Lecture 16 OUTLINE • The MOS Capacitor (cont’d) – Electrostatics
advertisement

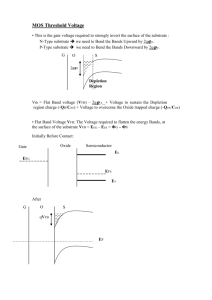
Lecture 16 OUTLINE • The MOS Capacitor (cont’d) – Electrostatics Reading: Pierret 16.3; Hu 5.2-5.5 Accumulation (n+ poly-Si gate, p-type Si) M VG < VFB 3.1 eV O S | qVox | Ec= EFM GATE - - - - - + + + + + + VG + _ Ev |qVG | xo Ec p-type Si 4.8 eV Mobile carriers (holes) accumulate at Si surface EE130/230A Fall 2013 |qfS| is small, 0 Lecture 16, Slide 2 EFS Ev VG VFB Vox Accumulation Layer Charge Density VG < VFB Vox VG VFB From Gauss’ Law: GATE - - - - - + + + + + + VG + _ Qacc (C/cm2) xo ox Qacc / ε SiO2 Vox x Qacc / Cox ox o where Cox ε SiO2 / xo p-type Si (units: F/cm2) Qacc Cox (VG VFB ) 0 EE130/230A Fall 2013 Lecture 16, Slide 3 Depletion (n+ poly-Si gate, p-type Si) M VT > VG > VFB qVox O S W Ec GATE + + + + + + VG + _ - - - - - - p-type Si Ec= EFM Ev Si surface is depleted of mobile carriers (holes) => Surface charge is due to ionized dopants (acceptors) EE130/230A Fall 2013 qfS 3.1 eV Lecture 16, Slide 4 4.8 eV qVG EFS Ev Depletion Width W (p-type Si) • Depletion Approximation: The surface of the Si is depleted of mobile carriers to a depth W. • The charge density within the depletion region is qN A (0 x W ) d ρ qN A • Poisson’s equation: dx ε Si ε Si (0 x W ) • Integrate twice, to obtain fS: qN A 2 fS W 2 Si EE130/230A Fall 2013 2 SifS W qN A Lecture 16, Slide 5 To find fs for a given VG, we need to consider the voltage drops in the MOS system… Voltage Drops in Depletion (p-type Si) From Gauss’ Law: GATE + + + + + + VG - - - - - - + _ Qdep (C/cm2) p-type Si ox Qdep / ε SiO2 Vox ox xo Qdep / Cox Qdep is the integrated charge density in the Si: Qdep qN AW 2qN A SifS 2qN A sifS VG VFB fS Vox VFB fS Cox EE130/230A Fall 2013 Lecture 16, Slide 6 Surface Potential in Depletion (p-type Si) 2qN A sifS VG VFB fS Cox • Solving for fS, we have 2 qN A si 2Cox (VG VFB ) 1 fS 1 qN A si 2Cox qN A si fS 2 2Cox EE130/230A Fall 2013 2Cox (VG VFB ) 1 1 qN A si 2 Lecture 16, Slide 7 2 Threshold Condition (VG = VT) • When VG is increased to the point where fs reaches 2fF, the surface is said to be strongly inverted. This is the threshold condition. VG = VT fS 2fF E i (bulk ) Ei ( surface) 2Ei (bulk ) EF Ei ( surface) EF Ei (bulk ) EF nsurface N A (The surface is n-type to the same degree as the bulk is p-type.) EE130/230A Fall 2013 Lecture 16, Slide 8 MOS Band Diagram at Threshold (p-type Si) M kT N A fS 2fF 2 ln q ni W WT qVox 2 Si (2f F ) qN A qfF Ec= EFM Ev EE130/230A Fall 2013 Lecture 16, Slide 9 O S WT qfF qfs Ec EFS Ev qVG Threshold Voltage • For p-type Si: 2qN A sifS VG VFB fS Vox VFB fS Cox 2qN A Si (2fF ) VT VFB 2fF Cox • For n-type Si: VT VFB 2fF EE130/230A Fall 2013 2qN D Si 2fF Cox Lecture 16, Slide 10 C. C. Hu, Modern Semiconductor Devices for ICs, Figure 5-8 Strong Inversion (p-type Si) As VG is increased above VT, the negative charge in the Si is increased by adding mobile electrons (rather than by depleting the Si more deeply), so the depletion width remains ~constant at W = WT (x) WT M O S GATE + + + + + + VG + _ x - - - - - - p-type Si fS 2fF Significant density of mobile electrons at surface (surface is n-type) EE130/230A Fall 2013 Lecture 16, Slide 11 2 si (2fF ) W WT qN A R. F. Pierret, Semiconductor Device Fundamentals, p. 575 Inversion Layer Charge Density (p-type Si) VG VFB fS Vox VFB 2fF (Qdep Qinv ) Cox 2qN A s (2fF ) Qinv VFB 2fF Cox Cox Qinv VT Cox Qinv Cox (VG VT ) EE130/230A Fall 2013 Lecture 16, Slide 12 fS and W vs. VG (p-type Si) 2fF fS: 2 qN A si 2Cox (VG VFB ) 1 fs 1 2 qN A si 2Cox 0 WT 0 accumulation EE130/230A Fall 2013 (for VFB VG VT ) VG accumulation V depletion V inversion FB T W: 2 2ε Si (2fF ) qN A 2 2 SifS Si 2Cox (VG VFB ) 1 W 1 (for VFB VG VT ) qN A Cox qN A si VFB depletion VT inversion Lecture 16, Slide 13 VG Total Charge Density in Si, Qs (p-type Si) Qacc Cox (VG VFB ) depletion 0 accumulation VFB accumulation inversion VT depletion inversion 0 VFB VG accumulation depletion inversion VT VG Qdep qN AW accumulation Qs Qacc Qdep Qinv VG depletion inversion 0 VFB 0 VT VG VT Qinv slope = -Cox Qinv Cox (VG VT ) EE130/230A Fall 2013 VFB Lecture 16, Slide 14