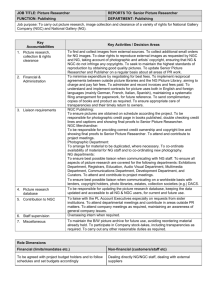
Zone 71, Master Map Normal View c e
advertisement

Zone 71, Master Map Bootes ζ M101 Alcor Mizar +52°00' c e κ2 κ1 +50°00' ι +54°00' Normal View Zone Master, Normal View, 10 deg FOV Alkaid +48°00' η Ursa Major f λ 14h 12m 14h 00m 13h 48m Whirlpool Galaxy M51 13h 36m 13h 24m d +46°00' Canes Venatici 13h 12m 13h 00m 12h 48m Zone 71, Map 1 Normal Image ζ Zeta UMa Mizar Bemporad 6 h2649 +53°00' STF 1695 +54°00' Alcor +55°00' Sky charts generated by TheSky Software; used by permission of Software Bisque Inc. +52°00' Espin 733 Canes Venatici +51°00' NGC 5225 STF 1718 STF 1770 +50°00' OS 263 Bemporad 4 A. G. 190 13h 36m 13h 30m 13h 24m 13h 18m 13h 12m 13h 06m 13h 00m 12h 54m Zone 71, Map 1 Mirror Image +55°00' Sky charts generated by TheSky Software; used by permission of Software Bisque Inc. Alcor Zeta UMaζ Bemporad 6 h2649 Espin 733 Canes Venatici +52°00' +53°00' STF 1695 +54°00' Mizar Espin 730 +51°00' NGC 5225 STF 1718 +50°00' OS 263 Bemporad 4 A. G. 190 12h 54m 13h 00m 13h 06m 13h 12m 13h 18m 13h 24m 13h 30m 13h 36m Zone 71, Map 2 Normal Image +50°00' Sky charts generated by TheSky Software; used by permission of Software Bisque Inc. Bemporad 4 STF 1758 +49°00' A. G. 190 h2642 +48°00' h2667 Espin 608 STF 1747 h2634 h2627 NGC 5194 +47°00' NGC 5195 Whirlpool Galaxy M51 NGC 5173 NGC 4800 +46°00' Espin 2646 NGC 5198 +45°00' OS 257 Kazeza 58 13h 36m 13h 30m 13h 24m 13h 18m 13h 12m 13h 06m 13h 00m 12h 54m Zone 71, Map 2 Mirror Image +50°00' Sky charts generated by TheSky Software; used by permission of Software Bisque Inc. Bemporad 4 +49°00' A. G. 190 STF 1758 +48°00' h2642 STF 1747 h2634 NGC 5195 M51 Whirlpool Galaxy NGC 5194 +47°00' h2627 Espin 2646 NGC 5198 NGC 5173 +46°00' NGC 4800 +45°00' OS 257 Kazeza 58 12h 54m 13h 00m 13h 06m 13h 12m 13h 18m 13h 24m 13h 30m 13h 36m Zone 71, Map 3 Normal Image NGC 5486 NGC 5485 Zeta UMa Mizar Alcor NGC 5473 +55°00' Sky charts generated by TheSky Software; used by permission of Software Bisque Inc. M101 NGC 5457 +54°00' ζ Bootes Bemporad 6 h2694 +53°00' NGC 5474 +52°00' STF 1795 Canes Venatici +51°00' NGC 5225 NGC 5480 +50°00' STF 1770 STF 1774 rej h2676 H VI 112 14h 06m A. G. 190 14h 00m 13h 54m 13h 48m 13h 42m 13h 36m 13h 30m 13h 24m Zone 71, Map 3 Mirror Image NGC 5486 NGC 5485 NGC 5473 Alcor Mizar Bootes h2649 M101 NGC 5457 Bemporad 6 h2694 +54°00' Zeta UMaζ +55°00' Sky charts generated by TheSky Software; used by permission of Software Bisque Inc. NGC 5474 +53°00' Espin 733 +52°00' STF 1795 Canes Venatici +51°00' NGC 5225 NGC 5480 +50°00' STF 1770 STF 1774 rej h2676 A. G. 190 13h 24m 13h 30m 13h 36m 13h 42m 13h 48m 13h 54m 14h 00m 14h 06m Zone 71, Map 4 Normal Image +50°00' Sky charts generated by TheSky Software; used by permission of Software Bisque Inc. STF 1774 rej h2676 η Eta UMa NGC 5448 +49°00' A. G. 190 H VI 112 13 Boo Alkaid STF 1758 LDS 5800 Ursa Major Bur 802 +48°00' STF 1806 h2667 Espin 608 NGC 5195 NGC 5377 NGC 5194 Espin 2646 NGC 5198 Whirlpool Galaxy M51 NGC 5173 +46°00' h2697 Swift 1 STF 1776 14h 00m 13h 54m 13h 48m +45°00' h2680 14h 06m +47°00' STF 1747 Canes Venatici 13h 42m 13h 36m 13h 30m 13h 24m Zone 71, Map 4 Mirror Image +50°00' Sky charts generated by TheSky Software; used by permission of Software Bisque Inc. STF 1774 rej h2676 η STF 1758 Eta UMa Alkaid NGC 5448 +49°00' A. G. 190 Ursa Maj Bur 802 h2667 Espin 608 STF 1747 +48°00' LDS 5800 NGC 5195 M51 NGC 5194 Whirlpool Galaxy +47°00' Canes V NGC 5377 NGC 5198 Espin 2646 NGC 5173 +46°00' h2697 Swift 1 STF 1776 +45°00' h2680 Kazeza 58 13h 24m 13h 30m 13h 36m 13h 42m 13h 48m 13h 54m 14h 00m 14h 06m Zone 71 Index 1 Reference Star, 21 Double Stars, 6 Galaxies A N A. G. 190 ............................................. 