Determinants of Demand Notes
advertisement
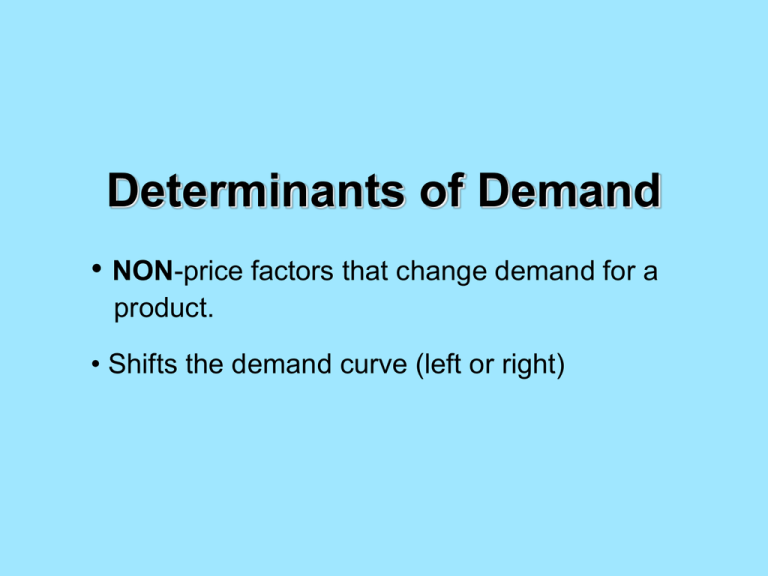
Determinants of Demand • NON-price factors that change demand for a product. • Shifts the demand curve (left or right) Consumer Tastes and Preferences • Popularity, “cool factor” • When a product becomes more popular, demand increases • When a product becomes less popular, demand decreases Market Size • When more businesses enter an industry, market size increases and more products become available. • When market size increases, demand increases • When market size decreases, demand decreases Income • The money a person earns affect his/her demand for goods/services • When income increases, demand increases • When income decreases, demand decreases Substitute Goods • A product that can be substituted for or replace another • Examples – margarine and butter, chicken and turkey • When the demand for a substitute good increases, demand for the original good will decrease. • When the demand for a substitute good decreases, demand for the original good will increase. Complementary Goods • A product that compliments or “goes with” another product • Examples – paint and paint brushes, hot dogs and hot dog buns • When demand for a complementary good increases, demand for the original good also increases. • When demand for a complementary good decreases, demand for the original good also decreases. Consumer Expectations • Reacting to an expected change in price or quality (future) • If consumers believe the price of a product will decrease tomorrow, their demand today will decrease. • If consumers believe the price of a product will increase tomorrow, their demand today will increase.