Poetry terms.doc
advertisement

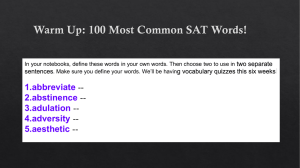
Abstractions—Words with no concrete reality or image Truth or beauty Apostrophe—Speaking to something that is inanimate “Death be not proud” (John Donne) Connotative—Associated meanings What the word connotes (associated meanings) “Gay”—happy or a sexual preference, can take on the connotative meaning “gay” being used to say something is dumb, silly or absurd. Denotative—What a word denotes Dictionary meaning Diction—Language that the writer chose Imagery—Images within a poem Visual Imagery—Words used to describe things that we can see Aural Imagery—Descriptions of things we hear Tactile Imagery—Describe things we can touch Gustatory Imagery—Words that describe taste Olfactory Imagery— Words used to describe a smell Metaphor—indirect comparison “Men are Dogs” Poetic diction—A system of words refined from the grossness of domestic use. Simile—comparing using “like” or “as” Men are like dogs Syntax—Order of words in writing “The strain is soft” can be turned around to say, “Soft is the strain”. When the words are rearranged, the new sound is less choppy.