15 Bemporad 4............................................ 8 Bemporad 6............................................ 9 Bur 802 ................................................ 16 NGC 5173 ............................................ 20 NGC 5194 ............................................ 17 NGC 5195 ............................................ 19 NGC 5198 ............................................ 20 NGC 5225 ............................................ 12 NGC 5377 ............................................ 19 E O Espin 2646 ........................................... 16 Espin 733 ............................................... 5 Eta UMa............................................... 13 OS 263 ................................................... 6 H h2634 ..................................................... 7 h2642 ..................................................... 8 h2649 ..................................................... 4 h2680 ................................................... 14 h2694 ................................................... 10 STF 1718................................................ 5 STF 1747................................................ 7 STF 1758.............................................. 15 STF 1770.............................................. 11 STF 1774 rej .......................................... 9 STF 1776.............................................. 13 STF 1795.............................................. 10 L Z LDS 5800............................................. 14 Zeta UMa ............................................... 2 B S -1- Zone 71 Zone 71, Map 1 Double Stars Easy Zeta UMa Rating: 2 E 79 UMa; Mizar; STF 1744ADS 8891; HD 116656; SAO 28737 Astronomical League Program: Double Star Club Position: 1324+5456 A B Magnitude 2.23 3.85 Separation PA — — 14.4 153 + Year — 1998 Spectra A2 V A2 V Colors W W Notes: Zeta was found to be a telescopic binary by Riccioli in 1650 and re-discovered by G. Kirch on September 7, 1700. It was first measured by Bradley in 1755. It was also the first binary photographed (in 1857 by G. P. Bond, Harvard Observatory). And, it is the first spectroscopic binary discovered (both stars A and B, by Pickering, 1889). Pease was the first astronomer to optically resolve this spectroscopic binary with the 20-foot interferometer at Mt. Wilson (1925). The Aa orbit only takes 20.5386 days. The Bb orbit takes 182.3 days. There also seems to be a third (invisible) companion with an orbit of 1,350 days. The two visible stars are at least 380 AU apart (5 times the diameter of Pluto's orbit). Both are infra-red sources. 