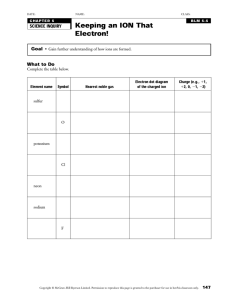
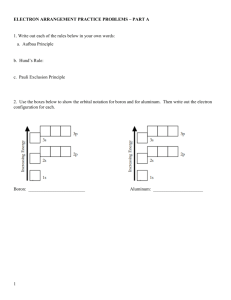
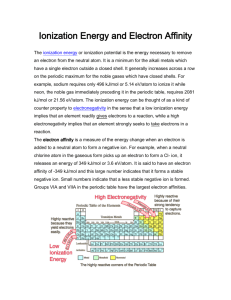
Electronic Structure Bonding
advertisement

CHEM 161: Exam 3 Name: Section: Page 1 Page 2 Page 3 Page 4 Page 5 Total out of 123 Exam Percentage (5) 1. Check all of the following statements that are true: a. Fewer air molecules are present at the top of Mt. Everest than in air at sea level. b. Gas pressure remains constant even if a sample of carbon monoxide at 25°C is heated. c. A sample of carbon dioxide gas will behave ideally at high pressures and high temperatures. d. If the density of oxygen gas at STP is eight times greater than the density of He, a sample of oxygen gas will exert eight times the pressure as an equal volume of He at STP. e. The flow of wine out of an airtight barrel eventually decreases because of the suction resulting from the vacuum produced. (6) 2. Check all of the following statements that are true: a. The Bohr Model of the atom cannot account for the electronic transitions in a helium atom. b. X-rays have shorter wavelengths than red light at 700 nm from a laser pointer. c. The Photoelectric Effect was experimental evidence that light exists as particles. d. The 3dxy, 3dyz, and 3dxz orbitals all have 4 lobes lying on two axes. e. The Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle is most relevant for matter with a large mass moving at very high velocities. f. The energy emitted for the electronic transition from n=3 to n=1 is greater than the energy emitted from the transition from n=5 to n=3. (6) 3. Check all of the statements below that are true: a. Elements within the same group will have the same number of valence electrons. b A possible excited state electron configuration for a neutral argon atom is [Ne] 3s2 3p5 4s1. c. In a hydrogen atom, all orbitals with the same principal quantum number are degenerate. d. All alkali metals have ground state electron configurations that end with ns2. e. The monatomic ions formed by the halogens are always isoelectronic with a Noble gas. f. An element with the following ionization energies, IE1=896 kJ/mol, IE2=1752 kJ/mol, IE3=14,807 kJ/mol, and IE4=17,948 kJ/mol, is probably an alkaline earth metal. (4) 4. Check all of the following for which the quantum numbers correspond to the indicated orbital: a. An electron in the 4dxy orbital: n=4, l=3, ml=1, and ms= ½. b. An electron in the 3py orbital: n=3, l=2, ml=1, and ms=+½. c. An electron in the 2s orbital: n=2, l=, ml=0, and ms=+½. d. An electron in the 2px orbital: n=2, l=1, ml=0, and ms=+½ CHEM 161 Exam 3 page 1 of 5 (10) 5. Write the formula for the element or compound in each blank below to rank the following in the order that each effuses when a tiny hole is made in a container containing equal amounts of each of the following gases: ammonia, neon, carbon monoxide, nitrogen, and chlorine. ___________ < ___________ < ___________ < ___________ < ___________ effuses slowest effuses fastest (12) 6. Using Noble-gas core notation, give the electron configuration for the following atoms and ions: a. cobalt ______________________ d. sulfide ion ______________________ b. Mo ______________________ e. silver ion ______________________ c. Te ______________________ f. zinc ion ______________________ (6) 7. Draw the atomic orbital diagram for the valence electrons in each of the following atoms: a. cobalt b. Te (5) 8. Check all of the statements below that are true: a. Triple bonds are longer and stronger than both single and double bonds. b. A fluorine atom will never form multiple bonds in a molecule. c. Although the PF5 molecule exists, the NF5 molecule cannot exist. d. The double bond in O3 oscillates between the two outer oxygen atoms in the molecule. e. According to the octet rule atoms bond in such a way that each atom in a molecule has 8 pairs of electrons, except hydrogen, which only needs two electrons. 9. Draw three different Lewis structures for cyanate ion (OCN) using the skeleton structures below: (6) i. Indicate the formal charge for each atom in each formula as indicated. (2) ii. Circle the most plausible Lewis structure based on the formal charges. O C N O C N O C N O: _____, C: _____, N: _____ O: _____, C: _____, N: _____ O: _____, C: _____, N: _____ CHEM 161 Exam 3 page 2 of 5 (16) 10. Draw the Lewis structure (including resonance structures when appropriate and minimizing formal charges) for each of the following molecules: a. nitrite ion b. COCl2 c. chlorine trifluoride, ClF3 d. carbonic acid, H2CO3 (6) 11a. Draw the Lewis structure for periodate ion (IO4). Minimize the formal charges and show resonance structures if appropriate. (3) b. In the periodate ion all of the oxygen atoms have the same formal charge, which is _______. For the problems below, SHOW ALL WORK, giving answers with the correct units and the correct number of significant figures to receive full credit. Circle your answer. (10) 12. A balloon has a volume of 1.50103 L of hot air at 0.995 atm and 25.00˚C. At an altitude of 20 km, the atmospheric pressure is 76.0 torr and the balloon’s volume is 1.15104 L. Calculate the temperature (in ˚C) when the balloon is at an altitude of 20 km. CHEM 161 Exam 3 page 3 of 5 For the problems below, SHOW ALL WORK, giving answers with the correct units and the correct number of significant figures to receive full credit. Circle your answer. 13. Copper reacts with nitric acid to produce nitrogen dioxide gas as follows, Cu(s) + 4 HNO3(aq) Cu(NO3)2(aq) + 2 NO2 (g) + 2 H2O(l) (12) A 2.550 g copper-plated penny was placed in a beaker containing excess nitric acid and produced 49.75 mL of nitrogen dioxide gas at 23.50˚C and 0.9975 atm. Calculate the mass percentage of copper in the penny. 14. One type of sunburn occurs with exposure to UV light with energy of 6.1110–19 J per photon. (4) a. Calculate the frequency (in Hz) corresponding to this energy. (5) c. Calculate the wavelength for this energy in nanometers. (5) b. Calculate the energy for a mole of these photons (in kJ/mol). CHEM 161 Exam 3 page 4 of 5 Extra Credit: (7 points) Dinitrogen pentaoxide decomposes as follows: 2 N2O5(g) 4 NO2(g) + O2(g) Assuming the dinitrogen pentaoxide decomposes completely when heated above 75C, what mass of dinitrogen pentaoxide must be decomposed in an evacuated (empty) 10.00 L chamber at 105C to obtain a gas mixture in which the total pressure is 5.00 atm? CHEM 161 Exam 3 page 5 of 5