Characterization of Contact Resistivity on InAs/GaSb Interface
advertisement

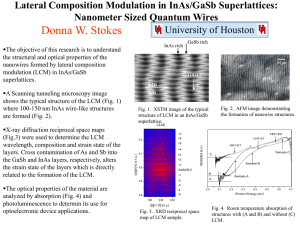
Characterization of Contact Resistivity on InAs/GaSb Interface Y. Dong, D. Scott, A.C. Gossard and M.J. Rodwell. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of California, Santa Barbara yingda@ece.ucsb.edu 1-805-893-3812 University of California Santa Barbara 2003 Electronic Materials Conference Yingda Dong Motivations Base resistance (RB) is a key factors limiting HBT’s high frequency performance. f max f 8 RB CBC E B RB fmax C Sub-collector Substrate University of California Santa Barbara Yingda Dong Base Resistance A large contribution to base resistance: E Contact resistance between metal and p-type base B C Sub-collector Substrate Contact resistivity on p-type material is usually much higher than on ntype material. Reason: holes have larger effective mass than electrons. Ec Ef Ev University of California Santa Barbara + Metal Tunneling Yingda Dong Base contact on n-type material Is it possible to make the base contact on n-type material? Base metal contact on ntype extrinsic base RB could be reduced Emitter contact metal Emitter Metal to base contact over field oxide CBC can be reduced Base metal Base metal N+ P+ N+ P+ P+ base Large emitter contact area RE can be reduced SiO2 Collector Metal N- collector SiO2 Collector Metal N+ subcollector High ft , fmax , ECL logic speed… University of California Santa Barbara S.I. substrate Yingda Dong Polycrystalline Base Contact in InP HBTs 1) Epitaxial growth 2) Collector pedestal etch, SiO2 planarization P+ base N- collector P+ base SiO2 subcollector N+ subcollector N+ subcollector S.I. substrate S.I. substrate University of California Santa Barbara SiO2 Yingda Dong Polycrystalline Base Contact in InP HBTs 3) Extrinsic-base regrowth 4) Deposit base metal, encapsulate with SiN, pattern base and form SiN sidewalls Base metal N+ extrinsic base P+ extrinsic base P+ base SiO2 subcollector Base metal N+ N+ P+ P+ P+ base SiO2 SiO2 subcollector N+ subcollector N+ subcollector S.I. substrate S.I. substrate University of California Santa Barbara SiO2 Yingda Dong Polycrystalline Base Contact in InP HBTs 5) Regrow emitter n+/p+ interface Emitter contact metal Is it rectifying or ohmic? Emitter If ohmic, is the interfacial contact resistivity low Base metal Base metal N+ P+ enough? N+ P+ P+ base SiO2 Collector Metal N- collector SiO2 Collector Metal N+ subcollector S.I. substrate University of California Santa Barbara Yingda Dong P+ GaSb / N+ InAs Heterostructure We propose to use p+ GaSb capped with n+ InAs as the extrinsic base. InAs-GaSb heterostructure forms a EC broken-gap band lineup P+ GaSb Mobile charge carriers tunnel between the p-type GaSb’s valence band and EC the neighboring n-type InAs’s conduction band ohmic p-n junction University of California Santa Barbara EV Ef N+ InAs EV Yingda Dong Early Interests in InAs(n)/GaSb(p) Material System InAs(n)/GaSb(p) heterostructure has been studied in 1990s with focuses on: Negative differential resistance (NDR) Application in high frequency tunneling diodes Current Density 1x105 A/cm2 Applied Bias University of California Santa Barbara Yingda Dong Focus of This Work The contact resistivity across the InAs(n)/GaSb(p) interface at relatively low current density (<104 A/cm2). (No NDR at low current density) The dependence of contact resistivity on the doping concentration in InAs and GaSb layers. University of California Santa Barbara Yingda Dong MBE Growth of Test Structures Samples grown in a Gen II system 1000Å n+ InAs Silicon doped cracked 100Å p+ GaSb 500Å p+ Grading from GaAs0.51As0.49 400Å p+ GaAs0.51Sb0.49 S.I. InP Sb source valved and CBr4 delivered through high vacuum leak valve Carbon doped Layer structure designed for InP HBT’s extrinsic base for processing reasons, total thickness constrained University of California Santa Barbara Yingda Dong Measurement of Interfacial Contact Resistivity 1) Transmission line patterns defined, Ti/Pt/Au contact metal deposited and lifted-off. 1000Å n+ InAs 100Å p+ GaSb 500Å p+ Grading from GaAs0.51As0.49 400Å p+ GaAs0.51Sb0.49 S.I. InP University of California Santa Barbara Yingda Dong Measurement of Interfacial Contact Resistivity 2) Mesa defined to limit the current flow. 1000Å n+ InAs 100Å p+ GaSb 500Å p+ Grading from GaAs0.51As0.49 400Å p+ GaAs0.51Sb0.49 S.I. InP University of California Santa Barbara Yingda Dong Measurement of Interfacial Contact Resistivity 3) Contact resistivity between metal and n+ InAs layer measured. 