1820: 14.6 @ 146. Over 100 measurements. The stars share common proper motion. This star is a member of the Ursa Major moving stream. From James Kaler's Star Notes: Alcor is a fourth magnitude (4.01) white class A (A5) star with a temperature of 8,000 Kelvin and a luminosity 12 times that of the Sun. It appears coupled with Mizar, but is it really a physical companion? We are still not sure. Mizar itself is a quadruple star on the "double-double" theme (two double stars in orbit about each other.) Precision parallaxes with the Hipparcos satellite show Mizar to be 78.1 light years away, but Alcor to be 81.1 light years distant. Mizar and Alcor are part of the Ursa Major cluster, whose core consists of the middle five stars of the Big Dipper. A separation of over three light years, almost the distance between here and Alpha Centauri, would make a gravitational pairing unlikely as the neighboring stars -2- Zone 71 would pull them apart. The measured errors, however, allow a separation as close as 0.7 light years. The errors in the distances are suspected of being greater than listed, and the analysis of the orbit of Mizar A suggests that Mizar might actually be FARTHER than Alcor! If they are actually at the same distance, their minimum separation is only 0.27 light years, making them close enough so that they could truly orbit, though with a long period of three-quarters of a million years. For a time Alcor was thought to be double, but it now appears that early astronomers were fooled and that it is really single, rendering Mizar and Alcor together a "quintuple star." While the Mizar stars are slow rotators with peculiar chemical compositions as a result of element separation, Alcor is a rapid spinner (218 kilometers per second, over 100 times solar). As a result, its atmosphere is stirred and its composition normal. It is, however, a slight pulsating variable. The inner five stars of the Big Dipper are all at roughly the same distance and all are normal hydrogen fusing main sequence dwarfs. Alcor's faintness next to the them is a vivid reminder of the role that mass plays in the stars. Alcor's mass is around 1.6 times that of the Sun. Alioth, on the other hand, with twice Alcor's mass, is almost 10 times brighter! On Mizar: One of the most famed stars of the sky, second magnitude (2.27) Mizar is the Zeta star of Ursa Major, the Greater Bear, the second star in from the end of the handle of the Big Dipper, and the Dipper's fourth brightest star. In large part its fame comes from the coupling of the star with a nearby visual companion, fourth magnitude Alcor, only 12 minutes of arc (a fifth of a degree) to the northeast. The two, Mizar and Alcor, termed the "horse and rider" by the Arabians, are a good test of minimal vision. The star's Arabic name derives from a word meaning "the groin" of the celestial Bear that plods silently around the north celestial pole (the name mistakenly drawn from Merak, in the Dipper's bowl). However even without Alcor, Mizar takes its place in the celestial hall of fame as the first known "double star," one that consists of a pair of stars that orbit each other. Found to be double in 1650, Mizar is a prime target for someone with a new telescope, as the components are an easy 14 seconds of arc apart (at least 500 astronomical units), the two taking at least 5,000 years to make their orbit about each other. More remarkably, each of these two components is again double. The brighter of the two contains a very close pair a mere 7 or 8 