Curriculum 2.0 Presentation
advertisement

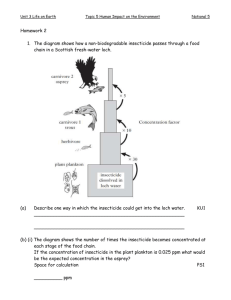
OUTCOMES • Receive a general overview of Curriculum 2.0 • Hear how your child will learn the new Thinking and Academic Success Skills • Hear about math upgrades in Curriculum 2.0 • Learn more about Standards Based Grading & Reporting (new Report Cards) CONSENSOGRAM PLEASE PLACE THE DOT (FOUND IN YOUR FOLDER) ON THE CONSENSOGRAM INDICATING YOUR LEVEL OF KNOWLEDGE ABOUT CURRICULUM 2.0. Also, in your folder you will find several notecards. Please use these to write down any questions you have during the presentation. We will collect and address them throughout the meeting. Schools in our Past TEACHER CENTERED SHIFT TO STUDENT CENTERED WHY CHANGE THE CURRICULUM? Many students have excelled in reading and math since 2001. We noticed that students who had the most success in advanced reading and math had certain characteristics as students – • Successful students are critical thinkers. • Successful students are creative. • Successful students know how to learn. What is MCPS Curriculum 2.0? New Internationally-driven standards in math, reading, and writing. Renewed focus on teaching the whole child. Integrates thinking, reasoning, and creativity for a lifetime of learning. What is better in Curriculum 2.0? Staying The Same Strong focus on reading and math • Separate times for art, music, and physical education and other specials • Classroom teachers providing instruction in science and social studies Thinking skills included in content areas Upgrade Internationally-driven standards in math, reading, and writing Integration of content areas through Thinking and Academic Success Skills • Specific instruction on Thinking and Academic Success skills across content areas • Clearly defined critical thinking, creative thinking, and academic success skills 550 2003 PISA - Math OECD Average U.S.A. 500 450 400 350 300 Slide Credit: EdTrust.org Data Source: Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD), PISA 2006 Results, http://www.oecd.org/ Differences Among Assessments Most U.S. standardized tests are designed to assess whether students learned what they were taught in school, focusing on recall and recognition of facts. Assessments in high-achieving nations increasingly emphasize learning designed to assess if students can apply what they’ve learned to new problems and situations, focusing on inquiry and explanations of ideas. (U.S. Assessment) National Assessment of Educational Progress 8th- and 12thGrade Science 1. What two gases make up most of the Earth's atmosphere? A) Hydrogen and oxygen B) Hydrogen and nitrogen C) Oxygen and carbon dioxide D) Oxygen and nitrogen 2. Is a hamburger an example of stored energy? Explain why, or why not. ______________________________________ ______________________________________ (International Assessment) A PISA Task: Science FLIES Read the following information and answer the questions which follow. A farmer was working with dairy cattle at an agricultural experiment station. The population of flies in the barn where the cattle lived was so large that the animals' health was affected. So the farmer sprayed the barn and the cattle with a solution of insecticide A. The insecticide killed nearly all the flies. Some time later, however, the number of flies was again large. The farmer again sprayed with the insecticide. The result was similar to that of the first spraying. Most, but not all, of the flies were killed. Again, within a short time the population of flies increased, and they were again sprayed with the insecticide. This sequence of events was repeated five times: then it became apparent that insecticide A was becoming less and less effective in killing the flies. The farmer noted that one large batch of the insecticide solution had been made and used in all the sprayings. Therefore he suggested the possibility that the insecticide solution decomposed with age. Source: Teaching About Evolution and the Nature of Science, National Academy Press, Washington, DC, 1998, p. 75. 1. The farmer's suggestion is that the insecticide decomposed with age. Briefly explain how this suggestion could be tested. 2. The farmer's suggestion is that the insecticide decomposed with age. Give two alternative explanations as to why "insecticide A was becoming less and less effective ..." How the Demand for Skills Has Changed Mean task input as percentiles of the 1960 task distribution Economy-wide measures of routine and nonroutine task input (U.S.) Routine manual 65 Nonroutine manual 60 55 Routine cognitive 50 Nonroutine analytic 45 Nonroutine interactive 40 1960 1970 1980 1990 2002 The dilemma of schools: (Frank Levy and Richard Murnane, 2005)that are easiest to teach and The skills test are also the ones that are easiest to digitize, automate, and outsource Art Math Music Health Information Literacy Reading Science Social Studies Writing Renewed focus on teaching the whole The Thinking and Academic Success Skills are the common thread that integrate content areas. Content areas still maintain their separate goals and objectives. Students learn more when making connections across content areas – natural areas for connections are provided. Thinking and Academic Success Skills (TASS) Each grade level will focus on 2 TASS for each quarter. Quarter One Analysis Collaboration Grade 1 X X Grade 2 Grade 3 X X Fluency X X Students will be evaluated on each TASS across all content areas. Report cards will indicate student progress on each TASS as Demonstrating, Progressing or Not Yet Evident. What is Analysis? Breaking