Crime and Deviance in America
advertisement
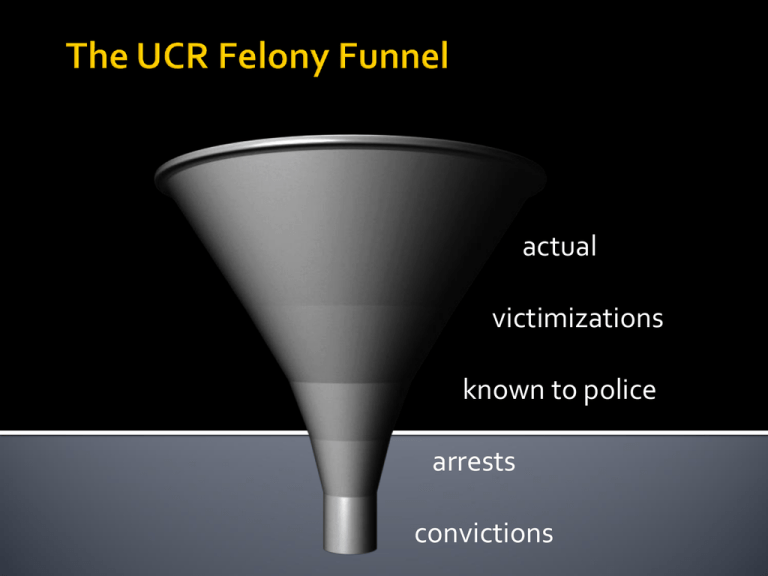
actual victimizations known to police arrests convictions Murder – between 8,500 to 9,000 Rape – 30,000 to 35,000 Robbery – 40,000 to 45,000 Aggravated Assault – 100,000 to 105,000 Burglary – 95,000 to 100,000 Larceny – 125,000 to 130,000 Drugs – 370,000 to 380,000 Total – roughly 1.1 million actual victimizations known to police arrests 1.1 M convictions Prison – 40% Jail – 30% Probation – 30% Mean Prison Sentence – approx. 60 months Mean Jail Sentence – approx. 6 months Mean Probation Sentence – approx. 40 months Murder – between 10,000 and 11,000 Rape – 20,000 to 21,000 Robbery – 90,000 to 100,000 Aggravated Assault – 370,000 to 380,000 Burglary – 230,000 to 250,000 Larceny – 1.2 to 1.3 million Auto Theft – 65,000 to 70,000 Drugs – 1.5 to 1.6 million Total Index Arrests – 2.0 to 2.1 million actual victimizations known to police 2.0 M 1.1 M arrests convictions Violent crimes – roughly 500,000 Property crimes – 1.5 to 1.6 million Total index crimes – 2.0 to 2.1 million Year Total Rate Murder Rape Robbery 1980 13.4M 5,950 23,040 82,990 565,840 1990 14.5 M 5,820 23,440 102,560 639,270 2000 11.6 M 4,124 15,586 90,186 407,842 2010 10.33 M 3,346 14,748 84,767 367,832 2014 9.44M 2,961 14,249 84,041 325,802 actual victimizations 9.4 M 2.0 M known to police arrests 1.1 M convictions 1960 – 4.7 1970 – 8.3 1980 – 10.2 1990 – 9.4 2000 – 5.5 2005 – 5.6 2010 – 4.8 2014 – 4.5 Reported crime rates are a function of a variety of factors: l. Department size 2. Citizen trust in the police 3. Education level of the officers 4. Confidence of the victim in the justice system 5. Education level of the victim 6. Social class of the victim 7. Race of the victim 8. If the victim had insurance 9. Overall fiscal resources of the victim 10. Relationship of the victim to the offender 11. Victim’s concern over unwanted publicity/embarrassment 12. Fear of reprisal from the offender if report 13. Unwilling to deal with the trauma of reporting 14. Aware you have been victimized 15. Victims sometimes don’t know where or how to report 16. Ethnic and social mores 17. Social class and status of the offender 18. Cumulative factor 19. Social significance, context, and relevance of the crime 21. Department communication equipment 22. Fiscal resources of the police department 23. Mobility of the police officers 24. Visibility of the crime 25. Department policies Year Total Property Violence 2000 25.9 M 19.3 M 6.6 M 2005 23.4 M 18.0 M 5.2 M 2010 20.3 M 15.4 M 4.9 M 2014 20.7 M 15.3 M 5.4 M actual 20.7 M 9.4 M 2.0 M 1.1 M victimizations known to police arrests convictions Overall – 5.4 M Rape – 284,350 Robbery – 664,210 Agg. Assault – 1.1 m Simple Assault – 3.3 m Overall – 15.3 M Household Burglary – 3.o m Auto Theft – 534,370 Larceny/Theft – 11.8 m Assault (aggravated) – 58% Assault (simple) – 40% Auto Theft – 83% Household Burglary – 60% Larceny/Theft – 29% Rape – 34% Robbery – 61% ***************************************** Overall Violent Crime – 46% Overall Property Crime – 37% Honduras – 58 Venezuela – 48 Brazil – 26 Russia – 16.5 Mongolia – 12.8 Mexico – 10 Thailand - 8.5 U.S. - 5.6 Philippines - 4.3 Turkey – 3.8 Finland – 2.8 Sweden 2.4 Malaysia - 2.4 Korea – 2.2 Canada - 1.9 France - 1.6 England - 1.4 Australia - 1.3 New Zealand – 1.2 Japan – 1.1 Germany .98 Austria .81 Norway .78 Hong Kong - .63 Singapore - .49 Morocco - .47 International average is 7.6/100,000. Western world tends to run below 2.0. Not counting nations involved in armed conflicts, there are roughly 500,000 homicides a year in the world at present. Gun accessibility Alcohol accessibility Externally based bio-chemical imbalances Internally based bio-chemical imbalances Psychological abnormalities Overexposure to violence Endless poverty Lack legitimate means of responding to conflict Gang wars Social disorganization Co-habitation Instinctual violence Turning points/tipping points actual ?? 20.7 M 9.4 M 2.0 M 1.1 M victimizations known to police arrests convictions 1. 2. 3. Men fear being the victims of different types of crime than do women. Men and women engage in different types of risk avoidance in response to their fears. Men are less fearful of becoming a victim, and consequently make fewer adjustments. Though the elderly have the lowest victimization rate, they have the highest fear of crime. This is due largely to their low rebound factor. In the end, it is not the extent of crime, but the fear of crime that drives the field of pragmatic criminology.