thousandths of a second of arc apart (an angle made by a penny at a distance of 300 miles) that has an orbital period of 20.5 days, days; the fainter of them contains a pair with a period of about half a year. Mizar is thus actually a quartet of stars, a double-double. It is moving through space together with its more-distant companion, Alcor. Mizar and Alcor together therefore probably make a quintuple star, Alcor taking at least 750,000 years to make a single round trip around its quadruple companion. All of the stars are similar, all "main sequence" hydrogen-fusing stars like the Sun, but of white class A (the brighter both A2, the fainter probably both A5 or A7) with temperatures -3- Zone 71 ranging between around 7,500 and 9,000 degrees Kelvin and luminosities from 10 to 30 times solar. The orbit of the brighter double that makes Mizar has been observed with a sophisticated "interferometer" that makes use of the interfering properties of light. Analysis shows the component stars to have masses 2.5 times that of the Sun; the masses of the fainter pair are estimated at around 1.6 solar. The stars have odd chemical abundances as a result of slow rotation, which allows for quiet atmospheres and chemical separation. The brighter of the pair seen through the telescope is rich in silicon and strontium, whereas the fainter is a "metallic line star" that is deficient in aluminum and calcium but high in silicon and in rare earths like cerium and samarium. Observations: C8 at 104x. Webb saw A as gW. Scale model (in which the Sun is the size of a baseball): Diameter: A = 8.40 inches; B = 8.40 inches. Separation: AB = 1.93 miles; Aa = 3.94 feet; Bb = 16.9 feet. Distance (LY): 78 Total luminosity (Suns): 82.1 h2649 HD 238213; SAO 28714 Rating: 3 E Position: 1318+5420 A B Magnitude 10.21 10.64 Separation PA — — 21.3 345 + Notes: 1880: 23.4 @ 344. 11 measurements. Observations: C11 at 115x. -4- Year — 1991 Spectra K0 Colors Y W Zone 71 STF 1718 Hussey 643; SAO 28628 Rating: 4 E Position: 1306+5100 A B Magnitude 9.50 10.07 Separation PA — — 13.1 272 = Year — 1991 Spectra F8 Colors W? W? Notes: 1831: 13.2 @ 272. 16 measurements. The stars share common proper motion. Hussey doubled A (9.5m, 10.5m; 0.3 @ 203). Observations: C8 at 83x. Espin 733 ADS 8869; HD 234031 Rating: 5 E Position: 1321+5321 A B Magnitude 10.03 10.80 Separation PA — — 6.1 = 212 + Year — 1993 Notes: 1904: 6.1 @ 211. 4 measurements. Observations: C11 at 115x. Scale model (in which the Sun is the size of a baseball): Diameter: A = 18.9 inches. Separation: AB = 1.13 miles. Distance (LY): 119 Total luminosity (Suns): 0.162 -5- Spectra G0 Colors Y bW Zone 71 Moderate OS 263 ADS 8843; HD 115477 Rating: 4 M Position: 1317+5034 A B Magnitude 8.83 9.89 Separation PA — — 1.8 136 + Year — 1998 Notes: 1843: 2.2 @ 132. 44 measurements. Observations: C8 at 280x. Scale model (in which the Sun is the size of a baseball): Diameter: A = 20.4 inches. Separation: AB = 1.54 miles. Distance (LY): 550 Total luminosity (Suns): 13 -6- Spectra G5 Colors W W Zone 71 Zone 71, Map 2 Double Stars Easy STF 1747 ADS 8910; SAO 44617 Rating: 4 E Position: 1328+4745 A B Magnitude 9.24 10.12 Separation PA — — 15.0 = 346 - Year — 1991 Spectra K0 Colors O dO Notes: 1831: 15.0 @ 347. 