Kindergarten Grade Rubrics Content Area: Math Report Card Language:
advertisement
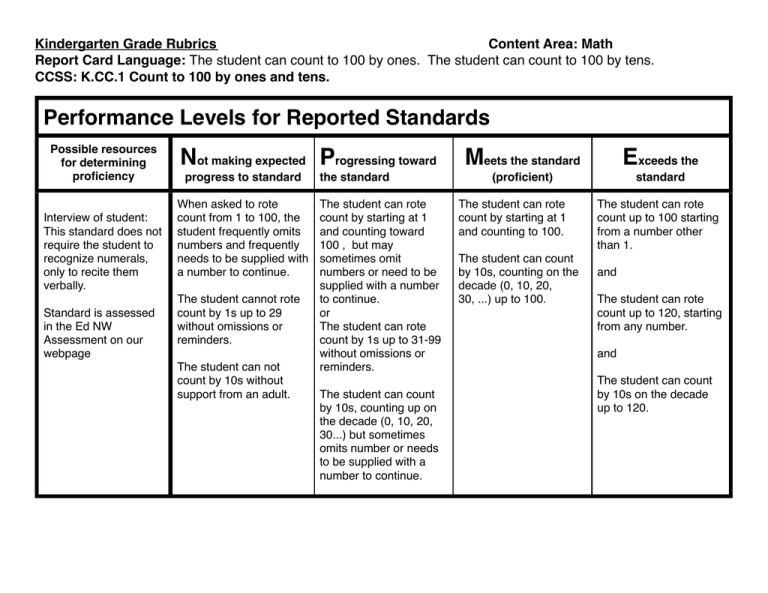
Kindergarten Grade Rubrics ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! Content Area: Math Report Card Language: The student can count to 100 by ones. The student can count to 100 by tens. CCSS: K.CC.1 Count to 100 by ones and tens. Performance Levels for Reported Standards Possible resources for determining proficiency Interview of student: This standard does not require the student to recognize numerals, only to recite them verbally. Standard is assessed in the Ed NW Assessment on our webpage Not making expected Progressing toward progress to standard When asked to rote count from 1 to 100, the student frequently omits numbers and frequently needs to be supplied with a number to continue. The student cannot rote count by 1s up to 29 without omissions or reminders. The student can not count by 10s without support from an adult. the standard The student can rote count by starting at 1 and counting toward 100 , but may sometimes omit numbers or need to be supplied with a number to continue. or The student can rote count by 1s up to 31-99 without omissions or reminders. The student can count by 10s, counting up on the decade (0, 10, 20, 30...) but sometimes omits number or needs to be supplied with a number to continue. Meets the standard Exceeds the (proficient) standard The student can rote count by starting at 1 and counting to 100. The student can count by 10s, counting on the decade (0, 10, 20, 30, ...) up to 100. The student can rote count up to 100 starting from a number other than 1. and The student can rote count up to 120, starting from any number. and The student can count by 10s on the decade up to 120. Kindergarten Grade Rubrics ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! Content Area: Math Report Card Language: The student can write numerals 0-20. CCSS: K.CC.3 Write numbers from 0-20. Represent a number of objects with a written numeral 0-20 (with 0 representing a count of no objects). Performance Levels for Reported Standards Possible resources for determining proficiency Ask students to write the numerals and identify the written numeral that represents a set. To extend assessment, go beyond 20. Not making expected Progressing toward progress to standard With significant adult support, the student can write some but not all of the numerals 0-9. the standard The student can write the numerals 0-9 and use the written numerals 0-9 to represent the amount within a set. Meets the standard Exceeds the (proficient) standard The student can write the numerals 0-20. The student can write numerals above 20 (up to 120 is the 1st grade standard). Classroom observations Classroom products NOTE: Place value is important, but individual number reversals are ok. Standard is assessed in the Ed NW Assessment on our webpage Note: Using a numeral to represent the number of objects in a set is in the next reported standard. Kindergarten Grade Rubrics ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! Content Area: Math Report Card Language: The student can understand the relationship between numerals and quantities of objects up to 20. CCSS: K.CC.4 Understand the relationship between numbers and quantities; connect counting to cardinality and K.CC.5 Count to answer “how many?” questions about as many of 20 things arranged in a line, rectangular array or circle, or as many as 10 things in a scattered configuration; given a number from 1-20, count out that many objects. Performance Levels for Reported Standards Possible resources for determining proficiency Student interview Classroom observations Classroom products Standard is assessed in the Ed NW Assessment on our webpage Not making expected Progressing toward progress to standard The student does not consistently demonstrate understanding of “one to one correspondence” and is not able to answer “how many” questions without adult support and prompting. Student can only count sets of less than 5 objects. the standard The student demonstrates understanding of “one to one correspondence” (e.g., they count objects one at a time and use counting words for each object) but are not able to consistently answer “how many” with sets of objects up to 20. Students may forget which items have been counted and double count some items or forget others. Students are able to demonstrate counting of sets of less than 10 objects. Meets the standard Exceeds the (proficient) standard The student can use correct counting procedures by pointing to one object at a time, using one counting word for every object, and answer the question “How many are there” by understanding that the last number stated represents the total number of objects. Up to 20 Students remember which items have been counted (and which have not) to keep track of items in a set. The student