Pertemuan 03 Distribusi Frekuensi – Metoda Statistika Matakuliah
advertisement

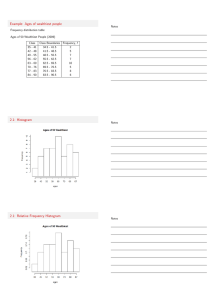
Matakuliah Tahun Versi : I0134 – Metoda Statistika : 2005 : Revisi Pertemuan 03 Distribusi Frekuensi 1 Learning Outcomes Pada akhir pertemuan ini, diharapkan mahasiswa akan mampu : • Mahasiswa dapat menjelaskan tentang distribusi frekuensi. 2 Outline Materi • • • • Diagram dahan dan daun Distribusi Frekuensi Histrogam dan Poligon Frekuensi kumulatif dan ogif 3 Distribusi Frekuensi Table with two columns listing: – Each and every group or class or interval of values – Associated frequency of each group • Number of observations assigned to each group • Sum of frequencies is number of observations – N for population – n for sample Class midpoint is the middle value of a group or class or interval Relative frequency is the percentage of total observations in each class – Sum of relative frequencies = 1 4 Frequency Distribution x Spending Class ($) 0 to less than 100 100 to less than 200 200 to less than 300 300 to less than 400 400 to less than 500 500 to less than 600 f(x) Frequency (number of customers) f(x)/n Relative Frequency 30 38 50 31 22 13 0.163 0.207 0.272 0.168 0.120 0.070 184 1.000 • Example of relative frequency: 30/184 = 0.163 • Sum of relative frequencies = 1 5 Cumulative Frequency Distribution x Spending Class ($) 0 to less than 100 100 to less than 200 200 to less than 300 300 to less than 400 400 to less than 500 500 to less than 600 F(x) Cumulative Frequency 30 68 118 149 171 184 F(x)/n Relative Cumulative Frequency 0.163 0.370 0.641 0.810 0.929 1.000 The cumulative frequency of each group is the sum of the frequencies of that and all preceding groups. 6 Histogram A histogram is a chart made of bars of different heights. – Widths and locations of bars correspond to widths and locations of data groupings – Heights of bars correspond to frequencies or relative frequencies of data groupings 7 Histogram Example Frequency Histogram 50 50 Frequency 40 30 38 31 30 22 20 13 10 100 200 300 400 500 600 Dollars 8 Histogram Example Relative Frequency Histogram 0 .3 R e la ti ve F r e q u e n c y 0 .2 7 1 7 3 9 0 .2 0 6 5 2 2 0 .2 0. 1 6 8 4 7 8 0 .1 6 3 0 4 3 0. 1 1 9 5 6 5 0 .1 0.0 7 0 6 5 2 100 200 300 400 500 600 Dollars 9 Methods of Displaying Data Pie Charts – Categories represented as percentages of total Bar Graphs – Heights of rectangles represent group frequencies Frequency Polygons – Height of line represents frequency Ogives – Height of line represents cumulative frequency Time Plots – Represents values over time 10 Pie Chart Fig. 1-8 Telecommunications Headquarters Other (8.0%) U.S. (30.0%) Europe (25.0%) Britain (8.0%) Japan (29.0%) 11 Bar Chart Fig. 1-9 Airline Operating Expenses and Revenues 12 Average Revenues Average Expenses 10 8 6 4 2 0 American Continental Delta Northwest Southwest United USAir A i r li n e 12 Frequency Polygon and Ogive Ogive Frequency Polygon 0.3 1.0 0.2 0.5 0.1 0.0 0.0 0 10 20 Sales 30 40 50 0 10 20 30 40 50 Sales 13 Time Plot M o n thly S te e l P ro d uc tio n (P ro b le m 1 -4 6 ) Millions of Tons 8.5 7.5 6.5 5.5 Month J F M A M J J A S ON D J F M A M J J A S ON D J F M A M J J A S O 14 • Selamat Belajar Semoga Sukses. 15