Horsemanship Standards Knowledge Level 3
advertisement

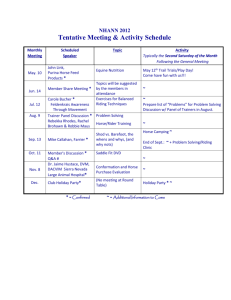
Maryland 4-H Horsemanship Standards Knowledge Level 3 Dr. Amy Burk University of Maryland Extension Horse Specialist Kristen M. Wilson University of Maryland Extension Horse Specialist Rev. 8/16/11 Knowledge Testing Schedule 1. Written Test Copies from County Extension Office Allow 45 minutes 2. Oral Practicum Cover information on the knowledge testing sheet for each level Everything else covered on the written test Knowledge Level Sections Breeds, Conformation, Movement Grooming and Bandaging Health Care and Veterinary Knowledge Nutrition Stable Management and Safety Tack and Equipment Transportation and Travel Safety Parts of Horse Breed Types Light Breed Know different characteristics that define breed type Draft Breed Coat Colors Variations of the gray coat color- i.e. rose gray, steel gray, dapple gray, flea bitten gray etc. Front Leg Conformation (Horses, 2000) Hind Leg Conformation (Horses, 2000) Conformation Faults Grooming Give reasons for clipping a horse, and name and describe at least 3 types of body clips that can be used Describe safety precautions for bathing Trimming/Clipping for Show Face hair Ears Bridle path Fetlock Coronet band Body Clipping Body Hunter Trace Blanket Bathing a Horse Never stand directly in front or behind a horse when bathing them Have the horse securely and safely tied or have someone hold them Keep the hose out from under the horse’s feet Go slowly… don’t surprise them! Reasons for Bandaging Protection of the legs, particularly while riding or trailering the horse Prevention of swelling after the horse works For treatment and protection of injuries Protective Boots Bell Boots Splint Boots Ankle Boots Health/Veterinary Care Name and describe 1 type of wound and how to treat it, especially those that need veterinary attention Explain why a regular vaccination plan is necessary and identify 3 diseases you would vaccinate your horse against each year Know signs that a hoof needs to be trimmed Locate parts of the hoof Equine Wounds Lacerations tearing of the skin, often require stitches Abrasions usually caused by rubbing, and will remove the epidermis, not as serious Punctures deep, narrow wounds that are usually caused by nails or splinters Vaccinations (Hill, 1997. Horse Health Care) Vaccination Schedules Hoof Care Parts of the Hoof Nutrition Basic rules for feeding Know how feeds are measured (including units) Explain feeding schedule to include amounts of roughage and concentrates for a particular horse or pony Basic Feeding Rules 1. Feeding horse’s properly takes knowledge of their digestive anatomy and physiology 2. Feed small forage-based meals frequently 3. Avoid abrupt changes in feed 4. Avoid poor quality feeds and forages 5. Offer fresh clean water and trace mineral salts at all times Weighing Feeds Important to measure by weight, not volume!! Types of Diets Forage Concentrate Forage Very important for proper digestion Types of hay: Legume Grass Mixed Horse will consume 1 ½ to 2% of body weight per day Common Hay Species Timothy Orchardgrass Alfalfa Concentrate Used to: Supplement and balance nutrients in forages Supplement higher caloric needs of working and lactating horses Stable Management and Safety Appropriate care of a horse after strenuous work including: cooling out, inspection of legs, watering and feeding Proper stall sizes for a horse and pony Management practices to prevent the spread of disease Safety concerns to consider when attaching a hay net/bag Care After Strenuous Exercise • Horse should be walked until all vital signs are back to normal • Inspect legs for any injuries • Limit access to feed and water Stall Dimensions and Designs Horse: 12x12 feet Pony : 10x10 feet The stall should be free of any sharp objects, the doors should shut securely, and no electrical wiring should be exposed How to Tie a Hay Net The most important thing to emphasize is that it stays out of the way of the horse’s feet It is run through a mounted ring, and then the excess tied up in a quick release knot Equine Disease Control Program 1. Optimize health and nutrition plans for animals 2. Use rodent, parasite and vector control programs throughout the year 3. Do not allow horse access to streams and waterways 4. Contract with a veterinarian and clearly post their contact information Equine Disease Control Program 5. Communication is key 6. Limit human access to barns if they are not clientele or workers 7. Clean and disinfect barns, stalls and equipment regularly 8. Discard all manure and bedding from stalls that house sick horses Equine Disease Control Program Become familiar with common diseases that affect horses Identify symptoms with the onset of a disease Vaccination Plan Deworming Plan Tack and Equipment 2 areas on tack that should be checked for safety Types of bits Identify a tie-down, breast strap, martingale, and breastplate Types of blankets and their purposes Unsafe Tack http://www.newrider.com/Library/Misc_Tips/tack_safety.html Horse Bits Other Equipment Martingale Breast Plate Tie-Down Breast Strap Horse Blankets Proper Loading/Unloading References and Resources Approved resources for state contests USPC Manual of Horsemanship: The Basics for Beginners through D Level, by S. E. Harris USPC Manual of Horsemanship: The Intermediate Horsemanship through C Level, by S. E. Harris USPC Manual of Horsemanship: The Advanced Horsemanship Through A Level, by S. E. Harris