Political Culture PP
advertisement

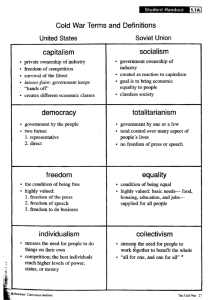
Political Culture The widely shared beliefs, values, and norms that citizens share about their government Characteristics Liberty (Freedom/Rights) Individualism/Rugged Individualism (as opposed to collectivism/statism) Learning Objective 2: Recognize the agents of political socialization and explain the impact the agents have on shaping the political views of individuals. Characteristics Equality Equality of opportunity more than results Political equality more than economic equality Free Enterprise: Capitalism/Free Markets; Competition Fosters Innovation American Dream (reverance for property, capitalism, chance for wealth) FDR’s second Bill of Rights (1944) ensuring economic security False consciousness (as opposed to class consciousness associated w/Europe) Dilemma Conflict between liberty associated with capitalism and equality associated with democracy– prompts federal action In progressive era to bring corporations under control (Early 1900’s) In 1930’s to smooth out ill effects of capitalism: New Deal In 1960’s with Great Society programs (LBJ) to combat poverty Characteristics (Cont’d) Democracy Civic Duty (includes voting, jury duty, etc.) “Social Capital” creates a strong society: Social Networks Robert Putnam (Bowling Alone) advances argument that number of bowlers has increased, but those participating in leagues has declined, therefore he assumes that with decline in social network, there is less likelihood of people coming together, listening to one another, exchanging ideas (creates smaller degree of civic duty) Civic Duty Key Club, Leadership, NHS, GO etc. Kiawanis, Rotary, Odd Fellows, Elks, Optimists. NAACP, Urban League, Junior League Scouts, Boys Club, Pop Warner, Little League, Kids Soccer, etc. Friends of Trees, Habitat for Humanity LWV, PTA Boards, Councils, Commissions Political parties Characteristics (Cont’d) Patriotism/Optimism (However, distrust of governmen has increased since 1960’s and Watergate, Viet Nam) Justice/Rule of Law - Belief in the rule of law. A “government of laws, not men.” Others: Political Efficacy - sense that one can both understand and influence public policy Political Tolerance - more in the abstract than concrete Pragmatism - Americans tend to be less ideological