1000Å n+ InAs 100Å p+ GaSb 500Å p+ Grading from GaAs0.51As0.49 400Å p+ GaAs0.51Sb0.49 S.I. InP University of California Santa Barbara Yingda Dong Measurement of Interfacial Contact Resistivity Y Axis intercept = Contact resistance between metal and InAs 4.0 3.5 R=0.09+0.24L Rsh=24 Ohm/Square 3.0 RC=1.0E-8 Ohmcm 2 R (Ohm) 2.5 2.0 1.5 1000Å n+ InAs 1.0 100Å p+ GaSb 500Å p+ Grading from GaAs0.51As0.49 0.5 0.0 0 400Å p+ GaAs0.51Sb0.49 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 Gap Spacing (m) S.I. InP University of California Santa Barbara Yingda Dong Measurement of Interfacial Contact Resistivity 4) Top InGaAs layer selectively etched n+ InAs n+ InAs n+ InAs n+ InAs 100Å p+ GaSb 500Å p+ Grading from GaAs0.51As0.49 400Å p+ GaAs0.51Sb0.49 S.I. InP University of California Santa Barbara Yingda Dong Measurement of Interfacial Contact Resistivity Y Axis intercept = Contact resistance between metal and InAs + contact resistance between InAs and GaSb 70 R=2.3+2.16L Rsh=216 Ohm/Square 60 R (ohm) 50 40 30 20 n+ InAs n+ InAs n+ InAs 100Å p+ GaSb 500Å p+ Grading from GaAs0.51As0.49 n+ InAs 10 0 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 Gap Spacing (m) 400Å p+ GaAs0.51Sb0.49 S.I. InP University of California Santa Barbara Yingda Dong Contact Resistivity’s dependence on p-type GaSb layer’s doping Silicon doping in n-type InAs layer 2 InAs-GaSb Interface Contact Resistivity (-cm ) fixed at 1x1017cm-3 Carbon doping in p-type GaSb varied n+ InAs n+ InAs n+ InAs n+ InAs 100Å p+ GaSb 500Å p+ Grading from GaAs0.51As0.49 400Å p+ GaAs0.51Sb0.49 3.0x10 -6 2.5x10 -6 2.0x10 -6 1.5x10 -6 1.0x10 -6 5.0x10 -7 17 Si doping in InAs layer: 1x10 cm 2x10 19 3x10 19 4x10 19 5x10 19 6x10 19 -3 7x10 19 -3 Carbon Doping Density in GaSb Layer (cm ) S.I. InP University of California Santa Barbara Yingda Dong Contact Resistivity’s dependence on n-type InAs layer’s doping Silicon doping in p-type GaSb varied. n+ InAs n+ InAs n+ InAs n+ InAs 100Å p+ GaSb 500Å p+ Grading from GaAs0.51As0.49 2 fixed at 4x1019cm-3 and 7x1019cm-3. InAs-GaSb Interface Contact Resistivity (-cm ) Carbon doping in p-type GaSb layer 2.0x10 -6 1.8x10 -6 1.6x10 -6 1.4x10 -6 1.2x10 -6 1.0x10 -6 8.0x10 -7 6.0x10 -7 4.0x10 -7 2.0x10 -7 19 -3 C doping in GaSb layer: 4x10 cm 19 -3 C doping in GaSb layer: 7x10 cm 10 17 10 18 10 19 10 20 -3 400Å p+ GaAs0.51Sb0.49 Silicon Doping Density in InAs Layer (cm ) S.I. InP University of California Santa Barbara Yingda Dong Resonant Enhancement of Current Density InAs/GaSb For the single InAs/GaSb interface, reflection occurs due to imperfect coupling of InAs conduction-band states and GaSb valence-band states EC EV EC EV InAs/GaSb/AlSb/GaSb EC Formation of a quantum well layer between the InAs/GaSb interface and an AlSb barrier resonant enhancement of the current density EV EC EV University of California Santa Barbara Yingda Dong Experiment Result InAs/GaSb Contact resistivity: 6.0x10-7 -cm2 Si: 1x1017 cm-3 EC C: 7x1019 cm-3 EV EC EV 12Å AlSb InAs/GaSb/AlSb/GaSb EC Si: Contact resistivity: 5.4x10-7 - cm2 1x1017 cm-3 C: 7x1019 cm-3 EV EC EV University of California Santa Barbara Yingda Dong Comparison with metal on p+ InGaAs Doping Density of p-GaSb (cm-3) Doping Density of n-InAs (cm-3) Contact Resistivity (Ω-cm2) 2x1019 1x1017 2.8x10-6 2x1019 6x1017 3.0x10-6 4x1019 1x1017 1.3x10-6 4x1019 1x1019 1.6x10-6 4x1019 5x1019 9.0x10-7 7x1019 1x1017 6.0x10-7 7x1019 1x1019 8.2x10-7 7x1019 5x1019 4.2x10-7 Lowest interfacial contact resistivity obtained: ~ 4x10-7 -cm2 Contact resistivity of metal on p+ InGaAs: ~1x10-6 -cm2 University of California Santa Barbara Yingda Dong Questions Answered n+/p+ interface Is it rectifying or ohmic? -- YES Emitter contact metal Emitter Base metal If ohmic, is the interfacial contact resistivity low enough? -- YES Base metal N+ N+ P+ P+ P+ base SiO2 Collector Metal N- collector SiO2 Collector Metal N+ subcollector S.I. substrate University of California Santa Barbara Yingda Dong Conclusions Propose to use InAs(n)/GaSb(P) as extrinsic base of InP HBT Investigate the contact resistivity between InAs(n)/GaSb(p) interface and its dependence on doping densities on both sides of the heterojunction. Compare the InAs(n)/GaSb(p) interfacial contact resistivity with that of metal on p+ InGaAs. University of California Santa Barbara Yingda Dong Acknowledgement This work was supported by the DARPA—TFAST program University of California Santa Barbara Yingda Dong