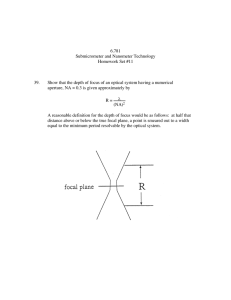
03b) Optical Invariant_1_18.docx
advertisement

ECEN 4616/56/16 1/30/2013 The Optical Invariant and Information Throughput: n’ n h u i’ u’ O’ i O l’ l Magnification is defined as M O . O ni ni (Snell' s law) O O i , i h h u , u l l l l Since: But: nO nO nu M l l nu nl M nl From the two expressions for M: O ' nu M , O nu we get nuO nuO This quantity is constant through any number of lenses (or groups of lenses) in a system, and is called the Optical Invariant, usually designated by H. The optical invariant (plus the wavelength) allows one to calculate the maximum number of spots (linear) that the system can pass – hence the information capacity of the system: Using the Rayleigh criteria for resolvable spot size, and making some approximations: 1.22 1.22 2O x # of spots , N 0.61H sin nu x