Physics 131 Test/Exam Problems: Oscillations
advertisement
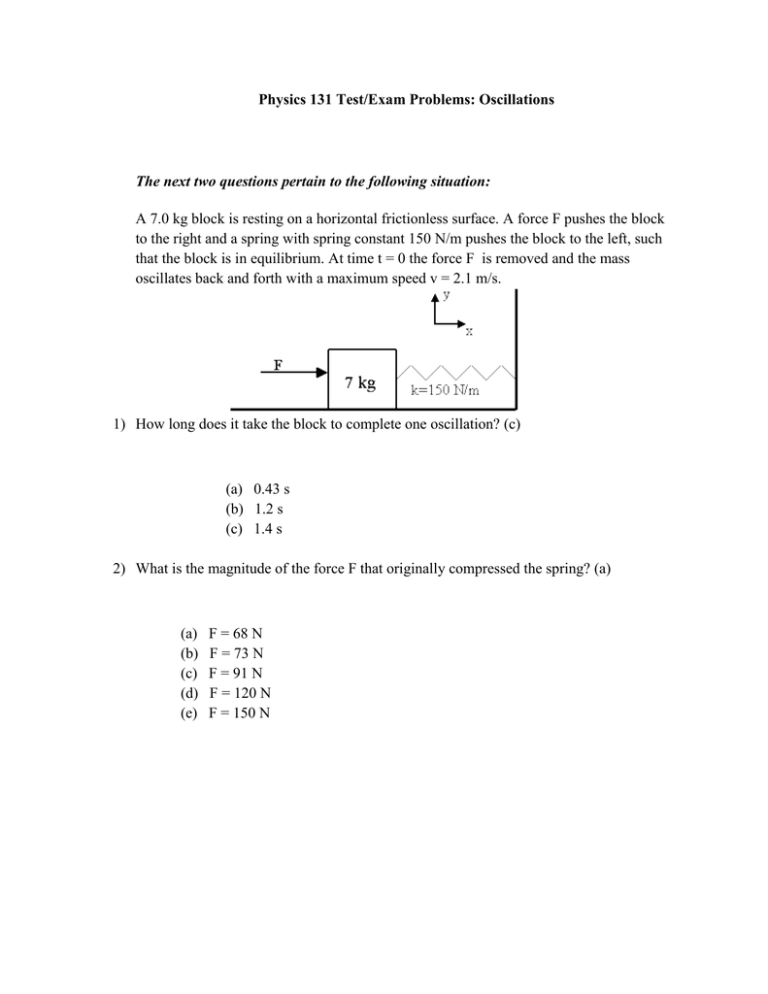
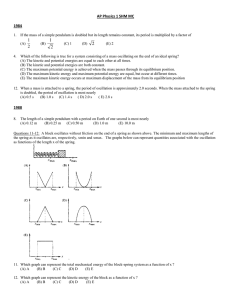
Physics 131 Test/Exam Problems: Oscillations The next two questions pertain to the following situation: A 7.0 kg block is resting on a horizontal frictionless surface. A force F pushes the block to the right and a spring with spring constant 150 N/m pushes the block to the left, such that the block is in equilibrium. At time t = 0 the force F is removed and the mass oscillates back and forth with a maximum speed v = 2.1 m/s. 1) How long does it take the block to complete one oscillation? (c) (a) 0.43 s (b) 1.2 s (c) 1.4 s 2) What is the magnitude of the force F that originally compressed the spring? (a) (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) F = 68 N F = 73 N F = 91 N F = 120 N F = 150 N 3) A pendulum hanging from the ceiling of an elevator is swinging with the period of 2 seconds when the elevator is at rest. Assume that the elevator is near the surface of the earth. Suddenly, the elevator undergoes vertical acceleration and the period of the pendulum has changed to 2.2 seconds. (b) What is the direction of acceleration? (a) upward (b) downward The next four questions pertain to the following situation: An object of mass m is hanging from a vertical spring of spring constant k (= 20 N/m) near the surface of the earth. In equilibrium, the spring is stretched by 10 cm relative to the relaxed length of the spring. The spring is then compressed by 1 cm relative to the equilibrium position and is released into oscillation at time t = 0. The height of the object relative to the equilibrium height oscillates as shown below as a function of time. 4) Among the three time points marked A and B and C, when is the speed of the object the greatest? (a) (a) A (b) B (c) C 5) Between the two time points marked A and B, when is the acceleration of the object the largest in magnitude?(b) (a) A (b) B 6) What is the mass m of the object? (c) (a) 0.10 kg (b) 0.15 kg (c) 0.20 kg 7) Which of the following curves would best describe the height vs. time curve, if the mass of the object is quadrupled with all other quantities remaining the same? (b) The next two questions pertain to the following situation: A 5 kg block is hanging from a spring. The spring is supported rigidly from above. The equilibrium position of the block is where the block hangs when it is not oscillating. The block is made to oscillate such that the displacement of the block from its equilibrium position is 0.1 m. The speed of the block is measured, and it is determined that the speed of the block when it passes through the equilibrium position is 1 m/s. 8) What is the spring constant? (a) (a) 500 N/m (b) 750 N/m (c) 1500 N/m 9) What is the approximate period of the oscillation? (c) (a) 0.34 s (b) 0.43 s (c) 0.63 s The next two questions pertain to the following situation: 10) A pendulum is made of a small weight of mass 1.5 kg attached to a string of length 2 m. The mass is released gently with the initial angle displacement of 5°. How long does it take for the mass to reach its lowest point for the first time? (c) (a) 2.84 s (b) 1.42 s (c) 0.71 s What is the maximum kinetic energy of the pendulum? (c) (a) 0.33 J (b) 0.22 J (c) 0.11 J The next two questions pertain to the following situation: 11) A mass M = 2 kg is suspended by a spring with spring constant k = 8 N/m. Initially the mass is at its resting position, y = 0. At t = 0 it is struck sharply from below by a hammer so that the mass begins to move with speed 0.1 m/s. What is the period with which the mass oscillates? (c) (a) 1.1 s (b) 2.1 s (c) 3.1 s (d) 4.1 s (e) 5.1 s 12) Suppose the setup was placed on the moon (where the gravitational acceleration is smaller than for Earth); the period of oscillation would be (c) (a) smaller. (b) larger. (c) the same. 13) Which of the following equations best describes the position of the mass? (a) (a) y = 0.05 sin(2t) m (b) y = 0.05 cos(2t) m (c) y = 0.1 sin(2t) m (d) y = 0.1 cos(2t) m (e) y = 0.1 cos(4t) m 14) What is the maximum acceleration of the mass? (b) (a) 0.1 m/s2 (b) 0.2 m/s2 (c) 0.3 m/s2 (d) 0.4 m/s2 (e) 0.5 m/s2