Lec 0B.ppt
advertisement
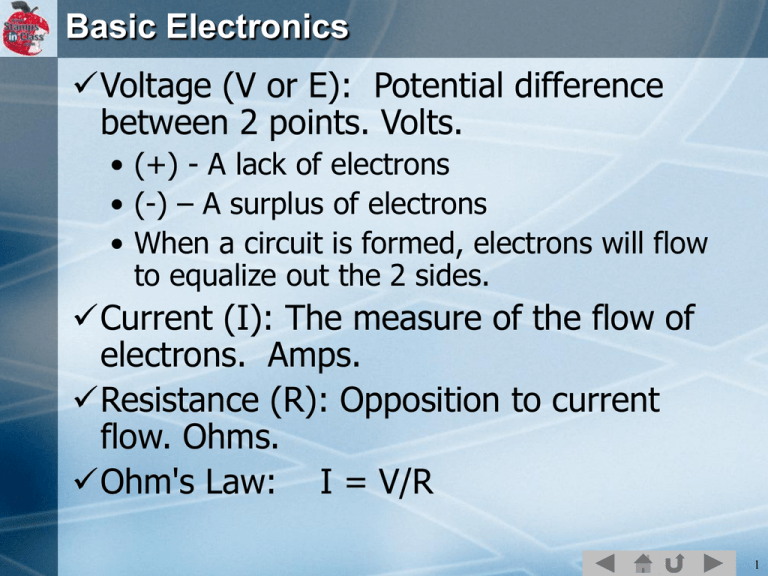
Basic Electronics Voltage (V or E): Potential difference between 2 points. Volts. • (+) - A lack of electrons • (-) – A surplus of electrons • When a circuit is formed, electrons will flow to equalize out the 2 sides. Current (I): The measure of the flow of electrons. Amps. Resistance (R): Opposition to current flow. Ohms. Ohm's Law: I = V/R 1 2 Resistors Devices used to insert resistance, or oppose current flow. Used to limit current flow. Color codes are used to indicate the value. 3 From Appendix C 4 The LED LED: Light Emitting Diode Diode: Device which allows current to flow in only one direction. To operate, is must be installed correctly with respect to polarity. 5 A regular LED can be damaged if current exceed 20mA (milliamps). Apply ohm's law to find the resistor size that will limit current to 20mA with a 5V supply. I = V/R 6 LED Circuit Schematic 7 The BreadBoard Breadboards are used to make connections between devices. 8 Building the Circuit 9 Pictorial or Wiring Diagram 10 Code to Blink LEDs 11 Task Perform Chapter 2 up to this point (page 52), including "Your Turn- Blink the other LED" 12 Additional – The Speaker/Buzzer A small piezoelectric speaker is included with your kits. A frequency can be sounded on it using the FREQOUT command. FREQOUT pin, duration, frequency • pin: Pin it is connected to. • duration: Length of time in milliseconds. • frequency: Frequency to play, measured in Hertz (Hz). 13 Sound the Speaker for 1 second at 1000Hz 14 Group Task Write a program that will: • Display in DEBUG Window "Stop! Police!" • Turn ON P12 LED • Sound a tone for ½ second at 1000Hz • Turn OFF P12 LED • Turn on P13 LED • Sound a tone for ½ second at 2000Hz • Turn off P13 LED • Repeat sequence 15 Individual Task Develop a program to act as a "Ray Gun" movie prop. Use appropriate lights and sound sequences. 16