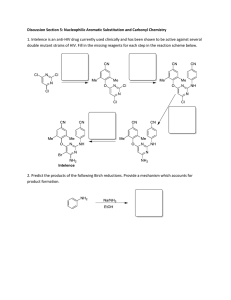
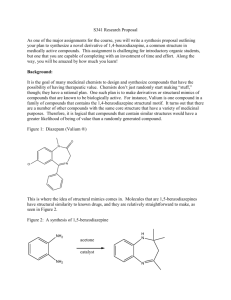
Course Outcomes List
advertisement

Course Outcomes List Chemistry 231: Organic Chemistry II Students will correctly employ reaction mechanisms to describe the progress of organic reactions, including reactions involving more than four steps. Given the molecular formula of a compound of basic to intermediate complexity and spectral data (including a combination of IR, 1H NMR, 13C NMR/DEPT, and MS spectra), students correctly identify important structural features of the compound and synthesize the information obtained to elucidate the compound's structure. Given a specified target molecule of intermediate complexity, students develop a retrosynthesis to a specified starting material, and construct a valid synthesis scheme based on the retrosynthesis, employing protecting groups where appropriate. Students predict the products of reactions of benzene and mono- or di-substituted aromatic compounds in electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions and nucleophilic aromatic substitution reactions. Students determine correct IUPAC and common names for compounds containing one or more of the following functional groups: alcohol, amine, aldehyde, ketone, carboxylic acid, ester, amide. Students correctly predict the major product(s) of compounds containing carbon-oxygen double bonds with common reagents. Students predict the product(s) of reactions of dienes, including (1) reactions employing kinetic or thermodynamic control to favor a particular regioisomer, and (2) reactions with dienophiles via the Diels-Alder reaction. Students correctly predict the products of reactions involving bio-organic compounds (carbohydrates, amino acids, etc.), including (1) synthesis of carbohydrates and their derivatives and (2) peptide synthesis. Page 1 of 1 Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org)