Step Response
advertisement

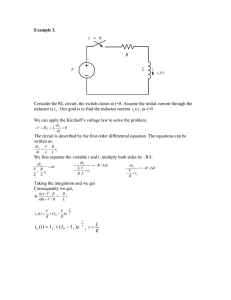
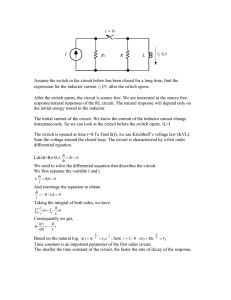
Step Response • Circuit’s behavior to the sudden application of a DC voltage or current. • Energy is being stored in the inductor or capacitor ECE 201 Circuit Theory I 1 Step Response of an RL Circuit J1 Key = Space R 1kOhm i(t) Vs 12 V + v(t) L 1mH - The switch is closed at t = 0. Determine the current i(t) and the voltage v(t) for t>0. Allow for the possibility of an initial current I0. ECE 201 Circuit Theory I 2 Step Response of a RL Circuit J1 Key = Space R 1kOhm i(t) Vs 12 V + v(t) L 1mH - • Write KVL around the loop. di Vs iR L dt ECE 201 Circuit Theory I 3 di dt di iR Vs R V i s dt L L R R V di i s dt L R di R dt V L i s R t t dx R t Vs L 0 dy 0 x R V i (t ) s R Rt ln V L I0 s R V i (t ) s R R e L t V I0 s R Vs iR L V V i (t ) s I 0 s R R R L t e ECE 201 Circuit Theory I 4 Look at the result • Consider the case when there is no initial current in the inductor. Vs Vs i (t ) I 0 e R R R t L R Vs Vs L t i (t ) e R R R t Vs i (t ) 1 e L R ECE 201 Circuit Theory I 5 Plot the current i(t) ECE 201 Circuit Theory I 6 Determine the voltage v(t) Vs Vs i (t ) I 0 e R R di v(t ) L dt R t L Vs R v(t ) L I 0 e R L v(t ) Vs I 0 R e R t L R t L ECE 201 Circuit Theory I 7 Plot the voltage v(t) ECE 201 Circuit Theory I 8 Example 7.5 • The switch has been in position “a” for a long time. At time t = 0, the switch moves from position a to position b. The switch is a “makebefore- break” type: that is, the connection at position b is established before the connection at position a is broken, so there is no interruption of the current through the inductor. R1 b 2 Ohm a J1 V 24 V + i(t) v(t) Key = Space R2 8 Ohm I 8A L 200mH - ECE 201 Circuit Theory I 9 Determine the initial value of the current R1 b 2 Ohm a J1 V 24 V Key = Space I0 = - 8A R2 8 Ohm I 8A L 200mH The 200mH inductor looks like a short circuit and carries an initial current of 8A upwards. Therefore, I0 = -8A. ECE 201 Circuit Theory I 10 Determine the final value of the current and the time constant R1 b 2 Ohm a J1 V 24 V Key = Space i(∞) R2 8 Ohm I 8A L 200mH • The final value of the current is (24V/2Ω) = 12A • The time constant is (L/R) = (200mH/2Ω) = 100ms ECE 201 Circuit Theory I 11 R1 b 2 Ohm a J1 V 24 V R2 8 Ohm Key = Space i(t) I 8A L 200mH R Vs Vs L t i (t ) I 0 e R R 2 24 24 0.2 t i (t ) 8 e 2 2 i (t ) 12 20e 10t A ECE 201 Circuit Theory I 12 Complete Solution for the Current and Voltage • The current in an inductor cannot change instantaneously – Let t = (0-) be the time just before the switch is opened, and t = (0+) be the time just after the switch is opened – Then i(0-) = i(0+) =I0, and i (t ) I 0 e R - t L ,t 0 RL v(t ) i (t ) R I 0 R e t , t 0 ECE 201 Circuit Theory I 13 Determine the initial voltage across the inductor just after the switch moves to “b” R1 2 Ohm V 24 V b a J1 Key = Space R2 8 Ohm I 8A L 200mH di v(t ) L dt v(t ) 0.2 200e 10t v(t ) 40e 10tV v(0 ) 40V ECE 201 Circuit Theory I 14 Does this result make sense? R1 b 2 Ohm - vR(0+) V 24 V a J1 + i(0+) Key = Space + R2 8 Ohm I 8A L vL(0+) 200mH - vL i (0 )(2) 24 0 vL i (0 )(2) 24 Voltage @ R1 adds to the battery voltage vL (8)(2) 24 16 24 vL 40V ECE 201 Circuit Theory I 15 Determine the time it takes for the inductor voltage to reach 24 Volts v(t ) 40e 10t 24 24 10 t e 40 24 10t ln 40 1 24 t ln 0.1(0.5108) 10 40 t 0.05108s 51.08ms ECE 201 Circuit Theory I 16 Plot i(t) and v(t) ECE 201 Circuit Theory I 17 ECE 201 Circuit Theory I 18 Oscilloscope Results v(t ) 40e10t i(t ) 12 20e10t ECE 201 Circuit Theory I 19