Can You Differentiate the Ammonia Oxidizers in Soil? Michelle Land
advertisement

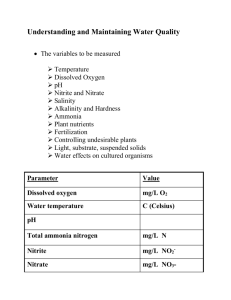
Can You Differentiate the Ammonia Oxidizers in Soil? Michelle Land Neeraja Vajrala Luis Sayavedra-soto Daniel Arp Botany and Plant Pathology Department Nitrification Influences Benefits – In terrestrial ecosystems: • nitrogen supply to plants – removal of high levels of ammonia in wastewater Downside – less than 30% of the applied N fertilizer is taken up by plants – increases loss of soil nitrogen through leaching and volatilization – increases nitrate pollution of ground waters • eutrophication – nitrifiers compete with plants for ammonia – The generation of nitrous oxide • A green house gas Roles Played Both Nitrosomonas europaea and Nitrosopumilus maritimus convert ammonia (NH3) into nitrite (NO2-). This project studies ammonia-oxidizing organisms. Big Picture Aim: To differentiate between ammoniaoxidizing archaea and bacteria and study their contributions to global nitrification. Prediction: There could be some inhibitors or inactivators that can specifically inhibit one of these communities. Metabolic Reaction of Ammonia-Oxidizing Bacteria and Archaea Ammonia Oxidizing Bacteria (AOB) Ammonia monooxygenase (amoABC) Hydroxylamine (NH2OH) Nitrite (NO2-) Ammonia (NH3) Ammonia monooxygenase (amoABC) Hydroxylamine oxidoreductase (HAO) ??? ??? Ammonia Oxidizing Archaea (AOA) Project Methylhydrazine Hypothesis: Methylhydrazine only effects the HAO enzyme in ammonia oxidizing bacteria. Prediction: Ammonia oxidizing bacteria will stop producing nitrite in the presence of methylhydrazine and ammonia oxidizing archaea will be unaffected. Methylhydrazine Affect on N. europaea NO MH 1 µM MH OD 600nm 2 µM MH 5 µM MH Control - 10µM MH MH Added to Control Days of Incubation Methylhydrazine Affect Nitrite (µM) on N. maritimus NO NOMH MH 1µM MH 2 µM MH Days of Incubation Soil Slurry Preparation • 20g of soil • phosphate buffer at PH=8 • 1.1 mM potassium chlorate solution (to stop the conversion of nitrite to nitrate) • 0.4 mM ammonium sulfate (energy source) Analysis of Nitrite Formation The soil slurry is filtrated and then tested Sulfanilamide + NNEQ + Nitrite Reddish Purple Azo Dye This solution is then placed in a spectrophotometer at 540nm and the absorbency is taken. Nitrite Standard Curve absorbancy at 540 nm 0.6 0.5 y = 0.1075x - 0.0081 R² = 0.9994 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 -0.1 Concentration of Nitrite (µg) Standard curve is used to calculate the nitrite concentration in the soil slurries. µg of Nitrite per gm of Soil Methylhydrazine Affect on Soil 140 130 120 110 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 NO NO Methylhydrazine MH 10 µMMethylhydrazine MH 10µM 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 Days of Incubation 7 8 9 Conclusion At the concentrations tested both ammoniaoxidizing archaea and bacteria were inhibited by methylhydrazine. Therefore these concentrations of methylhydrazine can not be used to differentiate the ammonia-oxidizing activity of AOB and AOA. Future Area of Study Metabolic Reaction of Ammonia-Oxidizing Bacteria and Archaea Ammonia Oxidizing Bacteria (AOB) Ammonia monooxygenase (amoABC) Hydroxylamine (NH2OH) Nitrite (NO2-) Ammonia (NH3) Ammonia monooxygenase (amoABC) Hydroxylamine oxidoreductase (HAO) ??? ??? Ammonia Oxidizing Archaea (AOA) Acknowledgements • • • • • Dr. Neeraja Vajrala Dr. Luis Sayavedra-soto Dr.Daniel Arp Dr. Kevin Ahern HHMI Undergraduate Internship Program • SBI Undergraduate Internship Program