2nd Grade Rubrics Content Area: Math Report Card Language:
advertisement
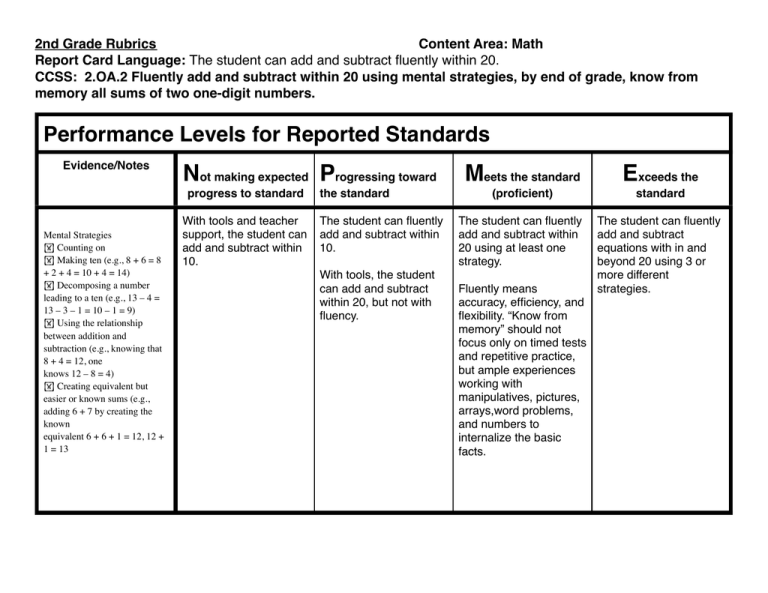
2nd Grade Rubrics! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! Content Area: Math Report Card Language: The student can add and subtract fluently within 20. CCSS: 2.OA.2 Fluently add and subtract within 20 using mental strategies, by end of grade, know from memory all sums of two one-digit numbers. Performance Levels for Reported Standards Evidence/Notes Not making expected Progressing toward progress to standard Mental Strategies ! Counting on ! Making ten (e.g., 8 + 6 = 8 + 2 + 4 = 10 + 4 = 14) ! Decomposing a number leading to a ten (e.g., 13 – 4 = 13 – 3 – 1 = 10 – 1 = 9) ! Using the relationship between addition and subtraction (e.g., knowing that 8 + 4 = 12, one knows 12 – 8 = 4) ! Creating equivalent but easier or known sums (e.g., adding 6 + 7 by creating the known equivalent 6 + 6 + 1 = 12, 12 + 1 = 13 With tools and teacher support, the student can add and subtract within 10. the standard The student can fluently add and subtract within 10. With tools, the student can add and subtract within 20, but not with fluency. Meets the standard Exceeds the (proficient) standard The student can fluently add and subtract within 20 using at least one strategy. The student can fluently add and subtract equations with in and beyond 20 using 3 or more different strategies. Fluently means accuracy, efficiency, and flexibility. “Know from memory” should not focus only on timed tests and repetitive practice, but ample experiences working with manipulatives, pictures, arrays,word problems, and numbers to internalize the basic facts. 2nd Grade Rubrics! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! Content Area: Math Report Card Language: The student can represent and solve problems involving addition and subtraction within 100. CCSS: 2.OA.1 Use addition and subtraction within 100 to solve one- and two-step word problems involving situations of adding to, taking from, putting together, taking apart, and comparing, with unknowns in all positions by using drawings and equations with a symbol for the unknown number to represent problem. Performance Levels for Reported Standards Evidence/Notes Not making expected Progressing toward progress to standard Examples of two-step problems: There are 9 blue marbles and 6 red marbles in the bag. Maria put in 8 more marbles. How many marbles are in the bag now? 9+6+8=! There are 9 peas on the plate. Carlos ate 5 peas. Mother put 7 more peas on the plate. How many peas are on the plate now? With significant teacher support the student can use drawings and equations to represent and solve one step word problems within 100. The student can identify the parts of the word s Meets the standard Exceeds the (proficient) standard The student can use drawings and equations to represent and solve one step word problems within 100. The student can use drawings and equations to represent and solve one and two step word problems within 100. Example of One Step: The student can find the answer to problems with the unknown in different places in the equation, and can represent the unknown with a symbol. The student can use drawings and equations to represent and solve two step word problems within 100. The student must show two or more ways to solve the problem and be able to communicate the process. the standard There are 15 stickers on the page. Brittany put some more stickers on the page. There are now 22 stickers on the page. How many stickers did Brittany put on the page? 9 –5 + 7 = ! 15 + ! = 22 22 – 15 = ! *Multistep problems should focus on single digit addends. The steps in the problems may have the same or different operations for each step. The addends in the problem may be single or double-digit numbers. 2nd Grade Rubrics! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! Content Area: Math Report Card Language: The student can work with equal groups of objects to prepare for multiplication. CCSS: 2.OA.4 Use addition to find the total number of objects arranged in rectangular arrays with up to 5 rows and up to 5 columns, write an equation to express the total as a sum of equal addends. Performance Levels for Reported Standards Evidence/Notes Not making expected Progressing toward progress to standard With significant teacher support the student can use a rectangular array up to 5x5 the student can solve for the sum of array. Even with teacher support, the student may not be able to find the sum of the rectangular array. the standard The student can use a rectangular array up to 5x5 and the student can solve for the sum of array, but cannot write a equation to express the total as a sum of equal addends. Meets the standard Exceeds the (proficient) standard The student can use a rectangular array up to 5x5, the student can write an equation to express the sum of equal addends. The student can use a rectangular array up to 10x10, the student can write an equation to express the sum of equal addends. The student may begin to use multiplication equations to express the value of the array. 2nd Grade Rubrics! