x-Ray Beam Size Monitor
advertisement

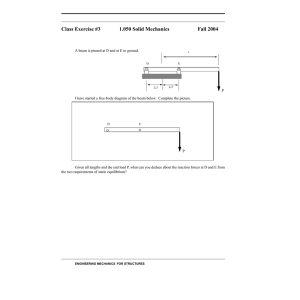
x-Ray Beam Size Monitor J. Alexander, C. Conolly, N. Eggert, J. Flanagan (KEK), E. Fontes, W. Hopkins, B. Kreis, H. Liu, A. Lyndaker, D. Peterson, P. Revesz, J. Savino, R. Seeley and M. Palmer (Cornell, unless noted) Abstract: We report on the performance goals and design of the CESRTA x-ray beam size monitor (xBSM). The xBSM resolution must be sufficient to measure vertical beam sizes down to 10~20um. The xBSM images 2-4keV synchrotron radiation photons onto a one-dimensional InGaAs photodiode array. Instrumentation in the dedicated x-ray beam line includes upstream interchangeable optical elements (slits, Coded Apertures, and Fresnel Zone Plate) and the photodiode detector. To provide sufficient x-ray flux in 2 GeV beam energy operation, the beam line is evacuated, with only a thin diamond window isolating the detector vacuum from the damping ring. The readout is a beam-synchronized FADC that is sufficient to measure consecutive bunches independently in a 4ns bunch spacing configuration. Layout Detector Box 5 GeV Results Pinhole Image The evacuated detector box contains the monochromator, detector, and collimating slits. High-Energy Coded Aperture Image 5 GeV beam profiles with Pinhole (left) and high-energy Coded Aperture (right). The horizontal axis is measured in diodes, which are 50 microns each. The vertical axis measures intensity in arbitrary units. Results of fits to these images (and at 2 GeV, the images below) provide the raw beam size information for the live beam size update. 2 GeV Results Fresnel Zone Plate Image Low-Energy Coded Aperture Image Optics Assembly Pinhole Low-energy Optics High-energy Optics Optics Optics are mounted on remotely controlled assembly. Can quickly change optics on the fly. Low Energy •Fresnel Zone Plate •Requires monochromatic light for best resolution, but monochromator reduces intensity by factor of 140 •Coded Aperture •Analysis shows 2x the sensitivity of the FZP with white light, but requires template fitting method. Most promising in the long run. High Energy •Pinhole •Horizontal slit acts as 1-D pinhole optic. Resolution limited to ~30 microns. •Coded Aperture •More robust than low-energy CA to withstand higher x-ray intensity. The 2 GeV beam size is measured with a Fresnel Zone Plate (left) or low-energy Coded Aperture (right). After we have developed the fitting procedure for the Coded Aperture image it is expected to provided improved beam-size sensitivity. Live Beam Size Updates The x-ray beam size monitor provides beam size measurements averaged over 100 turns and updated once per second to CESR control room for low-emittance tuning. The horizontal axis is time; the vertical axis is beam size in engineering units. In this example, the CESR horizontal and vertical tunes have been moved close to a coupling resonance providing an ability to apply an increase in the beam size. The figure demonstrated that the xBSM is sensitive to the applied vertical size increase. Model vs. Data Future Plans •Electronics redesign for 4 ns bunch spacing (currently 14 ns) •Optics (Coded Aperture, Fresnel Zone Plate with white light) •Faster live updates (Currently limited by DAQ, will be upgraded for 4ns redesign) For this plot, the vertical size was modulated by varying a tune coupling. Observed beam sizes (green) were measured with the Live Beam Size Updates (above). A prediction of the beam size increment due to the variation of the tune coupling is shown in red. (The offset is observed because the prediction is an increment over the base beam size.) LEPP, the Cornell University Laboratory for Elementary-Particle Physics, has joined with CHESS to become the Cornell Laboratory for Accelerator-based Sciences and Education (CLASSE). LEPP's primary source of support is the National Science Foundation. Visit us on the web at: www.lepp.cornell.edu