Calmodulin and Phosphorylase Interaction
advertisement
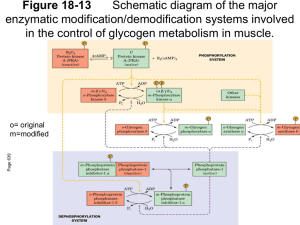
Calmodulin and Phosphorylase Interaction By James Proestos Biochemistry and Biophysics Department Dr. Sonia Anderson’s Lab Agriculture and Life Science Building Calcium • Activator of many cellular processes (cell signaling) – Triggers muscle proteins to contract – Activates many enzymes Calmodulin Information • Is found in all animal and plant tissues • Binding of calcium controls its ability to bind to a protein to regulate the target protein’s activity. Calmodulin Structure Ca Ca Ca Target Calmodulin Ca Ca Ca Bound Calmodulin Target Protein Bound Calmodulin Bound Protein Bound Calmodulin Glycogen Phosphorylase Information • Found in fast twitch muscle tissue • It catalyzes the breakdown of glycogen • Controlled by phosphorylation/dephosphorylation The Phosphorylated and Unphosphorylated States of Glycogen Phosphorylase B A Glucose Serine Cascade of Reactions in Glycogen Degradation The Interaction of Proteins in Glycogen Cascade • Phosphorylase Kinase becomes active by calcium binding to the intrinsic calmodulin • The phosphorylase kinase interacts with the glycogen phosphorylase • It is not known if the calmodulin can readily bind with glycogen phosphorylase in this interaction • Phosphorylase binds to calmodulin Hypothesis • Malencik and Anderson proposed that calmodulin binding regions are often sites of regulation by serinethreonine phosphorylation/dephosphorylation • Phosphorylase binds to calmodulin Hypothesis • Malencik and Anderson proposed that calmodulin binding regions are often sites of regulation by serinethreonine phosphorylation/dephosphorylation Question • Is the calmodulin binding region of phosphorylase b the same as the phosphorylation site and how does phosphorylation affect this binding to calmodulin? Purification of Phosphorylase B • Grind rabbit muscle • Spin in a centrifuge • Remove the pellet • Ammonium sulfate precipitation and crystallize • Repeat crystallization several times Phosphorylase Purification • Scan of phosphorylase gel 96 K 68 K 42 K 29 K 18 K 12 K Phosphorylase Purification Phosphorylase Purification • Scan of concentrated protein Purification of Calmodulin • Grind bovine brain • Spin in centrifuge and remove pellet • Pass the supernatant through several columns Purification of Calmodulin Purification of Calmodulin Scan of calmodulin gel 96 K 42 K 29 K 18 K 12 K Experimental Plan • Cleave the glycogen phosphorylase protein into peptides • Isolate peptides of interest by conventional column chromatography • Determine the binding of the peptides using a calmodulin affinity column • Identify the peptide(s) from the calmodulin affinity column by mass spectrometry and/or amino acid analysis • Phosphorylate the peptide(s) and compare its affinity for calmodulin to that of the unphosphorylated peptide (by fluorescence). Cleavage of Phosphorylase B 1 14 841 Subtilisin 1 14 Hydroxylamine CNBR RXN 264 1 1 265 14 14 134 91 841 135 242 350 351 428 442 604 259 260 497 498 841 Cleavage of Phosphorylase B Cyanogen bromide is our tool to cleave at methionine residues The resulting peptides will be the focus of the binding of calmodulin Cleavage of Phosphorylase B Num From-To MW 1 1- 91 11054.63 phosphorylation 2 92- 99 921.07 3 100-119 2184.45 4 120-147 2940.24 5 148-176 3229.75 6 177-224 5662.32 7 225-241 1938.17 8 242-350 12565.35 9 351-428 9322.85 10 429-441 1446.71 11 442-604 19129.32 12 605-615 1102.30 13 616-618 349.47 14 619-679 6480.42 15 680-682 425.57 16 683-692 991.20 17 693-699 735.79 18 700-713 1591.74 19 714-764 6134.86 20 765-766 263.38 21 767-800 4333.90 22 801-840 4545.12 pI 10.17 Residue that will be observed, serine-14 is site of 11.15 2.74 3.35 8.80 4.95 6.81 8.51 7.36 7.02 9.64 9.80 10.20 4.59 9.75 6.96 2.91 2.87 4.45 6.96 8.61 10.20 Separation of Glycogen Phosphorylase Peptides • Gel filtration – Separation based on size • Cation exchange – Separation based on charge (pI >7) • High Performance Liquid Chromatography – Separation based on hydrophobicity • Analyze peptides – Peptide 1-91 – Synthetic peptide 6-25 – Calmodulin binding peptide Cleavage of Phosphorylase B 1 14 841 CNBR RXN 1 14 91 242 350 351 428 442 604 Gel Filtration Peptide Fragments Cation Exchange 1.0 CNBr separation of Peptides on SP-Sephadex 0.8 Absorbance 280 nm Peptide 351-428 Peptide 1-91 0.6 0.4 Peptide 242-350 (unproven) 0.2 0.0 0 50 100 Tube Number 150 200 Amino Acid Analysis of Glycogen Phosphorylase Synthesized Peptide 1 91 14 MW= 11054.63 DQEKRKQISVRGLAGVENVT MW= 2228 HPLC Purification of Peptide 6-25 Mass Spectrometry of Peptide 6-25 Calmodulin/Phosphorylase B Interaction Phosphorylase peptides bound calmodulin gel peptides that do not bind to calmodulin Analysis of Calmodulin/Glycogen Phosphorylase Interaction Isolated peptides A)Peptide(1-91) B)Peptide(6-25) C)CaM Binding Peptide Determine affinity of calmodulin-peptide complex Phosphorylate peptides and recheck affinity Analysis of Phosphorylation Interaction Peptide -P +P Intact phosphorylase +++ ND CNBr digest (mixture) +++ + + + Peptide 1-91 ++++ ++ Synthetic peptide (6-25) none none Glutathione (control) none none Peptide 351-408 Future Work • Determine and verify phosphorylation and stoichiometry of the various peptides by the use of ATP32 • Determine the affinity of the peptides quantitatively by the use of fluorescence titration • Complete sequence and/or mass spectroscopy information on the petide/s that bind to the solid support calmodulin column and, if enough material is isolated, to perform calmodulin binding • Redetermine the binding of peptide 6-25 utilizing different approaches, if necessary, to verify that it does not bind to calmodulin • Subfragment peptide 1-91 and redetermine its binding to calmodulin Acknowledgements Howard Hughes Medical Institute Dr. Sonia Anderson Dean Malencik Department of Biochemistry and Biophysics Kevin Ahern Cleavage of Phosphorylase B

![Anti-Calmodulin antibody [J4D8] ab75207 Product datasheet 1 References 1 Image](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/012961983_1-fbc3a125831a6d5a42cfe8d3e7d70ccc-300x300.png)