N09
advertisement

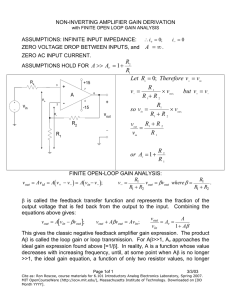
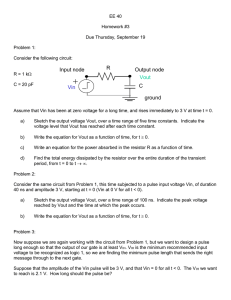
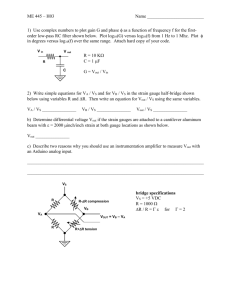
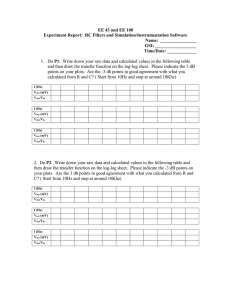
N09 page 1 of 8 Op-Amps Ideal op-amp model open loop gain saturation VOUT GVB VA G = 106 nominal +VS VS VOUT VS VB + common unipolar supply +VS = +5 VDC, -VS = 0 V common bipolar supply +VS = +15 VDC, -VS = -15 VDC LM 324 unipolar supply range LM 324 bipolar supply range VA VOUT - +3V to +32V -VS ±1.5V to ±16V Golden Rules of Op-amps adapted from Horowitz and Hill, The Art of Electronics, Cambridge Press, 1990 1) Inputs draw no current. 2) With feedback, the output will adjust to make the voltage difference between the inputs equal to zero. Unity gain voltage follower (impedance buffer) VIN VB prevents impedance loading (inputs draw no current) closed loop gain open loop VA V K OUT 1 VIN VOUT GVB VA VOUT GVIN VOUT using second golden rule feedback VOUT GVIN GVOUT VB VA VIN VB VA VOUT and + - VB VIN VOUT G 1 VIN G 1 VOUT VA VOUT VIN VOUT N09 page 2 of 8 Non-inverting amplifier VIN prevents impedance loading gain K VB + VA VOUT - VOUT R 1 2 VIN R1 R2 R1 VOUT check with Golden Rules i VOUT R1 R 2 VA i R 1 VOUT VIN VB VA VOUT R2 R1 R1 R 2 R1 R1 R 2 VA i i=0 R1 VOUT R 1 R 2 R 1 2 VIN R1 R1 compare to unity gain follower VIN K 1 VB VIN + VA R2=0 R1=∞ R2 0 1 1 R1 VB + VOUT VA - VOUT N09 page 3 of 8 Inverting amplifier R2 can cause impedance loading R1 VIN gain VA V R K OUT 2 VIN R1 - VB VOUT + VOUT is opposite polarity to VIN check with Golden Rules i R1 VIN R2 VOUT VA VB 0 i VIN R1 VOUT i R 2 i=0 R2 VIN R1 VA=0 R2 input A is a virtual ground VIN R1 input A is also called a summing junction VA VB virtual ground + VOUT N09 page 4 of 8 Summing amplifier RF can cause impedance laoding VOUT R1 V1 V V V R F 1 2 3 R1 R 2 R 3 VA VB R2 V2 + R3 V3 Four-bit digital to analog converter (DAC) VIN 8K b3 b2 b1 bi = 0 open b0 1K 2K 4K 8K bi = 1 closed V V V V VOUT 8K IN b 3 IN b 2 IN b1 IN b 0 2K 4K 8K 1K VOUT VIN 8b 3 4b 2 2b1 b 0 use transistors in place of SPST switches 2n resistor ladder can be problematic due to resistor precision for n = 10, largest resistor will be 512K 1% precision = 5.12K which is larger than three smallest resistors most DACs use R-2R resistor ladders VOUT VA VB + VOUT N09 page 5 of 8 R2 Differential amplifier can cause impedance loading VOUT V1 R2 V2 V1 R1 R1 - V2 VOUT + R1 R2 Simple instrumentation amplifier prevents impedance loading V1 VOUT R 2 V2 V1 R1 + R1 R2 - VOUT + V2 AD623 instrumentation amplifier single supply +5VDC rail-to-rail output swing gain set with one external resistor G=1 to G=1000 variable offset reference + R1 R2 N09 page 6 of 8 Integrator can cause impedance loading VOUT 1 VIN dt RC C VIN R reset VOUT = 0 when SPST switch is closed VA VB - VOUT + Differentiator can cause impedance loading VOUT RC dVIN dt can be very noisy R C VIN VA - VB + VOUT N09 page 7 of 8 LM 324 quad op-amp chip 1out 1 1- 2 - 1+ 3 + +Vs 14 4out 1 4 - 13 4- + 12 2+ 4 11 -Vs 2+ 5 + 2- 6 - 2out 7 2 3 + 10 3+ - 9 38 3out Practical considerations 1) limited current output maximum 30 mA 2) saturation or clipping rail-to-rail performance limited rail performance VS VOUT VS VS 1.5V VOUT VS 1.5V 3) offset need 741 or 747 op-amp with offset null inputs 4) thermal drift need 741 or 747 op-amp with offset null inputs N09 page 8 of 8 5) slew rate maximum dV = 0.5V / sec dt V Vo sin 2 f t f MAX max slew 2 Vo Vo _ MAX max slew 2 f dV Vo 2 f cos2 f t dt Vo = ±15 V f = 10 KHz 2 f Vo max slew fMAX = 5.90 KHz Vo_MAX = ±7.96 V