Vigilant Sensing Technology VST1000 Remote Sensing System Preliminary Design Review
advertisement

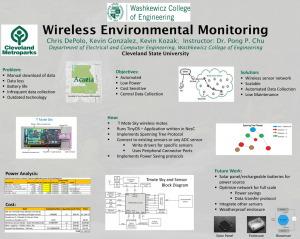
Vigilant Sensing Technology VST1000 Remote Sensing System Preliminary Design Review Development Team: Patrick Hauser Joel Keesecker Mark Kien Review Outline • • • • • • • Project Objectives Motivation System & Module Descriptions Division of Labor Condensed Schedule Risks & Mitigation Questions Project/System Objectives • • • • Seamless turnkey operation Broadband pipeline for expandability Selection of narrowband sensors Clandestine packaging of remote units Motivations • Provide generic, economical remote sensing ability for use in public safety and medical environments. • Use non-dedicated lines to communicate with the sensors in the field. System Level Diagram System Modules • • • • Master Control Unit RF Remote Sensing Unit Power Line Remote Sensing Unit PC Interface System Interfaces POWER LINE REMOTE SENSING UNIT Keyboard/ Mouse/Monitor Outside World Host PC MASTER CONTROL UNIT Power Packet OFDM HomePlug 1.0 Standard 2.4 GHz Wireless RS232/RS485 RF REMOTE SENSING UNIT Master Control Unit (MCU) MCU Basic Functions • • • • • LCD: Sensor data, errors, and status Status LEDs: Tx, Rx, Power, Error Liaison between Remote Unit and Host PC Store data when com link is lost (100 Recs) Error monitoring and detection routines MCU Module Interfaces Power Line Modem LCD Display Off the shelf Microcontroller General Purpose Serial Interface (GPSI) 14Mbs RS232/RS485 TBA 2.4 GHz RF Modem MCU Microcontroller Requirements • Single Board Microcontroller • Memory to support the following: – Buffering and storage of sensor data (record size TBA). – Operating firmware (code size TBA). • Ports: 1-GPSI, 2-RS232, 16-GPIO • Speed to support data movement. MCU Power Line Modem Requirements • • • • Support serial high speed data – 14Mbps Provide P/S for MCU or use single supply FCC approved for industrial use Small and easy to assimilate into MCU MCU RF Modem Requirements • • • • 2.4 GHz FCC Unlicensed Band Operation Support serial high speed data – 250Kbps Single power supply Small and easy to assimilate into MCU MCU Power Supply Requirements • • • • Highly efficient design – switching Will supply all modules with specific needs Strive for single supply solution High likelihood for final design group build Remote Sensor Unit (RSU) RSU Basic Functions • Monitor sensors, send data when critical threshold is reached • Format and communicate sensor data to MCU • Respond to commands from MCU • Status LEDs: Tx, Rx, Power, Error, Low Battery • Report RSSI to monitor link quality • Custom PCB • Unique ID for each sensor Sensors • Original Idea: Radiation Detection • Possible Sensors: – Temperature – Wireless Signal Detection • Possibly ADL5500 – Motion – Air Quality (eg. Clean Room) • Board capable of supporting a variety of sensors RSU Interfaces ICSP Sensors Additional I/O for expandability, I2C, SPI, etc GPIO/ ADC Power Line Modem General Purpose Serial Interface (GPSI) 14Mbs Microcontroller RS232/RS485 Status LEDs 2.4 GHz RF Modem RSU Microcontroller Requirements • Same architecture for both boards (TI / Freescale / Atmel) • • • • • Low power consumption At least 2 channel 8-bit onboard ADC Onboard UART Real time clock Ports: 1 GPSI/RS-232/RS-485, 8-16 GPIO, ICSP/ISP RSU Power line Sensor • GPSI Interface to power line transceiver – Possibly using Asoka PL80-9105-001 • If broadband power line communication proves to difficult fall back to narrowband. • AC-DC switching power supply RSU Wireless Sensor • 2.4 GHz wireless communication – Using Xbee or RS-232 Wireless Modem • Battery, Charger, and monitor – 9-12 V Lithium-ion Battery – Charger Purchased or own design • DC-DC switching power supply • Low standby power consumption PC Interface Temp RF Remote Sensing Unit RF Remote Sensing Unit 2.4 GHz Cell Traffic 2.4 GHz Cell Traffic Power Line Remote Sensing Unit - GUI on Host PC We don’t want the system to be User Friendly. This way we assure ourselves job security. Master Controller Unit ` Serial Interface Temp RF Over Power Communication Link Power Line Remote Sensing Unit GUI/Host PC Basic Functions • • • • • • Interface through RS232 to the MCU View historic and “real time” sensor data Control data acquisition Store data to database Monitor sensor status (RSSI, Battery life) Error monitoring and detection routines GUI Data Viewer • • • • • Table of detects Detailed info of selected detect Detailed info on most recent detect Get Detect from wireless device Get Detect from power line device GUI Sensor Information • • • • • Battery power (wireless device) Sensor unit RSSI Number of sensors on power line unit Number of sensors on wireless unit ID mapping – ID number and corresponding sensor Host PC RS232 Communication • Script to read and write to port – On read, update database • Communicates with master controller • Continuous/Scheduled update • Fetch data upon GUI request GUI - If Time Permits • Website – Data viewing only – Way to view data from anywhere • Historical Info – Plot user defined historical data – Scatter or bar graph depending on data • Ex. Temperature over time • Ex. Number of Motion detects/day over 1 week Division of Labor Pat Hauser Joel Keesecker Mark Kien Primary Primary Primary •GUI Development •PC Interface •Remote Unit Circuit & PCB Design •Research •H/W Testing •Sensor Development •Embedded Software •Project Manager •Power Supply Design Secondary Secondary Secondary •Embedded Software •Research •Testing •Embedded Software •Power Supply Design •Testing •Circuit Design (remote) All: Documentation Condensed Schedule Risks & Mitigation • Noisy lines could make power line communications difficult – Down grade to narrow band modems or drop Power Line Modem option altogether. • Part availability – Address part concerns well in advance of need • Resources limited – Reduce scope and/or leverage additional dev. tools. Questions / Suggestions