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! Content Area: Math Report Card Language: The student can use place value (groups of ones, tens, and hundreds) to represent and compare numbers up to 1000. CCSS: 2.NBT.4 Compare two three-digit numbers based on meanings of the hundreds, tens, and ones digits using >, =, and < symbols to record the results of comparisons. Performance Levels for Reported Standards Evidence/Notes Not making expected Progressing toward progress to standard With significant teacher support the student can compare two digit numbers using the >,=, and < symbols. the standard The student can fluently compare two digit numbers using the >,=, and < symbols. Meets the standard Exceeds the (proficient) standard The student can fluently compare three digit numbers using the >,=, and < symbols. The student can fluently compare beyond 1000 using the >,=, and < symbols. 2nd Grade Rubrics! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! Content Area: Math Report Card Language: The student can add and subtract within 1000 using place value strategies. CCSS: 2.NBT.7 Add and subtract within 1000, using concrete models or drawings and strategies based on place value, properties of operations, and/or the relationship between addition and subtraction, relate the strategy to a written method. Understanding the use of place value and need to compose or decompose tens or hundreds. Performance Levels for Reported Standards Evidence/Notes Not making expected Progressing toward progress to standard Concrete models include base ten and number lines. Using a standard algorithm of carrying or borrowing is not an expectation at the grade level. With significant teacher support the student can add and subtract within within 100 (using concrete models to communicate) with and without regrouping. the standard The student can add and subtract within within 100 (using concrete models to communicate) with and without regrouping. Meets the standard Exceeds the (proficient) standard The student can add and subtract within within 1,000 (using concrete models to communicate) with and without regrouping. The student can add and subtract within 1,000 (using concrete models to communicate) with and without regrouping. Example: 354 + 287 = _ The student can add or subtract within 1000 with ease by using an algorithm or strategy based on place value. The student can use multiple strategies, such as applying the commutative or associate property. I started at 354 and jumped 200. I landed on 554. I then made 8 jumps of 10 and landed on 634. I then jumped 6 to land on 640. Then I jumped 1 more and landed on 641. 354 + 287 = 641 (student shows this on a number line) 2nd Grade Rubrics! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! Content Area: Math Report Card Language: The student can measure and estimate lengths using units such as inches, feet, centimeters and meters. CCSS: 2.MD.1 Measure the length of an object by selecting and using appropriate tools such as rulers, yardsticks, meter sticks, and measuring tapes. 2.MD.3 Estimate lengths using units of inches, feet, centimeters, and meters. Performance Levels for Reported Standards Evidence/Notes Not making expected Progressing toward progress to standard With significant teacher support the student can order objects by length, can measure using nonstandard units. the standard The student can order objects by length, can measure using nonstandard units. They may use some of the units of measurement accurately, but not all. Meets the standard Exceeds the (proficient) standard The student can accurately estimate, measure and record lengths in inches, feet, centimeters and meters. The student can measure and record accurate measurements in inches, feet, centimeters, and meters using halves, and quarters. 2nd Grade Rubrics! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! Content Area: Math Report Card Language: The student can relate addition and subtraction to length. CCSS: 2.MD.5 Use addition and subtraction within 100 to solve word problems involving lengths that are given the same units by using drawings (such as drawings of rulers) and equations with a symbol for the unknown number to represent the problem. Performance Levels for Reported Standards Evidence/Notes Not making expected Progressing toward progress to standard With significant teacher support the student can solve addition and subtraction word problems within 50 involving lengths that are given in the same units by using drawings and equations to represent the problem and solution. the standard The student can solve addition and subtraction word problems within 50 involving lengths that are given in the same units by using drawings and equations to represent the problem and solution. Meets the standard Exceeds the (proficient) standard The student can solve addition and subtraction word problems within 100 involving lengths that are given in the same units by using drawings and equations to represent the problem and solution. The student can solve addition and subtraction word problems within 100 involving lengths that are given in the same units by using two or more strategies to represent the problem and solution. The student begins to understand the concept of measuring area as it relates to addition and multiplication (can begin to measure areas by placing one inch square tiles on a shape and counting them). 2nd Grade Rubrics! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! Content Area: Math Report Card Language: The student can tell and write time to the nearest five minutes using analog and digital clocks. CCSS: 2.MD.7 Tell and write time from analog and digital clocks to the nearest five minutes, a.m and p.m. Performance Levels for Reported Standards Evidence/Notes Not making expected Progressing toward progress to standard With significant teacher support the student can tell and record time from analog and digital clocks to the nearest hour, half hour including AM and PM. the standard The student can tell and record time from analog and digital clocks to the nearest hour, half hour including AM and PM. Meets the standard Exceeds the (proficient) standard The student can tell and record time from analog and digital clocks to the nearest five minutes including AM and PM. The student can tell and record time from analog and digital clocks to the nearest minute and/or seconds including AM and PM. 2nd Grade Rubrics! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! Content Area: Math Report Card Language: The student can solve word problems involving money. CCSS: 2.MD.8 Solve word problems involving dollar bills, quarters, dimes, nickels, and pennies, using $ and ¢ symbols appropriately Performance Levels for Reported Standards Evidence/Notes Not making expected Progressing toward progress to standard With significant teacher support the student can solve word problems involving nickels. dimes, and quarters using the dollar sign and cents sign appropriately. the standard The student can solve word problems involving nickels. dimes, and quarters using the dollar sign and cents sign appropriately. Meets the standard Exceeds the (proficient) standard The student can solve word problems involving dollar bills, quarters, dimes, nickels and pennies using the dollar sign and cents sign appropriately. The student can solve word problems involving dollar bills, quarters, dimes, nickels and pennies using the dollar sign and cents sign appropriately, including making correct change and going beyond $10. 2nd Grade Rubrics! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! Content Area: Math Report Card Language: The student can recognize and draw shapes given a specified set of characteristics. CCSS: 2.G.1 Recognize and draw shapes having specified attributes, such as a given number of angles or a given number of equal faces. Identify triangles, quadrilaterals, pentagons, hexagons, and cubes. Performance Levels for Reported Standards Evidence/Notes Not making expected Progressing toward progress to standard Terms for students: properties attributes quadrilateral open figure closed figure Rhombus polygon partition With significant adult support, the student can identify and create basic shapes based on their characteristics and can identify the defining and non-defining characteristics of shapes. The student is only able to draw and recognize shapes based on defining characteristics with the most basic shapes of square, triangle, circle, and rectangle. the standard The student can identify and create basic shapes based on their characteristics and can identify the defining and non-defining characteristics of shapes. The student is able to recognize and draw some of the shapes based on defining characteristics, but not all shapes (e.g., is inconsistent with pentagons, trapezoids, etc.). Meets the standard Exceeds the (proficient) standard The student can recognize and draw shapes based on a set of attributes (e.g., draw a shape that has 5 equal faces. What is that called?) The student can understand that shapes in different categories (i.e., rectangles, rhombuses, and others) may share attributes and that the shared attributes can define a The student can identify larger category (e.g., all basic shapes and can quadrilaterals). correctly use the terms to describe shapes as The student can triangles, quadrilaterals, recognize rhombuses, pentagons, hexagons, or rectangles, and squares cubes. as examples of quadrilaterals AND draw examples of quadrilaterals that do not belong in any of these subcategories. 2nd Grade Rubrics! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! Content Area: Math Report Card Language: The student can divide circles and rectangles into two, three, or four equal parts. CCSS: 2.G.3 Partition circles and rectangle into two, three, or four equal shares, describe the shares using the words halves, thirds, half of, a third of, etc. and describe the whole as two halves, three thirds, four fourths. Recognize that equal shares of identical wholes need not have the same shape. Performance Levels for Reported Standards Evidence/Notes Not making expected Progressing toward progress to standard With significant teacher support the student can partition and label halves of a whole. the standard The student can partition and label halves of a whole. Meets the standard Exceeds the (proficient) standard The student can partition and label halves, thirds and fourths of a whole. The student shows an understanding that fractional parts may not be symmetrical. The student can partition and label halves, thirds and fourths on three or more polygons. Teacher: Partition each rectangle into fourths a different way. Student: I partitioned this rectangle 3 different ways. I folded or cut the paper to make sure that all of the parts were the same size. The student can express the area of each part as a unit fraction of the whole. For example, can partition a shape into 4 parts with equal area and describe the area of each part as 1/4 of the area of the shape.