.M. About mechanism of the coherent structures origin and downstream evolution in the laminar and turbulent round jets // Vestn. NSU. Seria: Physics. 2008. Т. 3. Vip. 1. pp. 12–22, in Russian. 2. Kozlov V.V., Grek G.R., Kozlov G.V., Litvinenko Yu.A. Physical aspects of subsonic jet flows evolution // The collection of proceedings «Successes of mechanics of continuum» to the 70-anniversary of academician V.A. Levin, 2009. Dalnauka, Vladivostok, pp. 331-351, in Russian Scheme of the coherent structures development at initial region of the turbulent round Jet: Guinevskiy А.S., Vlasov E.V., Karavosov R.K. Acoustics control by the turbulent jets // Moscow: Nauka, 2001. pp. 1–239, in Russian (see, page of notes) Scheme of the jet set – up and measurement and visualization technique Jet set - up scheme: 1 – Vitoshinsky nozzle; 2 – honeycomb; 3 – set of grids; 4 – settling chamber; 5 – extension pipe of 150 mm; 6 – turbulizator; 7 –micromanometer; 8 – smoke generator; 9 – video camera; 10 – dynamic loudspeaker; 11 – hot – wire probe; 12 – hot – wire anemometer; 13 – ADC; 14 – computer; 15 – fan. General view of the jet set - up with the long channel of 150 mm length. General view of round jet set – up for the laminar round jet realization General view of round jet set – up for the turbulent round jet realization Smoke visualization patterns of the laminar round jet: а – general view of the jet; b – streaky structures in the jet; c – transverse sections of the jet at different distances from the nozzle exit downstream, U0 = 4 m/s (Re U0 d / ν = 5300) Smoke visualization patterns of the turbulent round jet: а – general view of the jet; b – streaky structures in the jet; c – transverse sections of the jet at different distances from the nozzle exit downstream; d – longitudinal section of the jet near at the nozzle exit, U0 = 4 m/s (Re U0 d /ν = 5300) Mean velocity profiles of the laminar 1 and turbulent 2 round jet measured in transverse direction at different distances from the nozzle exit (a–d, at x = 1, 2, 5 and 20 mm, respectively), U0 = 4 m/s (Re U0 d /ν = 5300) Fluctuation velocity distributions of the laminar 1 and turbulent 2 jets measured in transverse direction at different distances from the nozzle exit (a–e, at x = 1, 2, 5 and 20 mm, respectively). Fluctuation velocity distribution in transverse direction of the laminar round jet (d , at x = 60 mm), U0 = 4 m/s (Re U0 d /ν = 5300) Distributions of the velocity fluctuations in transverse direction of the turbulent 1 and laminar 2 round jet at different distances downstream from the nozzle exit (a – c, at x = 2, 5 and 20 mm, respectively), U0 = 4 m/s (Re U0 d /ν = 5300) Key points: Main features of the laminar jet instability including generation of the ring vortices and their interaction with the longitudinal structures of perturbations apply to the turbulent jet, as well. Quantitatively, almost the same response of laminar and turbulent jets to external acoustic forcing at generation of the ring vortices is found.