Analyzing Structure.ppt
advertisement

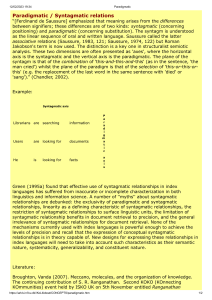
Analyzing Structure • Meaning arises from the differences between signifiers • Differences: syntagmatic (positioning) and paradigmatic (substitution/associative) • Syntagmatic is horizontal, while paradigmatic is vertical • Syntagm: Combination of this and this and this • Paradigm: selection of this or this or this Syntagm and Paradigm • Syntagm: possibilities of combination • Paradigm: functional contrasts involving differentiation • Syntagm: intratextual and co-present • Paradigm: intertextual to signifiers absent from the text Value of the Signs • Determined by paradigmatic and syntagmatic relations • Syantagm and paradigms provide a structural context within which the signs make sense • Paradigmatic operation: signifiers or signified • A paradigm: a set of associated signifiers which are all members of defining category but in which each is significantly different. • Grammatical paradigms: verbs, nouns, adjectives, Paradigmatic Relations • The use of one signifier shapes the preferred meaning • Contrastive • Associative • Mental association of form (homophones) • and meaning (synonyms) • Include visual mode Syantagm • Orderly combination of interacting signifiers which form a meaningful whole within a text. • A sentence is a syntagm of words • Syntagmatic relations: Conceptual relation • Expository (topic, introduction, body, paragraph, conclusion) Masculine • Masculine: tight, orderly, logical arguments leading to the main point, defensive, excludes the woman’s way of knowing • Say what you are going to say, then say it, then say what you have already said • Semiotician: try to find elementary constituent segment within a text: its syntagm. • Narrative is based on sequential relation • Film and TV: causal relationship • Semioticians: search for grammar leaks, seams, and scaffolding and for what has been denied, hidden, or excluded. • About before and after Spatial relation • - Syntagmatic and includes: above/below In front/behind Close/distant Left/right north/south/west/east Inside/outside (center/periphery) Top/bottom Center/margin Orientational metaphors are linked to culture. Sequential significance • Left hand/right hand visual image: sense of before and after. • Left hand/right hand are related to “Given” and “new” • Given: already given, a familiar, wellestablished and agreed upon point of departure, assumed and self-evident. • New: not yet known, more surprising, problematic, and contestable. Compositional axis • Up: goodness, virtue, happiness, consciousness, health, life, the future, high status, having control or power, and rationality. • Down: badness, depravity, sickness, death, low status, being subject to control or power, and with emotion. • Men tend to be located higher than woman in ads symbolically reflecting the routine subordination of women to men in society. • Vertical axis: upper = the ideal, abstract and generalized possibilities: lower = the real, factual detail, down-toearth • Upper: what might be, lower: what is (more informative and practical. Center VS Margin • • • • Center: nucleus information Margin: ancillary, dependent element Center=figure, margin = ground Dominant shape = figure and located centrally Sequential relation • Narrative: left/right spatial structure • Has beginning and ending • Narrative syntagm: equilibrium-disruptionequilibrium (beginning, middle, end) • Causation and goal-turn story • Give structure, predictability and coherence. • To naturalize the content of narrative itself Structural Reduction • Stories: the villain, the donor, helper, sought for person, dispatcher, hero, the false hero. • A myth: can be reduced to a small number of simple types. • Message from our ancestors about humankind our relationship to nature. • Myth is a language • Mythemes: breaking myths into the shortest possible sentences (morpheme) • Mythemes: functions Greimas (Paris School) • Grammar or narrative: 3 Narrative syntagms • Performanciels (task and struggle) • Contractuel: the establishment or breaking contract • Disjonctionel: departure and arrival Actions and character types: actant