Questions (26)
advertisement
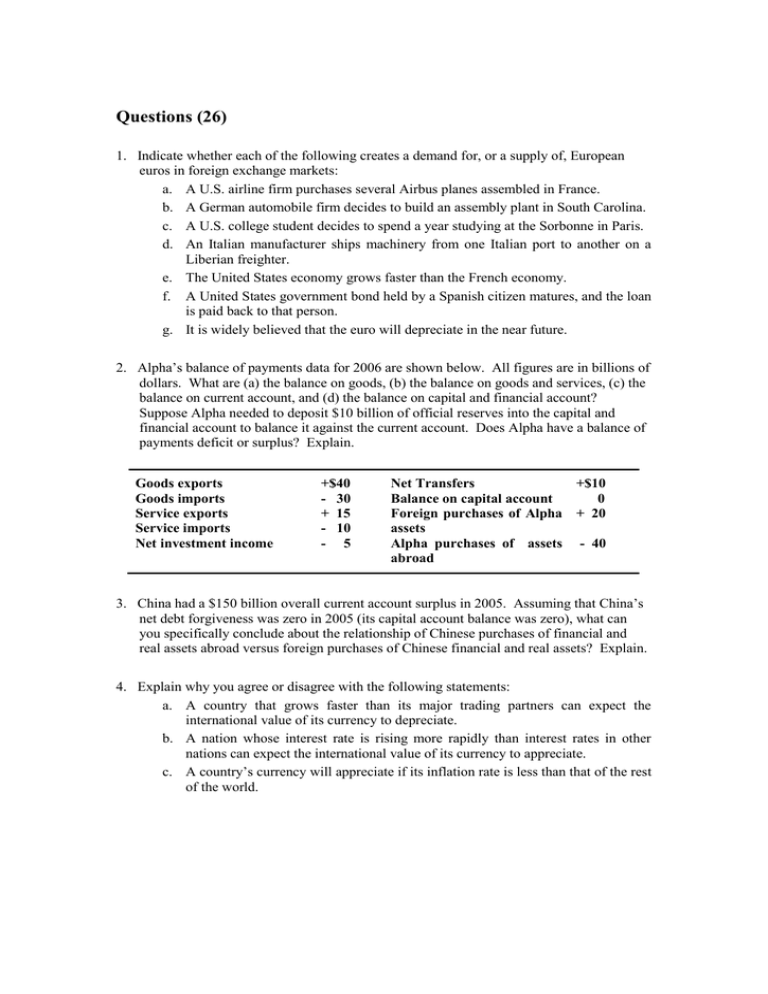
Questions (26) 1. Indicate whether each of the following creates a demand for, or a supply of, European euros in foreign exchange markets: a. A U.S. airline firm purchases several Airbus planes assembled in France. b. A German automobile firm decides to build an assembly plant in South Carolina. c. A U.S. college student decides to spend a year studying at the Sorbonne in Paris. d. An Italian manufacturer ships machinery from one Italian port to another on a Liberian freighter. e. The United States economy grows faster than the French economy. f. A United States government bond held by a Spanish citizen matures, and the loan is paid back to that person. g. It is widely believed that the euro will depreciate in the near future. 2. Alpha’s balance of payments data for 2006 are shown below. All figures are in billions of dollars. What are (a) the balance on goods, (b) the balance on goods and services, (c) the balance on current account, and (d) the balance on capital and financial account? Suppose Alpha needed to deposit $10 billion of official reserves into the capital and financial account to balance it against the current account. Does Alpha have a balance of payments deficit or surplus? Explain. Goods exports Goods imports Service exports Service imports Net investment income +$40 - 30 + 15 - 10 - 5 Net Transfers +$10 Balance on capital account 0 Foreign purchases of Alpha + 20 assets Alpha purchases of assets - 40 abroad 3. China had a $150 billion overall current account surplus in 2005. Assuming that China’s net debt forgiveness was zero in 2005 (its capital account balance was zero), what can you specifically conclude about the relationship of Chinese purchases of financial and real assets abroad versus foreign purchases of Chinese financial and real assets? Explain. 4. Explain why you agree or disagree with the following statements: a. A country that grows faster than its major trading partners can expect the international value of its currency to depreciate. b. A nation whose interest rate is rising more rapidly than interest rates in other nations can expect the international value of its currency to appreciate. c. A country’s currency will appreciate if its inflation rate is less than that of the rest of the world. 5. Diagram a market in which the equilibrium dollar price of one unit of fictitious currency zee (Z) is $5 (the exchange rate is $5 = Z1). Then show on your diagram a decline in the demand for Zee. a. Referring to your diagram, discuss the adjustment options the United States would have in maintaining the exchange rate at $5 = Z1 under a fixed exchangerate system. b. How would the U.S. balance of payments surplus that is created (by the decline in demand) get resolved under a system of flexible exchange rates? See the graph illustrating the market for zees. 6. Compare and contrast the Bretton Woods system of exchange rates with that of the gold standard. What caused the collapse of the gold standard? What caused the demise of the Bretton Woods system? 7. Describe what is meant by the term “managed float.” Did the managed float system precede or follow the adjustable-peg system? Explain