Pertemuan 11 Tree & Binary Tree Matakuliah : T0026/Struktur Data
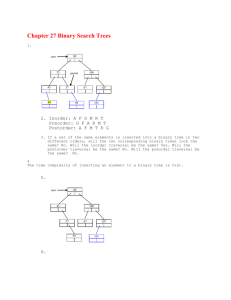
advertisement

Matakuliah
Tahun
Versi
: T0026/Struktur Data
: 2005
: 1/1
Pertemuan 11
Tree & Binary Tree
1
Learning Outcomes
Pada akhir pertemuan ini, diharapkan mahasiswa
akan mampu :
• Mahasiswa dapat mengembangkan
program modular yang menggunakan ADT
tree
2
Outline Materi
•
•
•
•
•
pengertian dan kegunaan TreeADT tree
Terminologi Tree
Pengertian Binary Tree
Operasi Traversal Tree
Representasi Tree: Array & linked-list
3
TREE
•
•
•
•
One-to-Many data relational (Hierarchy).
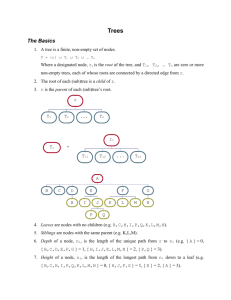
Definition : A tree is a finite set of one or more nodes such that :
– There is a specially designed node called the ROOT.
– The remaining node a partitioned into n>=0 disjoint sets
T1,…,Tn, where each of these set is a tree. T1,...,Tn are
subtrees of the ROOT.
There is an instance of recursive definition since the subtrees as
trees.
Two types of data presentation (genealogical) :
–
–
Pedigree chart (figure A: S ancestor)
Lineal chart (figure B : descendant)
Dusty
Honey Bear
Brundhilde
Brandy
Terry
Figure A. Pedigree Chart
Proto Indo-European
Italic
Osco-Umbrian
Hellenic
Germanic
Latin
Figure B. Lineal Chart
4
TREE
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Normally we draw trees with root at the top.
The degree of node is the number of subtrees of the node.
The degree of tree is the maximum degree of the node in the tree.
Height/depth is the maximum level of any node in the tree.
Parent-Child.
Siblings are Children of the same Parent
Ancestors
Descendant
DEGREE of C : 2
DEGREE of Tree : 3
Level 1
A
Level 2
B
HEIGHT: 3
C
D
PARENT of C : A
CHILDREN of A : B, C, D
Level 3
E
TREE
F
G
SIBLING of F : G
ANCESTOR of F : A, C
DESCENDANT of C :F, G
5
Binary Tree
• Set of nodes that is either empty or consist of a root and two disjoint
binary trees called left subtree and right subtree .
• Degree of any given node must not exceed two.
• Maximum number of nodes :
– On level i : 2i -1 , i >= 1
– In a Binary Tree of depth k : 2 k -1, k >=1
• Types
– Complete Binary Tree
– Skewed Binary Tree
k
• Full Binary Tree is Binary Tree that has maximum number of nodes
(2
-1)
A
B
D
A
C
E
Complete Binary Tree
C
G
Skewed Binary Tree
6
Binary Tree Traversals
•
•
Traversing is visiting each node in the tree.
Type/name of traversals :
1. PreOrder
(VLR)
2. InOder
(LVR)
3. PostOrder (LRV)
PreOrder :
–
Visit Root (N)
–
Move Left SubTree(T1)
–
Move Right SubTree(T2)
InOrder :
–
Move Left SubTree(T1)
–
Visit Root (N)
–
Move Right SubTree(T2)
PostOrder :
–
Move Left SubTree(T1)
–
Move Right SubTree(T2)
–
Visit Root (N)
Traversal Algorithms on Binary Tree
N
T1
T2
7
Traversal Implementations
PreOrder (ROOT n)
{
if (n != NULL){
printf(n->info);
PreOrder(n->Left);
PreOrder(n->Right);
}
}
InOrder (ROOT n)
{
if (n != NULL){
InOrder(n->Left);
printf(n->info);
InOrder(n->Right);
}
}
PostOrder (ROOT n)
{
if (n != NULL){
PostOrder(n->Left);
PostOrder(n->Right);
printf(n->info);
}
}
Traversals Code on C
8
Array Representation
•
•
•
•
Root’s Index is 0
Left Child’s Index is 2p + 1, p is parent’s index
Right Child’s Index is 2p + 2
Parent’s Index is (c-1)/2, c is child’s index
A
B
C
D
E
G
F
H
Binary Tree
0
1
2
A
B
C
3
4
5
6
D
E
F
7
8
9
10 11
12
G
H
Array
9
Linked List Representation
struct node {
Elemen_Type Data;
struct node *Left;
struct node *Right;
struct node *Parent;}
struct node {
Elemen_Type Data;
struct node *Left;
struct node *Right; }
Data
Left Right
Data
Left Right
NULL
NULL
Parent
Data
Left Right
Data
Left Right
Data
Left Right
NULL
NULL
Double Linked List
NULL
Parent
Data
Left Right
NULL
NULL
Parent
Data
Left Right
Parent
Data
Left Right
NULL
NULL
NULL
Multiple Linked List
10
Expression Tree
•
•
For each node contains operand or operator for arithmetic expression.
Traversals :
– InOrder, produce Infix
– PreOrder , produce Prefix
– PostOrder , produce Postfix
Traversal
+
x
5
7
8
Notasi
InOrder
5x8+7
PreOrder
+x587
PostOrder
58x7+
Expression Tree
11