Review 2
advertisement

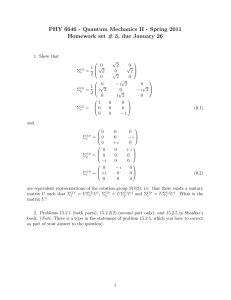
Physics 451 Quantum mechanics I Fall 2012 Review 2 Karine Chesnel Quantum mechanics EXAM II When: Tu Oct 23 – Fri Oct 26 Where: testing center • Time limited: 3 hours • Closed book • Closed notes • Useful formulae provided Quantum mechanics EXAM II 1. The delta function potential 2. The finite square potential (Transmission, Reflection) 3. Hermitian operator, bras and kets 4. Eigenvalues and eigenvectors 5. Uncertainty principle Quantum mechanics Square wells and delta potentials V(x) Physical considerations incident x Aeikx reflected x Beikx Scattering States E > 0 transmitted x Feikx x Symmetry considerations Bound states E<0 even x even x odd x odd x Quantum mechanics Square wells and delta potentials Continuity at boundaries Delta functions d dx is continuous is continuous except where V is infinite d D dx 2 ma 0 2 h Square well, steps, cliffs… d dx is continuous is continuous Quantum mechanics The delta function potential V x a x d 2 a ( x) E 2 2m dx 2 For x0 d 2 2mE 2 2 dx Quantum mechanics The delta function well Bound state E0 ma ma x / h 2 x e h ma 2 E 2h 2 Ch 2.5 Quantum mechanics The delta function well/ barrier V x a x E 0 Scattering state right x Feikx left x Aeikx Beikx A F B x 0 Reflection coefficient 1 R 1 2 2 E / ma 2 Transmission coefficient T 1 1 ma 2 / 2 2 E “Tunneling” Quantum mechanics The finite square well Bound state E0 Symmetry considerations V(x) The potential is even function about x=0 The solutions are either even or odd! x Ae kx even -V0 D cos lx Ae kx Quantum mechanics The finite square well Bound states 2 z0 tan z 1 z where z la z0 a 2mV0 Quantum mechanics The finite square well Scattering state E 0 (2) V(x) (1) (3) +a -a x A C,D F B -V0 Aeikx Beikx (1) Ceilx De ilx (2) Feikx (3) Quantum mechanics The finite square well V(x) A B F x -V0 Coefficient of transmission V0 2 2a T 1 sin 2 2m E V0 4E E V 0 1 The well becomes transparent (T=1) 2 2 when En V0 n 2m(2a)2 2 Quantum mechanics Formalism Wave function Operators Hˆ H ij Observables are Hermitian operators Vector Linear transformation (matrix) Q Q † Quantum mechanics Eigenvectors & eigenvalues For a given transformation T, there are “special” vectors for which: T a a a is an eigenvector of T is an eigenvalue of T Quantum mechanics Eigenvectors & eigenvalues To find the eigenvalues: T I a 0 det T I 0 We get a Nth polynomial in : characteristic equation Find the N roots 1, 2 ,...N Find the eigenvectors e1, e2 ,...eN Spectrum Quantum mechanics Hilbert space Infinite- dimensional space N-dimensional space e1 , e2 , e3 ,... eN 1 , 2 , 3 ... n ... b Hilbert space: functions f(x) such as f ( x) dx 2 a Inner product f g f ( x )* g ( x )dx f m f n nm Orthonormality f g f Schwarz inequality g f ( x)* g ( x)dx f ( x) dx g ( x) dx 2 2 Quantum mechanics The uncertainty principle Finding a relationship between standard deviations for a pair of observables A2 B 2 A, B 2i 2 Uncertainty applies only for incompatible observables Position - momentum Dx Dp 2 Quantum mechanics The uncertainty principle Energy - time DE Dt Derived from the Heisenberg’s equation of motion d Q dt i 2 Q H , Q t Special meaning of Dt Dt Q d Q dt Quantum mechanics The Dirac notation Different notations to express the wave function: • Projection on the energy eigenstates cn n eiE t / n n • Projection on the position eigenstates ( y, t ) ( x y )dy • Projection on the momentum eigenstates ( p, t ) 1 eipx / dp 2 Quantum mechanics The Dirac notation Bras, kets = inner product = matrix (operator) Operators, projectors en en projector on vector en