a whole into parts that may not be immediately obvious and examining the parts so that the structure of the whole is understood. What will Analysis look like in a 3rd grade classroom? Science: Find the relationship between a surface and the motion of an object. Math: Describe patterns on a multiplication table to understand multiplication facts with 0 and 1. Writing: Understand how different verb tenses change writing. What is Collaboration? Working together to achieve a shared goal or carry out a plan of action. What will Collaboration look like in a 1st grade classroom? Reading: Participating in a discussion with a guided reading group. Math: Working together to determine how to measure given objects in non-standard units. Science: Working with a group to design and carry out a plan to demonstrate how humans impact plants in the environment. HOW DO YOU THINK OF YOURSELF? Do you consider yourself a reader? Do you consider yourself a “math person?” Building a Stronger Foundation What Makes The Curriculum 2.0 Foundation Stronger? MCPS 2001 Curriculum Framework Curriculum 2.0 / Internationally-driven standards “Spiral” Curriculum – concepts introduced and mastered over several grade levels Concept introduced and mastered in one grade level Grade level standards not sufficiently challenging for most students Many standards are “pulled down” from upper grades. Language of standards was general and not specific – resulting in teaching to test. Fewer, higher, clearer standards provide direction for teaching and learning – not testing. Curriculum developed independently of all other subjects Curriculum integrated with other content areas and thinking and academic skills see it as sensible and useful to solving problems and making sense of the world. All students will reach proficiency in math – Understanding, Computing, Applying, Reasoning, and Engaging (UCARE). Goals of the MCPS Mathematics Program Develop students who love math and What is going deeper in math? Understanding Engaging Comprehending Concepts, Operations, & Relations Seeing math as sensible, useful, and doable Reasoning Computing Carrying out procedures Using logic to explain a solution Applying Formulating and solving mathematical problems Building a stronger foundation Understanding Engaging Comprehending Concepts, Operations, & Relations Seeing math as sensible, useful, and doable Reasoning Computing Carrying out procedures Using logic to explain a solution Applying Formulating and solving mathematical problems 1½ ÷ ½ = a. b. c. d. ½ ¾ 3 1 Write this problem as a question using words and not symbols. 3 2 3 2 1 How many halves are in one and one half? 1½ ÷ ½ = 3 Describe a situation requiring use of this concept. You have a yard and a half of ribbon to make bows. Each bow requires ½ yard. How many bows can you make? Understanding the Relationship Between Multiplication and Division 2 ? 1 2 1 4 How would you solve or interpret this division problem? 2 ? 1 2 4 1 29 Why does the algorithm work? 2 ? 1 2 1 4 How many fourths are in 2 12 ? 1 4 1 of what number is 2 2? 2 ? 1 2 4 1 30 Complete the number sentence with <, >, or = 352 < 360 114 > 113 What does going deeper mean? “I understand not only how and when to use an algorithm; I know why the algorithm is the most efficient way to solve a problem – and I can explain why!” 32 GRADING & REPORTING Standards-based grading involves measuring students' proficiency on welldefined standards. Standards-based grading reports tell us how students are performing on a set of clearly defined learning outcomes. EXAMPLE CONTENT: GRADE 3 – MATH MEASUREMENT TOPIC: OPERATIONS AND ALGEBRAIC THINKING PROFICIENCY STATEMENT: A student has demonstrated proficiency by: (Understanding) Representing and interpreting multiplication and division problems. Understanding the relationship between multiplication and division; (Computing) Fluently multiplying and dividing within 100; (Applying) Using multiplication and division within 100 to solve word problems. Applying properties of operations as strategies to multiply and divide. Applying strategies to solve two-step word problems using the four operations; (Reasoning) Explaining patterns in an addition or multiplication table. Explaining and justifying a solution to a problem or extending from something known to something not yet known; (Engaging) Seeing mathematics as sensible, useful, and doable-if you work at it-and being willing to do the work. How will students be assessed? Reading • Anecdotal Records from reading groups • Graphic Organizers • During Reading Assignment Tasks (post-its, organizers, questions) • Written responses Math • Anecdotal records within small group instruction • MCPS created formatives • Interactive Tasks • Open-ended word problems Where can I learn more? http://www.montgomeryschoolsmd.org/curriculum/ 2.0/ Definitions and examples of Thinking and Academic Success Skills Parent Guides for the content in each grade level – K-2 (what will my student learn?); National PTA Parent guides - http://www.pta.org/5307.htm Video examples of integration Video on Math changes Share your feedback with MCPS Detailed curriculum framework (philosophy, research, content area learning objectives) Questions To Ask Your Child’s Teacher Is my child reading at grade level? Can you show me books that are the right level for my child? How is my child doing in math? How can I help my child at home? How will you determine my child’s grade? How much time should my child be spending on homework? Aside from report cards, what are the best ways to keep up to date on my child’s progress?