can independently demonstrate one to one correspondence and cardinality with sets of any number, shape, or size, whether items are lined up or placed randomly. Can write the numeral associated with objects in the set, up to 20. Can write the numeral associated with objects in the set above 20. Kindergarten Grade Rubrics ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! Content Area: Math Report Card Language: The student can compare written numerals 0-10 (using greater than, less than, and equal to). CCSS: K.CC.6 Identify whether the number of objects in one group is greater than, less than, or equal to the number of objects in another group; and K.CC.7 Compare two numbers between 1 and 10 presented as written numerals. Performance Levels for Reported Standards Possible resources for determining proficiency Can be assessed through student interview or with a pencil/paper task when asked to circle or otherwise identify the numeral that is smaller/ greater, etc. To assess to exceeds, students would need to write the symbols in between two numbers on a paper pencil task. Standard is assessed in the Ed NW Assessment on our webpage Not making expected Progressing toward progress to standard The student cannot yet use matching and counting strategies to identify whether groups of objects is greater than, less than, or equal to the number of objects in another group without help from an adult. the standard The student can use matching and counting strategies to identify if the number of objects in one group is greater than, less than, or equal to the number of objects in a another group. Meets the standard Exceeds the (proficient) standard When shown two written numerals between 1-10, the student can recognize which number is more, less, or if they are equal. The student can use the standard symbols >, <, and = to compare written numerals. The student can compare numerals larger than 20. Kindergarten Grade Rubrics ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! Content Area: Math Report Card Language: The student can show addition as putting together and adding to OR show subtraction as taking apart and taking from. CCSS: K.OA.1 Represent addition and subtraction with objects, fingers, mental images, drawings, sounds, verbal explanations, expressions or equations. Performance Levels for Reported Standards Possible resources for determining proficiency Student interview is used to allow the student to demonstrate multiple ways to demonstrate their understanding. Classroom observations Classroom products Once students have this concept, they move on to word problems to solve simple addition and subtraction problems. Not making expected Progressing toward progress to standard The student requires adult support to demonstrate any understanding of putting together or taking apart objects. the standard The student can demonstrate adding to OR taking apart, but cannot demonstrate both. or The student can demonstrate adding to or taking apart but only through one or two methods. Meets the standard Exceeds the (proficient) standard The student can demonstrate the understanding of how objects can be joined together and separated in various ways: with objects, mental images, drawings, sounds, acting out situations, or verbal explanations, expressions, or equations. The student can put together or take apart and provide an answer without having to recount the set. For example, given 6 objects, and told to remove 2, they could identify the remaining set as 4 without having to recount (would have to do interview to determine this). Kindergarten Grade Rubrics ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! Content Area: Math Report Card Language: The student can solve word problems using numeral 0-10 with pictures and equations. CCSS: K.OA.2 Solve addition and subtraction word problems, and add or subtract within 10 by using objects or drawings to represent the problem. Performance Levels for Reported Standards Possible resources for determining proficiency This standard can be assessed via paper/ pencil tasks created by the teacher. Standard is assessed in the Ed NW Assessment on our webpage Not making expected Progressing toward progress to standard The student is unable to represent word problems with pictures or objects without adult support. the standard The student can accurately represent a word problem (within 10) with objects or pictures but calculation is incorrect. Conceptual understanding is present, but accuracy is not. Meets the standard Exceeds the (proficient) standard The student can accurately represent addition and subtraction word problems (within 10) with pictures or objects with a correct answer. Students only need to count with objects or drawings, not solve with equation symbols. The student can accurately represent a word problem with pictures, objects, AND an equation. Kindergarten Grade Rubrics ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! Content Area: Math Report Card Language: The student can fluently add and subtract numerals 0-5. CCSS: K.OA.5 Fluently add and subtract within 5. Performance Levels for Reported Standards Possible resources for determining proficiency Can be assessed using teacher created paper/ pencil tasks or student interview. Classroom observation Standard is assessed in the Ed NW Assessment on our webpage Not making expected Progressing toward progress to standard The student always relies on fingers, manipulatives or other counting strategies to solve simple addition or subtraction problems with inconsistent accuracy. the standard The student is able to arrive at a correct response but not with automaticity (e.g., does not add and subtract fluently). May use fingers, manipulatives, or other counting strategies. Meets the standard Exceeds the (proficient) standard The student is able to add and subtract numerals 0-5 fluently. Students are fluent when they display accuracy and efficiency (within about 3-5 seconds) when presented with a problem. Students do not need to rely on manipulatives or counting strategies. The student is able to fluently add and subtract numbers 0-10. Kindergarten Grade Rubrics ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! Content Area: Math Report Card Language: The student can compose (put together) and decompose (take apart) numerals 11-19 using ten and ones. CCSS: K.NBT.1 Compose and decompose numbers from 11 to 19 into tens and ones and some further ones, by using objects or drawings, and record each composition/decomposition by a drawing or equation. Performance Levels for Reported Standards Possible resources for determining proficiency Student interview or teacher created paper/ pencil tasks. Standard is assessed in the Ed NW Assessment on our webpage Not making expected Progressing toward progress to standard The student does not yet understand that the numbers 11-19 are composed of tens and ones. the standard Given a model, the student can identify “tens” and “ones” The student can compose a two digit number up to 19 using 10s and ones with adult support. Meets the standard Exceeds the (proficient) standard The student can compose and decompose numbers from 11 to 19 into ten ones and some further ones by using drawings, or objects. The student can compose and decompose 2-digit numbers above 19 with the understanding that there are multiple 10s and one or more ones in the number. The student can record the composition or decomposition by a drawing or equation. Kindergarten Grade Rubrics ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! Content Area: Math Report Card Language: The student can compare length and weight of objects. CCSS: K.MD.1 Describe measurable attributes of objects, such as length or weight. Describe several measurable attributes of a single object. K.MD.2 Directly compare two objects with a measurable attribute in common to see which object has “more of”/ “less of” the attribute, and describe the difference. Performance Levels for Reported Standards Possible resources for determining proficiency Choice of Investigations lessons Unit 4 and Unit 2 Student interview is a appropriate for this standard. Portions of this standard are on the Ed NW assessment on our webpage. Not making expected Progressing toward progress to standard The student cannot verbally describe specific measurable attributes to compare the difference between two objects. For example, they may just say something is “bigger.” With adult support can find two objects with similar attributes. the standard The student can describe one attribute of objects, but not several. The student is working on using specific verbal descriptions to compare and describe the difference between two objects but needs some adult support. Meets the standard Exceeds the (proficient) standard The student can describe measurable attributes of objects such as length and weight and describe several measurable attributes of an object (e.g., tall, heavy, red) The student can directly compare two objects with a measurable attribute in common to see which has less or more of the attribute and describe the difference (e.g., taller, lighter, darker) The student can order three objects by length and compare the lengths of two objects indirectly by using a third object. Kindergarten Grade Rubrics ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! Content Area: Math Report Card Language: The student can classify, sort, and compare object and count the number of objects in categories. CCSS: K.MD.3 Classify objects into given categories; count the number of objects in each category and sort the categories by count. Performance Levels for Reported Standards Possible resources for determining proficiency Can be assessed using student interview or Classroom observation Investigations attribute