Using HX-MS to Determine Protein Structure of AhpC 2, a Peroxiredoxin
advertisement

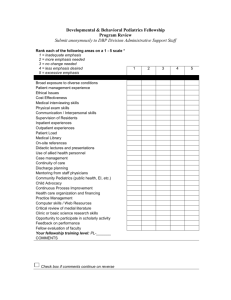
Using HX-MS to Determine Protein Structure of AhpC 2, a Peroxiredoxin Piper J. Klemm Faculty Advisor: Claudia S. Maier, PhD HHMI Fellowship, OSU August 20, 2008 PJK 2008 1 Hypothesis • Mass spectrometers (MS) can be used as tools to elucidate protein structure through proton exchange with their solvent. This structure can be used for the determination of protein functions and dynamics. PJK 2008 2 Hydrogen Exchange with Solvent • Deuterium solvent exchanges with structural protons without change in structure (A) • Protein unfolded in exchange process (B) • Wales & Engen 2006. PJK 2008 3 Alpha Helices • Hydrogen bonding in • alpha helices Limits proton-solvent exchange • http://wiz2.pharm.wayne.edu/biochem/nsphelix1.jpg PJK 2008 4 Beta Sheet • Plenty of surface area for solvent interaction •http://cnx.org/content/m11614/latest /beta_sheet_cartoon.JPG PJK 2008 5 Background • HX-MS to analyze protein structure PJK 2008 www.hxms.com/hxms.htm 6 Secondary Structure Background • http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore/remediatedSequence.do?st ructureId=1YF0&params.chainEntityStrategyStr=all&forceP PJK 2008 ageForChain=E#chainC 7 Protein Map Goal • Protein Map for PPARγ LBD. Each block has six distinct time points color coordinated with deuterium level (bottom right). • Hamuro, Yoshitomo et al. “Hydrogen/deuterium-exchange (H/D-Ex) of PPARg LBD PJK 2008 in the presence of various modulators.” Protein Science: 2006. 5, 1883–1892. 8 Peroxiredoxin Mutant • Threonine 77 replaced with valine PJK 2008 9 Background • Peroxiredoxin takes a catalytic pathway upon the binding of a peroxide substrate Poole.:Chapter 4: The catalytic mechanism of peroxiredoxins. In Peroxiredoxin Systems (Flohe et al.). 2007. PJK 2008 10 Robust Peroxiredoxin Fully Folded Locally Unfolded Wood et al. 2003 PJK 2008 11 Protocol 0621NNS5min 1333 (8.312) TOF MS ES+ 476 812.9929 100 813.5273 812.4819 811.4835 % 814.5618 Deuterium Level 0 0621NNS1min 1335 (8.337) TOF MS ES+ 366 812.4819 812.9929 100 4 813.5273 811.5067 Relative Deuterium Level (Da) 4 % 814.0504 3 814.5618 0 0621NNS0min 1336 (8.337) 3 775.00 TOF MS ES+ 365 812.5168 812.0059 813.0162 100 2 813.5505 811.5183 % 814.0620 2 814.5618 0 0621NNSControl 1340 (8.357) 1 TOF MS ES+ 458 811.4951 100 812.5168 1 % 813.0510 0 1 10 100 0 m/z 810 811 812 813 814 815 816 817 818 819 820 821 Time (min) PJK 2008 12 Instrumentation • Mass Spectrometry (MS) for biomolecular structure determination •QTOF LC-MS •MALDI TOF/TOF PJK 2008 13 MALDI Results • Peaks expand with longer deuterium exposure • Preliminary analysis PJK 2008 14 QTOF Results 0621NNS5min 1333 (8.312) TOF MS ES+ 476 812.9929 100 813.5273 812.4819 811.4835 % 814.5618 0 0621NNS1min 1335 (8.337) TOF MS ES+ 366 812.4819 812.9929 100 813.5273 811.5067 % 814.0504 814.5618 0 0621NNS0min 1336 (8.337) TOF MS ES+ 365 812.5168 812.0059 813.0162 100 813.5505 811.5183 % 814.0620 814.5618 0 0621NNSControl 1340 (8.357) TOF MS ES+ 458 811.4951 100 812.5168 % 813.0510 0 810 811 812 813 814 PJK8152008 m/z 816 817 818 819 820 821 15 QTOF Results Deuterium Level • m/z = 581.83 4 Relative Deuterium Level (Da) Th • Quadruple Charge State • Amino acids 1-20 4 3 3 2 581.00 2 1 1 0 1 10 100 Time (min) PJK 2008 16 QTOF Deuterium Graph AhpC (T77V) Deuteration Labels of Oxidized Form Deuterium Level 3.00 0.5" 1.00" 2.50 5.00" 10.00" 2.00 15.00" 30.00" 1.50 120.0" 1.00 0.50 0.00 1--20 21-35 36-43 51-60 61-67 68-76 88-95 96110 111122 123132 133147 177182 Peptide Fragments PJK 2008 17 QTOF Deuterium Graph with TCEP AhpC (T77V) Deuteration Labels at Six Labeling Time Points 6.00 1" 5" 10" 15" 20" 30" 4.00 3.00 2.00 1.00 -18 2 177 -17 6 156 -14 7 133 -13 2 123 -12 2 117 96116 96103 6887 4260 4350 3643 2135 2132 1-- 2 0 0.00 1-- 5 Deuterium Level 5.00 Peptic Fragments PJK 2008 18 Ribbon Structure Determined From Deuterium Graph PJK 2008 19 Future Work • Replication of deuterium label graph • Replication of HXMS to determine • accuracy of how reduction of disulfide bridges changed structure Determine any overall conformational changes occurring with reduction of disulfide bridges PJK 2008 20 Acknowledgements • • • • • Howard Hughes Medical Institute, OSU Claudia S. Maier, PhD Kevin Ahern, PhD The Maier Laboratory Department of Biochemistry and Biophysics, OSU • Department of Chemistry, OSU 21 PJK 2008 21