Establishment of a System to Replicate, Study the Antiviral Defense Response
advertisement
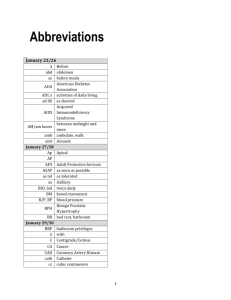
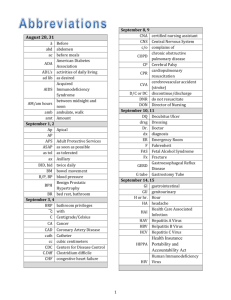
Establishment of a System to Replicate, Purify, and Use a Mutant RNA Virus to Study the Antiviral Defense Response in Plants Katie Brempelis Mentors: Dr. James C. Carrington, Dr. Kristin Kasschau, Dr. Hernan Garcia-Ruiz Dr. James C. Carrington Lab HHMI Program, Summer 2008 BACKGROUND • RNA Silencing • Used in antiviral defense and gene regulation • mRNA and viral ssRNA degradation, modification of DNA and histones, and translational repression • What happens when a plant is infected by a virus? • The plant enacts antiviral RNA silencing, producing virusderived small RNAs (siRNAs) • The virus produces suppressors proteins that counteract the plant’s RNA silencing response • Experiment Model • Arabidopsis thaliana and Nicotiana benthamiana • TuMV-GFP (Turnip mosaic virus with green fluorescent protein)wild type virus • TuMV-GFP-AS9 (silencing suppression deficient)mutant virus Components of RNA Silencing Pathways • Proteins: • DCLs- dsRNA-specific ribonucleases • RDRs- RNA-dependent RNA polymerases • AGOs- RNAse • RISC- RNA Induced Silencing Complex • RNA Components: • miRNA- gene regulation • tasiRNA- gene regulation • siRNA- antiviral defense RNA Silencing -hpRNA dsRNA -viral RNA Dicer siRNAs 21-26 nt RISC forms -Effector complex -Contains AGO protein -Incorporates one strand Targeted RNA cleaved by DCLs -mRNA -viral ssRNA RDR forms dsRNA - Signal Amplification Proposed Model • The Proposed Three-Phase Model for Antiviral Silencing •DCLs- recognition and cleavage •AGO- part of RISC •RDRs- amplification MOTIVATION • Effect of mutating A. thaliana genes is masked by the virus-encoded silencing suppressor • A suppressor-deficient virus is needed to provide a clear distinction between plant genes required and dispensable for antiviral RNA silencing upload.wikimedia.org SPECIFIC AIMS • Purification of TuMV-GFP-AS9 • To determine the requirement of A. thaliana genes in antiviral silencing people.whitman.edu Purification of TuMV-GFP-AS9 • Established protocol for wild type virus, using N. benthamiana as a host • Hypothesis: A highly concentrated inoculum of the mutant virus can be prepared using a similar approach • Prediction: A semi-pure mutant virus preparation will be highly infective • Method: Injection with Agrobacterium www.sgn.cornell.edu Purify virus www.focuscience.org Titrate on dcl2/3/4 mutants Maximizing Efficiency of AS9 Harvest • What is the best day to harvest AS9-infected N. Benthamiana leaves? Conclusions: •GFP does not necessarily indicate virus accumulation •Highest viral accumulation at 5 and 6 dpi •Leaves were senescing •Harvest leaves at 4 dpi Measuring Infectivity • What is the infectivity of the AS9 prep? Average GFP Foci per Leaf Titration of Wild Type TuMV-GFP and Mutant AS9 Conclusions: -The AS9 viral prep is infective 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 1x Mutant 1X Wt X/5 Wt Virus X/10 Wt -Use a 20-fold dilution of the wild type prep for similar infectivity with the mutant AS9 prep Proposed Model • The Proposed Three-Phase Model for Antiviral Silencing •DCLs- recognition and cleavage •AGO- part of RISC •RDRs- amplification Determining A. thaliana genes required in antiviral silencing • Hypothesis: Both DCL1 and RDR6 proteins are required for antiviral RNA-silencing • Prediction: AS9 mutant virus accumulation in dcll-7 and rdr6-15 mutants will be higher than in Col-0 wild type plants • Method Inoculate A. thaliana Col-0, dcl1-7, dcl2/3/4, and rdr1/2/6 Collect infected tissue at 7, 10, 15 dpi Western blot detection of TuMV-CP Inoculate A. thaliana Col-0, rdr1-1, rdr2-1, rdr6-15, rdr1/2/6, dcl2/3/4 Method for DCL1 Experiment A. thaliana Genotype Mutation Predictions AS9 Mutant Wild type dcl2/3/4 rdr1/2/6 Wild type Partial DCL1 activity Lacks DCL2, DCL3, & DCL4 dicing activity Lacks RDR1, RDR2, & RDR6 activity No infection Infection Infection Infection Infection Infection Infection Col-0 Infection dcl1-7 RESULTS • AS9 did not infect dcl1-7 mutants Probed for TuMV-CP, 7 dpi inflorescence clusters Wt AS9 Wt AS9 Wt AS9 Wt AS9 Method for RDR Experiment A. thaliana Col-0 rdr1-1 rdr2-1 rdr6-15 rdr1/2/6 dcl2/3/4 Lacks RDR1, RDR2, & RDR6 activity Lacks DCL2, DCL3, & DCL4 dicing activity Infection Infection Infection Infection Infection Infection Genotype Mutation Wild type Lack activity of a single RDR protein Predictions AS 9 Mutant Wild type No infection Infection RESULTS • AS9 infects all single RDR mutants 7 dpi Conclusions: Wt * •rdr1, rdr2, and rdr6 are all required in antiviral silencing Mutant •rdr1 seems to have the largest effect in local leaves * *Plants with systemic GFP ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS • Howard Hughes Medical Institute • Cripps Scholarship Fund, College of Science • Mentors: • Dr. James C. Carrington • Dr. Kristin Kasschau • Dr. Hernan Garcia-Ruiz • Dr. Kevin Ahern