21 measurements. The stars share common proper motion. Observations: C8 at 104x. h2634 SAO 44445 Rating: 5 E Position: 1303+4744 A B Magnitude 9.55 13.14 Separation PA — — 30.9 60 = Notes: 1906: 31.0 @ 60. 2 measurements. Observations: C11 at 115x. -7- Year — 1908 Spectra K5 Colors Y ? Zone 71 h2642 ADS 8793 Rating: 5 E Position: 1308+4907 A B Magnitude 10.46 11.26 Separation PA — — 9.1 = 177 - Year — 1992 Spectra F8 Colors W O? Notes: 1830: 9.1 @ 178. 12 measurements. Observations: C11 at 115x. Scale model (in which the Sun is the size of a baseball): Diameter: A = 17.1 inches. Separation: AB = 8.52 miles. Distance (LY): 600 Total luminosity (Suns): 2.71 Bemporad 4 Rating: 5 E Position: 1308+4955 A B Magnitude 11.56 11.66 Separation PA — — 21.8 + 2- Year — 1991 Notes: 1904: 21.2 @ 22. 2 measurements. Observations: C11 at 115x. Distance (LY): 62 Total luminosity (Suns): 0.014 -8- Spectra Colors W W Zone 71 Zone 71, Map 3 Double Stars Easy Bemporad 6 Rating: 4 E Position: 1334+5418 A B Magnitude 10.43 11.19 Separation PA — — 8.3 = 189 - Year — 1991 Spectra Colors W W? Notes: 1904: 8.3 @ 190. 6 measurements. Observations: C11 at 115x. STF 1774 rej C = h2676; ADS 8992; HD 119583; SAO 28860 Rating: 4 E Position: 1343+5002 A B C Magnitude 6.34 10.51 10.38 Separation — 17.3 27.6- PA — 135 + 126 + Year — 1999 1991 Spectra F8 V Colors W ? ? Notes: AB 1879: 17.9 @ 134. 10 measurements. Hipparcos/Tycho data show different distances for these stars; they may be optical. AC 1900: 29.7 @ 125. 7 measurements. Observations: C8 at 65x. -9- Zone 71 Scale model (in which the Sun is the size of a baseball): Diameter: A = 3.60 inches. Separation: AB = 18.9 miles. Distance (LY): 700 Total luminosity (Suns): 33 h2694 HD 121892; SAO 28940 Rating: 4 E Position: 1357+5354 A B Magnitude 7.97 11.70 Separation PA — — 39.2 84 = Year — 1912 Spectra K2 Colors Y pB Notes: 1906: 39.8 @ 84. 2 measurements. Observations: C8 at 104x. Scale model (in which the Sun is the size of a baseball): Diameter: A = 26.8 inches. Separation: AB = 85.6 miles. Distance (LY): 1,400 Total luminosity (Suns): 103 STF 1795 ADS 9077; HD 122200; SAO 28955 Rating: 4 E Position: 1359+5307 A B Magnitude 6.83 9.96 Separation PA — — 7.9 + 2- - 10 - Year — 1997 Spectra A2 IV/V Colors Y V Zone 71 Notes: 1832: 7.6 @ 3. 19 measurements. Observations: C8 at 104x. Scale model (in which the Sun is the size of a baseball): Diameter: A = 10.8 inches. Separation: AB = 5.78 miles. Distance (LY): 469 Total luminosity (Suns): 35 Moderate STF 1770 ADS 8979; HD 118741; SAO 28819 Rating: 2 M Position: 1338+5043 A B Magnitude 6.95 8.26 Separation PA — — 1.7 = 123 - Year — 1998 Spectra M2 II/III F3 III Notes: 1831: 1.7 @ 125. 53 measurements. The primary is an infra-red source. Observations: C8 at 280x. Webb saw them as Y and W or O and rW. Scale model (in which the Sun is the size of a baseball): Diameter: A = 1.20 inches. Separation: AB = 4.69 miles. Distance (LY): 1,770 Total luminosity (Suns): 720 - 11 - Colors O! B! Zone 71 Deep Sky Objects Difficult NGC 5225 Other Names: UGC 8540, H III 822 Rating: 5 D Position: 1333+5129 Type : Gal Surface brightness: 12.4 Class: S Dimensions: 42" Magnitude : 13.5 Observations: C11 at 140x. Very, very faint and small, without a nucleus. It lies 10 min E of 3 bright field stars. Radial velocity (km/sec): +4,622 - 12 - Zone 71 Zone 71, Map 4 Reference Star Eta UMa (85 UMa; Alkaid, "the chief of the mourners"; HD 120315; SAO 44752) Position: 1348+4919 Mag : 1.85 Spectrum : B3 V Color : W Assumed distance: 101 light years Assumed luminosity (suns): 700 Notes: Star A is a spectroscopic binary and an infra-red source. The primary rotates at 205 kps, and the whole system is part of the Cas-Tau OB1 Association. From James Kaler's Star Notes: With a surface temperature of about 20,000 degrees Kelvin, Alkaid is one of the hotter stars that can be seen with the naked eye, and therefore glows to us a soft bluewhite. Like the Sun, it is a "main-sequence" star that shines by fusing hydrogen into helium in its core. However its mass of six times that of the Sun renders it both hotter. Were Alkaid our Sun, we would have to be 25 times farther away to survive, almost to the orbit of Neptune. The star is just below the temperature limit at which stars produce strong X-rays as a result of shock waves in their winds, and is therefore only a weak source of X-rays. Double Stars Easy STF 1776 ADS 8996; HD 119348; SAO 44715 Rating: 4 E Position: 1342+4613 A B Magnitude 8.53 8.57 Separation PA — — 7.3 = 18 -? Year — 1991 Spectra G0 F0 Colors W W Notes: 1832: 7.3 @ 200. 39 measurements. The stars share common proper motion. Quadrant reversal? - 13 - Zone 71 Observations: C8 at 65x. Scale model (in which the Sun is the size of a baseball): Diameter: A = 17.5 inches; B = 10.8 inches. Separation: AB = 9.11 miles. Distance (LY): 800 Total luminosity (Suns): 40 h2680 ADS B6628 Rating: 4 E Position: 1346+4524 A B Magnitude 10.07 11.51 Separation PA — — 23.7 + 148 - Year — 1991 Spectra F8 Colors W W? Notes: 1896: 22.2 @ 154. 6 measurements. Observations: C8 at 104x. LDS 5800 SAO 44818 Rating: 4 E Position: 1358+4853 A B Magnitude 9.81 11.29 Separation PA — — 41.6 = 356 = Notes: 1902: 41.6 @ 356. 5 measurements. Observations: C11 at 115x. - 14 - Year — 1991 Spectra F8 Colors W B! Zone 71 Scale model (in which the Sun is the size of a baseball): Diameter: A = 16.6 inches. Separation: AB = 21.9 miles. Distance (LY): 338 Total luminosity (Suns): 1.34 Moderate A. G. 190 ADS 8964; HD 118376 Rating: 4 M Position: 1336+4939 A B Magnitude 9.26 9.44 Separation PA — — 2.6 = 12 = Year — 1999 Spectra K0 Colors Y Y Notes: 1902: 2.6 @ 12. 36 measurements. Observations: C8 at 280x. It lies 12 min NNW of a 6.5m star. STF 1758 ADS 8940; HD 117963; SAO 44650 Rating: 5 M Position: 1333+4909 A B Magnitude 7.98 8.24 Separation PA — — 3.5 294 - Year — 1999 Spectra G0 Colors W W Notes: 1832: 4.2 @ 311. 66 measurements. The stars have different proper motions. Observations: C8 at 206x. It lies 18 min WNW of 5m 24 CVn. Webb saw the primary as W, Bird saw it as Y. - 15 - Zone 71 Scale Model (in which the Sun is a baseball): Component Diameter, in A 16.9 B Scale model (in which the Sun is the size of a baseball): Diameter: A = 16.9 inches. Separation: AB = 1.38 miles. Distance (LY): 254 Distance, mi na 1.38 Total luminosity (Suns): 4.5 Espin 2646 ADS 8945; SAO 44658 Rating: 5 M Position: 1334+4648 A B Magnitude 8.81 12.50 Separation PA — — 8.9 343 - Year — 1979 Spectra G5 Colors yW ? Notes: 1911: 9.4 @ 344. 