lecture 35 - resolving, gratings
advertisement

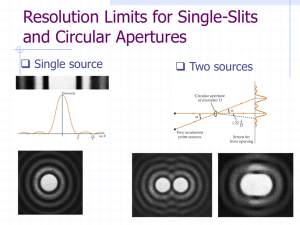
Announcements 11/19/10 Prayer TA won’t have office hours on Tuesday next week (even though Tuesday = Friday classes). Neither will I. (HW 36 = only 2 problems.) Addition to Monday’s reading assignment: also includes PpP chapter 10, “Modern optical devices” Reading Quiz What does Rayleigh’s criterion tell us? a. The angle at which both light polarizations have equal reflection coefficients b. The angle at which p polarized light has minimum reflection c. The angular separation resolvable by an imaging system d. The number of orders produced by a diffraction grating Circular Aperture, again What if there’s a lens in the hole? What if there isn’t a flat board? What if you have two light sources? pattern at infinity f superimposed pattern at focus patterns at focus What do you get in this situation? 2nd peak separated by at least as much as distance to first minimum Rayleigh Criterion Shape of curve involves a “Bessel function” (wait for some future Physics/Math class) plotted vs (qD/l) (using sinq q) Mathematica “FindRoot” command: qD/l = 1.21967 qmin.resolve 1.22 l D Rayleigh Criterion Back to 1-D slits, infinitely narrow 3 slits, equally spaced (created with parameters so period = 2p) Back to 1-D slits, infinitely narrow 4 slits, equally spaced Back to 1-D slits, infinitely narrow 5 slits, equally spaced Back to 1-D slits, infinitely narrow 10 slits, equally spaced Back to 1-D slits, infinitely narrow 20 slits, equally spaced Back to 1-D slits, infinitely narrow 100 slits, equally spaced What have we learned? The Grating Equation Where will maxima be? Resolving Power N=100 Goes to zero at x=0.0628 = 2p/100 width = 1/N separation of maxima 140 120 100 80 60 40 20 0.4 0.2 0.0 0.2 0.4 Resolving Power Red light vs. Green light HW 36-5: resolving power = Dl/l = Nm Demos Circular aperture Diffraction grating … with two lasers … with white light source Reading Quiz What do we call diffraction off of the ions in a crystal? a. Bragg diffraction b. Bohr diffraction c. Compton diffraction d. Raman diffraction e. Thompson diffraction X-ray Diffraction by Crystals Bragg equation http://commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/File:Bragg_diffraction.png http://l-esperimento-piu-bello-dellafisica.bo.imm.cnr.it/english/history/figuredett2.html Laue Patterns http://www.neutronoptics.com/laue.html