Document 15057528
advertisement

Course Name: High Level Programming Language
Year
: 2010
Introduction to Structural C Programming
Lecture 1
Learning Outcomes
At the end of this lecture, students are capable of:
• Explaining basic C programming, i.e.:
–
–
–
–
–
Structural Programming,
Variable Type,
I/O Routine,
Naming Convention, and
Comments.
3
Outline Contents
•
•
•
•
•
Structural Programming
Variable Type
I/O Routine
Naming Convention
Comments
4
Structural Program
• Simple Structural C Programming
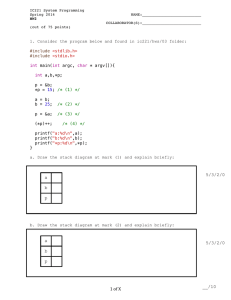
int main ( ) {
char a;
float f;
Beginning of Function
main ( )
Memory Allocation
a = 10 * 2;
Statements
f = 22 / 7;
return 0;
}
End of main() function
5
Structural Program
• Simple Structural C Programming
int main ( ) {
char a;
float f;
Beginning of Function
main ( )
Memory Allocation
a = 10 * 2;
Statements
f = 22 / 7;
return 0;
}
End of main() function
6
Structural Program
main( ) Function
• “main” is a special function that acts as an entry point every time the program
begins.
• Main’s function ends when statement “return” is called, so that the program will
return to its operating system, such as Windows 2000.
7
Structural Program
• Simple Structural C Programming
int main ( ) {
char a;
float f;
Beginning of Function
main()
Memory Allocation
a = 10 * 2;
Statements
f = 22 / 7;
return 0;
}
End of main() Function
8
Structural Program
• Memory allocation is called a variable declaration.
• Variable is a place to hold the data, e.g.: int a;
9
Structural Program
• Simple Structural C Programming
int main ( ) {
char a;
float f;
Beginning of Function
main()
Memory Allocation
a = 10 * 2;
Statements
f = 22 / 7;
return 0;
}
End of main() Function
10
Structural Program
Statements
• Statements are basic components that shape the whole program.
• Statement “Assignment” (operator =)
– a = 23; c = a * 3;
– b = 32 * a * cos(c);
• Statement “Conditional” (operator ==, !=, …)
– if (a == b)
– If (a != b)
11
Variable Type
• “byte” data type for integer
• 0 … 255
• 00000000 ...11111111
• Memory architecture uses “byte” as the smallest unit.
12
Variable Type
• “int” data type for integer
• -32.767 … 32.767
• 1000000000000000..0111111111111111
• Bit 16 = 1, berarti nilai negatif
• Implemented 2 byte on machine 80x86
• Implemented 4 byte by GNU C compiler
13
Variable Type
• “float” data type for rational number.
• 1.17549435x10-38 …3.40282347x1038
• 32 bit :
– 1 bit untuk sign bit
– 23 bit untuk mantissa
– 8 bit untuk exponent
• Implemented 4 byte (or equal to 32 bit), as one single rational number
(floating point number).
14
Variable Type
• “char” data type for character
• Implemented 1 byte as a symbol character based on ASCII (American Standard
Code for Information Interchange) standard
15
I/O Routine
• Output Data
– Printf ( ): to print data on screen
•
•
•
•
Printf(<format>, <var1>, <var2>, …)
<format>: in data type string, “…”
Every %<spec> on <format> is replaced by <var-i>
<spec> specifies the data format, e.g.:
– %f: float, %d: integer, %c: character
–
Cout << ……
•
C++ uses cout in replace of printf() function, you will use it in practical
laboratory.
16
• Output Data
I/O Routine
– Example of printf ( ):
int main ( ) {
int a;
Output:
float b;
a=2, b=3.142320, s=k
char s;
a = 2;
b = 3.14232;
s = ‘k’;
printf (“a=%i, b=%f, s=%c”,a, b, s)
return 0;
}
17
I/O Routine
• Input Data
– scanf ( ): input data via keyboard
• scanf(<format>, &<var1>, &<var2>, …)
• <format>: sama seperti pada perintah printf ( )
• Simbol ‘&’ digunakan karena data akan ditulis ke variabel, bukan dibaca
dari variabel
– In c++, cin >> …. will replace the scanf() function.
18
I/O Routine
• Input Data
– scanf ( ):
Output:
int main ( ) {
Masukkan satu bilangan: 2.758
b=2.758000
float b;
printf (“Masukkan 1 bilangan: “);
scanf (“%f ”, &b);
printf (“b=%f ”, b);
return 0;
}
Typed via keyboard, then
pressed Enter
19
Naming Convention
• Some general rules of Naming variable:
–
–
–
–
–
–
c-style naming: this_is_variable
camelCase
CamelCase
p_ -> pointer prefix
s_ -> static prefix
g_ -> global prefix
20
Comments
• Make a readable code programming, so that it can be changed easily.
• Do not influencse the performance of program.
• Comment is beginned with /* and ended with */
– Used as many as possible /* … */ !!!
• Always used comments, if you starts a new function.
21
Conclusions
• Main() function is the first function that is being called by
the operating system.
• Basic data type are byte, char, int, and float.
• Basic I/O routine for c++ are cin and cout objects.
• Naming convention is used to standardize the way
programmer writes a variable.
• Comments are very useful for programmer, used them if
you create a program of your own.
22
Topic For Next Week
• Pointer variable
• Assignments:
– Read an online book of “CppEssentials.pdf” Chap. 5 page 65 until 79.
– Do the following exercises (taken from “exercises” page 80 of book
“CppEssentials.pdf”):
1. Define two functions which, respectively, input values for the elements of an array of reals
and output the array elements:
void ReadArray (double nums[], const int size);
void WriteArray (double nums[], const int size);
23
Topic For Next Week
• Assignments:
2. Define a function which reverses the order of the elements of an array of reals:
void Reverse (double nums[], const int size);
3. The following table specifies the major contents of four brands of breakfast cereals.
Define a two-dimensional array to capture this data:
Fiber
Cereal A
Cereal B
Cereal C
Cereal D
Sugar
12g
22g
28g
32g
Fat
25g
4g
5g
7g
Salt
16g
8g
9g
2g
0.4g
0.3g
0.5g
0.2g
24