Computer Software 02/2/00
advertisement

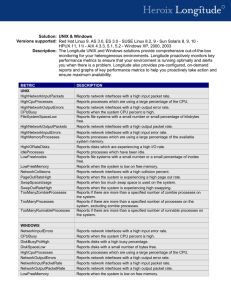
Software Technology Points Compile process Application Systems System software Operating system/network access Utilities User interface environments Languages & development tools (CASE) Databases Software Classification APPLICATION DEVELOPMENT SYSTEM Primacy of Software Software, not hardware, determines the actions of a computer. Source Code: program code intended to be written or read by people Machine Code: programs in binary form using the computer instruction set How Software Works: Step 1 How Software Works: Step 2 How Software Works: Step 3 How Software Works: Step 4 Computer Languages Language Translation Method interpreter compiler Level of Abstraction second-generation third-generation fourth-generation Procedural Versus Nonprocedural Command/Data or Object-Oriented Generations First - Machine language Second - Assembly language Third - High-level languages (COBOL, FORTRAN, BASIC, C,C++, Java, Ada) Fourth - 4GL (Focus, RAMIS, SQL) Fifth - Natural languages System Software Operating System provide an easier user interface manage system resources support multiple tasks and multiple users Systems Utilities Types of Interfaces Command- oriented interfaces prompt the user to type in a command that is translated into an instruction for the program to follow Menu- driven interfaces offer a list of choices or options, called a menu, as a way of letting a user choose from several different commands or functions Types of Interfaces Natural Language interfaces allow the user to input simple English statements that are translated into commands by the program. Graphical User Interfaces (GUI’s) Operating System Functions Booting Housekeeping Tasks (formatting, coordinating) Managing Computer Resources (memory and devices) Managing Files (i.e., copy, erase) Managing Tasks OS Components APPLICATION PROGRAMS SYSTEM PROGRAMS (COMPILERS, etc.) MEMORY OPERATING SYSTEM MACHINE LANGUAGE KERNEL MICROPROGRAMMING ROM PHYSICAL EXECUTION CPU Types of Tasks Multitasking 2 or more programs user concurrently on same computer with same CPU Multiprogramming 2 or more programs multiuser operating system, shared CPU Multiprocessing multiple CPUs Memory Management Virtual Memory PAGE NUMBER + OFFSET PAGE TABLE FRAME NUMBER + OFFSET PAGE TABLE PAGE TABLE Pages Page Frames Addresses Physical address: actual memory location. NEEDED BY THE CPU Relative address: offset from a reference physical address. NEEDED BY THE OPERATING SYSTEM Logical address: address within a programmed unit (e.g. page). NEEDED BY APPLICATION PROGRAMS Systems Software Network Operating Systems directing instructions communicating with the network security services directory services device management Workstation Functions REDIRECTION APPLICATION OPERATING SYSTEM CPU NETWORK INTERFACE NIC Client Functions Application execution Fat and thin clients Network access Network software and hardware (NIC) Application software maintenance Remote resources Client NOS Software Directs requests from the Client to the network Server Functions Shared resources File and print services Application management Network operating system Access to the network Higher layer functions Security Backup and professional support Server NOS Software Manages central services and external interfaces •Directory services •Translation protocol Access Centralized Legacy applications Client/Server Scalability Ownership Management Web JAVA, etc. Centralized Model Client/Server Model Two-tier Three-tier Multitier Web Model Mindshare Ownership Client Focus Bill Gates Net Focus Larry Ellison Issue: Desktop Ownership Who controls the desktop Standardization and version management Distribution Payment for access Application Software Make or Buy Integrated Solutions or Best of Breed Preparing for the Year 2000 Application Software Life Cycle SDLC Rapid Application Development Development Environments Desktop Systems Code Generators Development Systems and CASE Tools Middleware and other user environments Integrated Solutions (ERP) Year 2000 Replace Existing Software with Year 2000 Compliant ERP Products Repair Legacy Products Use Automated Tools Build Software that Will Intercept and Convert Dates as They Are Entered, Stored, or Output Software Acquisition Create Purchase Product Contract development Lease Seat Station 1+1=2