2 measurements. Observations: C11 at 115x. Scale model (in which the Sun is the size of a baseball): Diameter: A = 20.3 inches. Separation: AB = 11.8 miles. Distance (LY): 850 Total luminosity (Suns): 17.6 Bur 802 ADS 9030; HD 120475; SAO 44759 Rating: 5 M Position: 1349+4821 A B Magnitude 7.50 11.69 Separation PA — — 3.5 + 225 + - 16 - Year — 1992 Spectra F0 IV Colors Y ? Zone 71 Notes: AB 1881: 3.4 @ 224. 14 measurements. Observations: C8 at 206x. Scale model (in which the Sun is the size of a baseball): Diameter: A = 8.40 inches. Separation: AB = 1.79 miles. Distance (LY): 328 Total luminosity (Suns): 8.44 Deep Sky Objects Easy NGC 5194 Rating: 1 E Other Names: Whirlpool Galaxy; 4C 47; UGC 8493; Arp 85, M51 Astronomical Leage Program: Messier Club Position: 1330+4712 Type : Gal Surface brightness: 12.6 Class: SA(s)bc pec I-II Dimensions: 6' x 10' Magnitude : 8.7 PA: 163 Notes: Messier discovered it on October 13, 1773 while observing the Comet of 1773 and added it to his catalog on January 11, 1774. He wrote, "it is double, each having a bright center, separated by 4'35". The two atmospheres touch each other. One is fainter than the other." It was named "the Whirlpool" by Lord Rosse, who observed it with his 72-inch "Leviathin" telescope in 1845. In fact, the spiral pattern he noticed seemed to confirm a popular (but erroneous) theory of planetary system formation put forward by the French philosopher LaPlace, called the "nebular hypothesis", which resulted in astronomers thinking that the spiral nebulae were all condensing proto-star systems within the Milky Way. It was not until 1929 that Hubble, using his own work and that of several others in the 1910’s and 20’s, proved that the spiral nebulae were actually Milky Ways in their own right but at vast distances. - 17 - Zone 71 It is 100,000 light years in diameter and weighs in at about 160 billion solar masses. The center harbors a black hole with 2 million solar masses that is 100 light years in diameter. Infrared studies show the arms make three complete laps around the nucleus. It is also a Seyfert galaxy. The "connecting bridge" is an illusion as high magnification photos show that the satellite galaxy actually lies behind M51. Observations: C8 at 104x. It is mottled and splotchy; even the spiral arms are discernible (at high power). (Both Messier and Herschel missed the spiral structure.) The connecting bridge is also visible. At the Texas Star Party in 2001, I got the chance to view M51 through the 36-inch Cassegrain reflector at McDonald Observatory and clearly saw the two spiral arms and bridge (or arm extension) that cuts in front of NGC 5195. There is a 12m star just SW of the nucleus. Steve Coe points out that this has been turned in as a supernova many, many times, so don't bite the bait! C11 at 193x. The nucleus looks comma-shaped; the galaxy is heavily mottled and in moments of good seeing, spiral structure is suspected. Model (where the Sun is a baseball): Its diameter would be 33 million miles. Distance (LY): 35,000,000 Luminosity (suns): 31,800,000,000 Radial velocity (km/sec): +546 NGC 5194 (M51, the Whirlpool) Galaxy (SA(s)bc pec I-II) Observed with C8 on 5/20/95; s7, t6 Magnification: 100x - 18 - Zone 71 NGC 5195 Other Names: UGC 8494, H I 186 Astronomical League Program: Herschel 400 Club Rating: 4 E Position: 1330+4716 Type : Gal Surface brightness: 