Demand Elasticity WS
advertisement
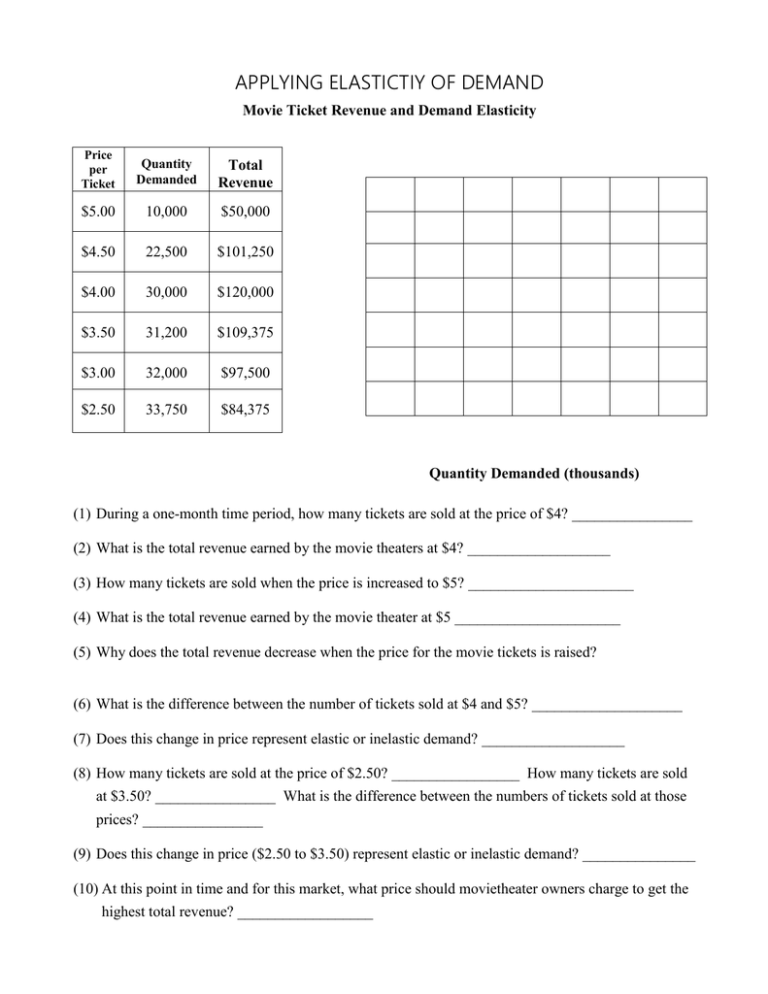
APPLYING ELASTICTIY OF DEMAND Movie Ticket Revenue and Demand Elasticity Price per Ticket Quantity Demanded Total Revenue $5.00 10,000 $50,000 $4.50 22,500 $101,250 $4.00 30,000 $120,000 $3.50 31,200 $109,375 $3.00 32,000 $97,500 $2.50 33,750 $84,375 Quantity Demanded (thousands) (1) During a one-month time period, how many tickets are sold at the price of $4? ________________ (2) What is the total revenue earned by the movie theaters at $4? ___________________ (3) How many tickets are sold when the price is increased to $5? ______________________ (4) What is the total revenue earned by the movie theater at $5 ______________________ (5) Why does the total revenue decrease when the price for the movie tickets is raised? (6) What is the difference between the number of tickets sold at $4 and $5? ____________________ (7) Does this change in price represent elastic or inelastic demand? ___________________ (8) How many tickets are sold at the price of $2.50? _________________ How many tickets are sold at $3.50? ________________ What is the difference between the numbers of tickets sold at those prices? ________________ (9) Does this change in price ($2.50 to $3.50) represent elastic or inelastic demand? _______________ (10) At this point in time and for this market, what price should movietheater owners charge to get the highest total revenue? __________________ Name _________________________________________ Per ____ Date _______________ Identifying Elasticity Directions – Identify whether each good is elastic or inelastic and explain why using the characteristics of elastic and inelastic demand. 1) A Subway Sandwich 2) A box of matches 3) Deodorant 4) Gap Jeans 5) Movie Theater Tickets 6) Gasoline 7) Pillows – 8) Laptop Computers 9) Cameras (general) – 10) Pork Chops 11) iPods – 12) Trip to Italy - Directions – For #13, please think of a good that is elastic and explain why. For #14, think of a good that is inelastic and explain why. 13) 14)