Document 15057518
advertisement

Course Name: High Level Programming Language
Year
: 2010
Variable/Dynamic Pointer
Lecture 3
Learning Outcomes
At the end of this lecture, students are capable of:
Understanding differences between constant pointer versus variable pointer.
3
Outline Material
• Dynamic Memory Allocation – Variable Pointer
• Arithmetic Pointer I, II
• Const and pointer
4
Dynamic Memory Allocation
• Use malloc() and sizeof() for dynamically
allocating memory
int *a = (int*) malloc(k * sizeof(int))
Don’t: int *b = (int*) malloc(k * 4)
// not portable
• malloc() returns generic pointer (void *),
thus typecast it to (int *)
• Free dynamically allocated memory with
free()
free(a);
5
Pointer Arithmetic I
• Use pointer arithmetic to access sequence of data cells
• int a[4], *b = a;
b+i points to (i+1)th element of a
a[0]
•
b
a[1]
a[2]
b+1
b+2
*(b+n) is the same as a[n]
a[3]
b+3
6
Pointer Arithmetic II
• Note: b+3 does not mean adding 3 to b, rather adding 3 times the
size of the data cell to b
• Subtraction: inverse to adding
int *b = &a[3];
b-1 points to a[2]
• Walking through array
int sumArray(int *a, int size)
{ int i = 0, sum = 0;
while (i<size) { sum += *a++; i++;}
return sum;
}
7
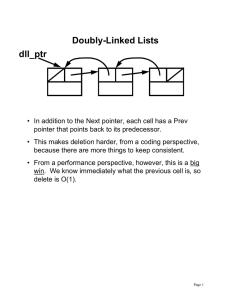
Const and Pointer
• What is the difference between const *p and * const p?
– “const” is an adjective that describes the following:
const * p
* const p
8
• const *p
Const and Pointer
– What is being pointed by a pointer is a constant
• Therefore the value *p can not be changed
void main (void) {
int a = 3;
100
int const * p;
3
p = &a;
(*p) ++;
p
a++;
p++;
printf( “%d”, p);
}
warning: increment of read-only
location
9
a
• * const p
Const dan pointer
– The value of a pointer (which is an address) is constant
• Therefore the pointer can not point to the other variable
void main (void) {
int a = 3;
100
int const * p;
3
p = &a;
(*p) ++;
p
a++;
p++;
printf( “%d”, p);
warning:assignment of read-only ‘p’
}
warning: increment of read-only variabel ‘p’
10
a
Conclusions
• Variable pointer is used to point out
several memory location, thus it is
named variable pointer.
• While constant pointer is used to point
only at one specific memory location.
11
11
Topic For Next Week
• Modularity
– Try to compile the following three files into one file which can be executed:
• File main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "satuperx.hpp"
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
float i;
i = 10.00;
cout << "Satu per " << i << "adalah" << 1/i << endl;
getchar();
return 0;
}
12
Topic For Next Week
•File oneperx.cpp
#include <cassert>
#include "satuperx.hpp"
double satuperx (int i) {
//variabel i harus selain angka 0!
assert(i!=0);
return 1/I;
}
•File oneperx.h
double satuperx (int i);
13