13.1 Class: I0 pec Dimensions: 2' Magnitude : 11.0 PA: 79 Notes: Photos suggest that it actually lies behind M51. It too is a Seyfert galaxy. It was discovered by P. Mechain on March 20, 1781. Messier mentions it in his 1781 catalog. SN 19545A was detected in this galaxy by Milton Humason. Observations: C8 at 83x. Bright. C11 at 193x. Very bright and round, srongly concentrated. Model (where the Sun is a baseball): Its diameter would be 7 million miles. Distance (LY): 36,000,000 Radial velocity (km/sec): +650 Luminosity (suns): 4,100,000,000 Moderate NGC 5377 Other Names: UGC 8863, H I 187 Rating: 3 M Position: 1356+4714 Type : Gal Surface brightness: 13.6 Class: (R)SB(s)a Dimensions: 3' x 0.6' Notes: This galaxy produced supernova 1992H (type IIp). - 19 - Magnitude : 12.0 PA: 20 Zone 71 Observations: C8 at 104x. Bright, with a suggestion of central lobes or knots. It magnifies poorly, though. It has a NE-SW axis. Distance: 85,000,000 light years Radial velocity (km/sec): +1,951 Luminosity: 9,000,000,000 Suns Difficult NGC 5173 Other Names: H III 672 Rating: 4 D Position: 1329+4635 Type : Gal Surface brightness: 11.9 Class: E0 Dimensions: 1.0' x 1.0' Magnitude : 12.1 Observations: C8 at 104x. A round ball of mist with no condensation. Radial velocity (km/sec): +2,506 NGC 5198 Other Names: H II 689 Rating: 5 D Position: 1330+4640 Type : Gal Surface brightness: 12.9 Class: E1-2: Dimensions: 2.0' x 1.7' Magnitude : 11.8 Observations: C8 at 104x. Averted vision and tube movement helped bring in this indistinct glow. Three very faint stars frame it. Distance: 110,000,000 light years Radial velocity (km/sec): +2,590 Luminosity: 18,100,000,000 Suns - 20 - Zone 71 Zone 71 Mini-Catalog Double Stars Designation Position Rating Map Zeta UMa 1324+5456 2E 1 h2649 1318+5420 3E 1 STF 1718 1306+5100 4E 1 STF 1747 1328+4745 4E 2 Bemporad 6 1334+5418 4E 3 STF 1776 1342+4613 4E 4 STF 1774 rej 1343+5002 4E 3 h2680 1346+4524 4E 4 h2694 1357+5354 4E 3 LDS 5800 1358+4853 4E 4 STF 1795 1359+5307 4E 3 h2634 1303+4744 5E 2 Bemporad 4 1308+4955 5E 2 h2642 1308+4907 5E 2 Espin 733 1321+5321 5E 1 STF 1770 1338+5043 2M 3 OS 263 1317+5034 4M 1 A. G. 190 1336+4939 4M 4 STF 1758 1333+4909 5M 4 Espin 2646 1334+4648 5M 4 Bur 802 1349+4821 5M 4 Component A B A B A B A B A B A B A B C A B A B A B A B A B A B A B A B A B A B A B A B A B A B - 21 - Mag 2.23 3.85 10.21 10.64 9.5 10.07 9.24 10.12 10.43 11.19 8.53 8.57 6.34 10.51 10.38 10.07 11.51 7.97 11.7 9.81 11.29 6.83 9.96 9.55 13.14 11.56 11.66 10.46 11.26 10.03 10.8 6.95 8.26 8.83 9.89 9.26 9.44 7.98 8.24 8.81 12.5 7.5 11.69 Separation — 14.4 — 21.3 — 13.1 — 15.0 = — 8.3 = — 7.3 = — 17.3 27.6— 23.7 + — 39.2 — 41.6 = — 7.9 + — 30.9 — 21.8 + — 9.1 = — 6.1 = — 1.7 = — 1.8 — 2.6 = — 3.5 — 8.9 — 3.5 + PA — 153 + — 345 + — 272 = — 346 — 189 — 18 -? — 135 + 27.6— 148 — 84 = — 356 = — 2— 60 = — 2— 177 — 212 + — 123 — 136 + — 12 = — 294 — 343 — 225 + Zone 71 Deep Sky Objects Object NGC 5194 NGC 5195 NGC 5377 NGC 5173 NGC 5198 NGC 5225 Position 1330+4712 1330+4716 1356+4714 1329+4635 1330+4640 1333+5129 Rating 1E 4E 3M 4D 5D 5D Map 4 4 4 4 4 3 Specifications Surface Type Mag Br Gal (SA(s)bc pec I-II) 8.7 12.6 Gal (I0 pec) 11.0 13.1 Gal ((R)SB(s)a) 12.0 13.6 Gal (E0) 12.1 11.9 Gal (E1-2:) 11.8 12.9 Gal (S) 13.5 12.4 - 22 - Pop.