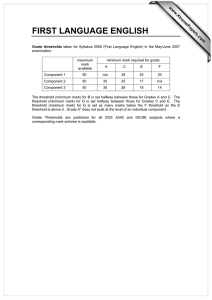
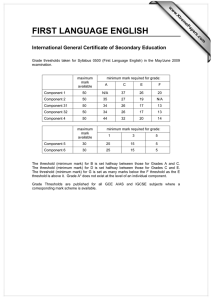
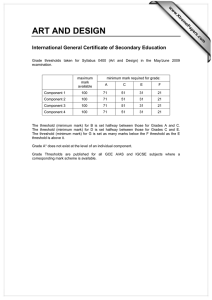
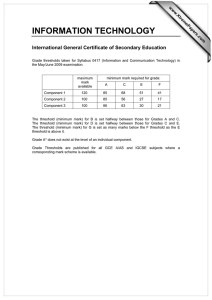
ex5m7_7.doc
advertisement

Random Signals for Engineers using MATLAB and Mathcad Copyright 1999 Springer Verlag NY Example 7.7 Minimax Criteria In the example we will derive a criteria for minimizing the cost or risk function when we have not selected the apriori probability that the cost function is based upon. In this case we will first select a threshold based on a given apriori probability and examine what happens to the cost function when the threshold remains the same but the apriori probability changes. Let us select a threshold as a function of the apriori probability or P(H1) = x for the case when d = 1. Select a group of values for P(H1) p1= 0.01:0.01:.99; lam=log((1-p1)./p1)+1/2; Risk function as a function of P(H1) from Equation 7.4-21 with c11 = c00 = 1 and c01 = c10 = 0 . Find the threshold for P(H1) = .3 and fix the design lam0=log((1-0.3)./0.3)+1/2 Risk0=(1-p1).*(1-cnorm(lam0,0,1))+p1*cnorm(lam0-1,0,1); lam0 = 1.3473 lam1=log((1-0.5)./0.5)+1/2 Risk1=(1-p1).*(1-cnorm(lam1,0,1))+p1*cnorm(lam1-1,0,1); lam1 = 0.5000 These are the Risk functions for an incorrect design point. We can now plot the Risk function for three conditions. Risk=(1-p1).*(1-cnorm(lam,0,1))+p1.*cnorm(lam-1,0,1); plot(p1,Risk,p1,Risk1,p1,Risk0) xlabel 'Probability' ylabel 'Risk' 0.7 0.6 0.5 Risk 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0 0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 Probability 0.7 0.8 0.9 1 We observe that when the risk function is chosen with an incorrect P(H1) the values can get as large as 0.61 for an incorrect value. A better choice would be with an L = 0.5 which given the minimum max values for all values of p(H1) and is equal to 0.31. For this case it is the threshold values for a p(H1) of the Risk curve where the slope is zero as shown in the figure.