blocks and cards Not making expected Progressing toward progress to standard With significant adult support, the student is able to sort objects by a single attribute. the standard The student is able to sort objects by a single attribute. Meets the standard Exceeds the (proficient) standard The student can identify similarities and differences between objects (e.g., size, color, shape) and use the attributes to sort a collection of objects. The student sorts objects by 2 attributes (e.g., small and round, small and square, big and round, big and square) and then counts and orders by quantity After sorting objects, the student can then arrange the groups by number of objects. The student is able to record the number of objects in each set to represent data. Example: student sorts buttons by color, counts the buttons in each group, and then organizes the groups by quantity. Kindergarten Grade Rubrics ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! Content Area: Math Report Card Language: The student can identify, describe, and compare two dimensional shapes. CCSS: K.G.1 Describe objects in the environment using names of shapes and describe the relative position of these objects (using terms such as below, above); K.G.2 Correctly name shapes regardless of their orientation or overall size; K.G.3 Identify shapes as two-dimensional (“flat”) or three dimensional (“solid”) Performance Levels for Reported Standards Possible resources for determining proficiency Assessed using student interview because of need to verbally describe and compare. Some portions are on the Ed NW assessment on our webpage. Not making expected Progressing toward progress to standard the standard Meets the standard Exceeds the (proficient) standard The student can distinguish between different shapes, but is inconsistent in naming and identifying shapes. The student can use informal words to locate and identify shapes in the environment (box, ball) or they can name some of the shapes. The student can use one or two positional words to describe objects, buy may need adults support. The student can The student can use describe shapes and some positional words to use position words to describe objects in the describe objects in the environment. environment. The student is not able to verbally compare shapes. The student uses informal language to compare shapes or is able to match shapes, but not describe why they match or don’t match. Can only do some of these skills. The student can locate and identify shapes in the environment (using the words such as triangle, square, circle) The student can compare shapes, for example by the number of sides or corners they have, straight sides versus round. The student uses defining versus nondefining characteristics to identify and compare shapes (number of sides is defining, orientation is nondefining). Kindergarten Grade Rubrics ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! Content Area: Math Report Card Language: The student can identify, describe, and compare three dimensional shapes. CCSS: K.G.1 Describe objects in the environment using names of shapes and describe the relative position of these objects (using terms such as below, above); K.G.2 Correctly name shapes regardless of their orientation or overall size; K.G.3 Identify shapes as two-dimensional (“flat”) or three dimensional (“solid”) Performance Levels for Reported Standards Possible resources for determining proficiency Can be assessed using student interview and/or teacher created paper/ pencil tasks, depending on the child’s ability to read and/or provide written responses. Portions of the standard are assessed in the Ed NW Assessment on our webpage Not making expected Progressing toward progress to standard the standard Meets the standard Exceeds the (proficient) standard The student can distinguish between different shapes, but is inconsistent in naming and identifying 3dimensional shapes. The student can use informal words to identify 3-dimensional shapes (such as box or ball) or they can name some of the shapes. The student can locate and identify 3dimensional shapes in the environment (using words such as cube, cone, cylinder, sphere) The student can use one or two positional words to describe objects, buy may need adults support. The student can use some positional words to describe 3-dimensional objects in the environment. The student can describe 3-dimensional shapes and use position words to describe objects in the environment. The student is not able to verbally compare shapes. The student is not able to compare 3dimensional or 2 dimensional shapes as flat or solid The student can compare 3-dimensional and 2-dimensional shapes as flat or solid. Student can consistently label and describe different 2- or 3dimensional shapes in a composite figure. The student can manipulate shapes to create a composite shape or picture (K.G.6).