Chapters 13-15 Net value and marginal analysis Present value analysis
advertisement

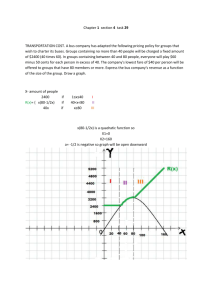
Chapters 13-15 Multiple Goal Decision Analysis I Net value and marginal analysis • Decision rules • Example Present value analysis • Reconciling present and future cash flows • Discounting Figures of merit • Weighted sum • Delivered system capability Corrections on slides 6, 7, 11 2015/10/05 Marginal Analysis: Definitions X C(X) TV(X) – Activity level of an alternative – Cost of alternative – Total value of alternative (in same units as cost) NV(X) – Net value of alternative NV(X) = TV(X) – C(X) MNV(X) – Marginal net value MNV(X) = d(NV) dx = d(TV) dx dC dx TV and C Cost and Total Value TV C X1 NVmax Xmax X2 Activity level x (a) MNV = d(TV)/dx – dC/dx Marginal Net Value Xmax (b) X Activity level Net Value vs. Activity Level NV = TV - C NVmax X Xmax X1 Investment Profitable (b) X2 Overinvestment Marginal Net Value Decision Rule • In the “profitable” segment – If MNV > 0, Increase activity level – If MNV < 0, Decrease activity level – If MNV = 0, Activity level is optimal MNV = d(TV) / dx – dC/dx • For Option B, with VT = value of each TR/sec, C(N) = 1007 + 20N; dC / dN = 20 TV(N) = VT(840N – 40N2); d(TV) / dN = VT(840 –80N) 20 = VT (840 – 80Nmax) Nmax = (840 VT – 20) / 80 VT = 10.5 – 1/(4VT ) Optimal Number of Processors vs. Transaction Value 10 8 Nmax 6 Nmax = 10.5 – 1 /(4 VT) 4 2 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 TPS Decision Problem 3 • Assuming use of composite option, we will acquire 5 processors/system and run option A for 2 years • Which acquisition option should we choose: -A1: Rent processors for 2 years at $2400/Mo. -A2: Purchase processors for $100,000. Resell them for $50,000 after 2 years. Interest Calculations • Option A2 ties up $50K for 24 months • How much would this be worth at an interest rate of .75%/month? V($50 K, 1) = $50 K (1.0075) V($50 K, 2) = $50 K (1.0075) (1.0075) … V($50 K, 24) = $50 K (1.0075)24 = $59,820 • For any sum X, V(X, 24) = X(1.0075)24 Present Value Calculations • What is the present value X of the $50K we will receive in 24 months? V (X, 24) = X (1.0075)24 = $50K X= $50K = $41,792 (1.0075)24 PV ($50K, .0075, 24) = F PV (F, r, n) = (1 +r)n $50K (1.0075)24 Present Value - Of a future cash flow F - At an interest rate per time period r - Over a number of time periods n F PV (F, r, n) = (1 +r)n 1 - Using the discount rate D = 1+r n PV (F, D, n) = FD Present Value, Series of Cash Flows • In option A1, we pay $2400 at the beginning of each month • How much is this worth in present value? PVS ($2400, D, 1) = $2400 PVS ($2400, D, 2) = $2400 + $2400 D PVS ($2400, D, 3) = $2400 (1 + D + D2) . . . PVS ($2400, D, 24) = $2400 (1 + D + … + D23) = $2400 (1 - D24) / (1 – D ) For D = 1/1.0075 = .9925558, PVS ($2400, 1/1.0075, 24) = $52,928 Present Value of A Series of Cash Flows • m equal cash flows or payments P – At the beginning of each time period • Constant discount rate D PVS (P, D, m) = P [(1-Dm)/(1-D)] Present Value Analysis Results Cost of A1 Simple Analysis $57,600 Present Value Analysis $52,928 Cost of A2 $50,000 $58,208 Present Value Comparison vs. Interest Rate Present value, $ 60622 60 57600 58208 55972 52908 50 55640 54420 52928 51494 50000 40 0 Option A2 0.25 0.5 0.75 Interest rate per month 1.0% Option A1 TPS Decision Problem 4 • Choose best vendor operating system – System A – Standard OS – System A Plus • Better diagnostics, maintenance features • $40K added cost Alternative TPS Operating System Characteristics Alternative Criterion System A System A Plus 0 $40K 2. Processor overhead 200 200 3. Multiprocessor overhead 80 80 4. Measurement capability Poor Good 5. Trace capability None Adequate 6. Diagnostics, error messages Adequate Good 7. Maintenance support Marginal Good 8. Accounting system Adequate Very Good 9. Usage summaries None Good 10. Documentation Good Adequate 1. Added Cost Meta-Decision Problems Lower cost More insight The system decision problem Lower Cost More Stability The system analysis decision problem Weighted Sum Figure of Merit • Assign weight Wi to criterion i Σi Wi = 1 • For each option j and criterion i, assign rating riJ (0 < rij < 10) • Compute figure of merit for each option j Fj = Σ Wi rij TPS Operating System Figure of Merit Calculation System A Criterion System A Plus Weight Characteristic Rating Weighted Rating Characteristic Rating Weighted Rating 1. Added Cost 30 $0 10 300 $40K 4 120 2. Processor overhead 10 200 3 30 200 3 30 3. Multiprocessor overhead 15 80 3 45 80 3 45 4. Measurement capability 7 Poor 2 14 Good 8 56 5. Trace Capability 8 None 0 0 Adequate 6 48 6. Diagnostics, error msgs 10 Adequate 6 60 Good 8 80 7. Maintenance Support 10 Marginal 4 40 Good 8 80 8. Accounting system 2 Adequate 6 12 Very good 10 20 9. Usage summaries 3 None 0 0 Good 8 24 10. Documentation 5 Good 8 40 Adequate 6 30 Total 100 541 533 Delivered System Capability (DSC) Figure of Merit DSC = (SC) (DC) (AV) • SC: System Capability = Σ Wi rij • DC: Delivered Capacity • AV: Availability The DSC Figure of Merit • Dimensionless • Covers effectiveness only • SC component handles many criteria • DC, AV components apply multiplicatively Gains from System A Plus - I • Reduction of $150K maintenance cost – Maintenance Support: 20% – Diagnostics, Error Msgs.: 10% – Documentation (worse): -10% ($30K) (15K) (-15K) $30K – Net Cost = $650K + 40 – 30 = $660K • Delivered capacity increase via measurement: 5% 2400 tr/sec (1.05) • 2520 tr/sec Availability increase via diagnostics, error messages, trace capability: 50% less downtime 0.95 0.975 Gains from System A Plus - II • System Capability Criteria Basic TPS Functions System A Weight Rating System A Plus Score Rating Score 1.0 0.950 1.0 0.950 Accounting Systems 0.95 0.01 0.6 0.006 1.0 0.010 Usage Summaries 0.01 0.0 0.000 0.8 0.008 OS Documentation 0.03 0.8 0.024 0.4 0.012 Total 0.980 0.980 TPS Comparison: Delivered System Capability Criterion System A System A Plus System capability (SC) 0.980 0.980 Delivered capability (DC) 2400 2520 Availability (AV) 0.95 0.975 Delivered system capability (DSC)=(SC)(DC)(AV) 2234 2408 $650K 3.44 $660K 3.65 Cost Capability/Cost ratio Revised TPS Weighted Sum Analysis System A Criterion System A Plus Weight Characteristic Rating Weighted Rating Characteristic Rating Weighted Rating 1. System capability (SC) 40 0.980 9 360 0.980 9 360 2. Delivered capacity (DC) 30 2400 8 240 2520 9 270 3. Availability (AV) 30 0.950 7 210 0.975 9 270 Total 100 810 900 Comparison of Weighted Sum and DSC Figures of Merit Relative advantages Weighted sum Delivered system capability Simpler More representative of many computer systems Better for assessing side effects of DC, AV factors Better for assessing wide variations in DC, AV factors Recommendation Use where DC, AV factors Use where DC, AV factors will not vary widely may vary widely