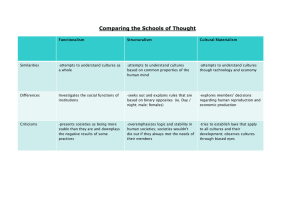
INTRODUCTION TO CULTURE, CULTURAL STUDIES, AND POPULAR CULTURE

INTRODUCTION TO CULTURE,
CULTURAL STUDIES, AND POPULAR CULTURE
This is our proposed model for reading images:
OBJECTIVE
Mahasiswa dapat menyebutkan pengertian culture, cultural studies dan popular culture. (C1)
MATERIALS
1.
What is Culture?
2.
What is Cultural studies?
3.
What is Popular Culture?
WHAT IS CULTURE?
What is culture?
1. A general process of intellectual, spiritual and aesthetic development;
2. A particular way of life, whether of a people, a period, a group or humanity in general;
3. The works and practices of intellectual and especially artistic activity.
(Williams, Raymond. 1983 Keywords: A Vocabulary of Culture and Society .
London: Fontana, 2 nd edn.)
Continued …
The different senses in which the concept of culture can be used can be illustrated as follows: (Baldwin, et.al, 2004: 7)
A play by Shakespeare might be said to be a distinct piece of cultural work (3) … to be a product of a particular (English) way of life (2)
… to represent a certain stage of cultural development (1) … .
Rock ‘n’ roll may be analysed by examining the skills of its performers (3); in terms of its association with youth culture in the late 1950s (2); and as a musical form, looking for its origins in other styles of music and also seeing its influence on later musical forms. (1)
Continued …
Issues and problems in the study of culture . (Baldwin, et.al: 7-23)
-
How do people become part of a culture?
- How does cultural studies interpret what things mean?
- How does cultural studies understand the past?
- Can other cultures be understood?
- How can we understand the relationships between cultures?
- Why are some cultures and cultural forms valued more highly than others?
- What is the relationship between culture and power?
-
How is ‘culture as power’ negotiated and resisted?
- How does culture shape who we are?
WHAT IS CULTURAL STUDIES?
What is Cultural Studies?
1. In cultural studies the concept of culture has a range of meanings which includes both high art and everyday life.
2. Cultural studies advocate an interdiciplinary approach to the study of culture.
3. While cultural studies is eclectic in its use of theory, using both structuralist and more flexible approaches, it advocates those that stress the overlapping, hybrid nature of cultures, seeing cultures as networks rather patchworks.
(Baldwin, Elaine. et.al. 2004. Introducing Cultural Studies . Harlow: Pearson
Prentice Hall. Revised first edition)
Continued …
Some features of cultural studies (Agger, 1992: 2-23)
- An expanded notion of culture.
- Culture is us.
- Culture is practice
- Culture is conflict
- Making space: The decentering and decanonising of culture.
- Production, distribution, consumption.
- Popular culture and populism.
- Dedisciplining.
- Cultural studies and archemedian problem.
- The rejection of absolute values.
WHAT IS POPULAR CULTURE?
What is Popular Culture?
... a set of generally available artefacts: films, records, clothes, TV programmes, modes of transport, etc. … Popular culture can be found in different societies, within different groups in societies, and among societies and groups in different historical periods. …
Popular culture for the mass culture critics is either fold culture in pre-industrial societies or mass culture in industrial societies.
For the Frankfurt School, popular culture is the culture produced by the culture industry to secure the stability and continuity of capitalism. The Frankfurt School thus shares a theory which sees popular culture as a form of dominant ideology with other versions of Marxism, such as those put forward by Althusser and Gramsci.
Continued …
The Marxist political economy perspective comes close to this understanding of popular culture, while variants of feminist theory define it as a form of patriarchal ideology which works in the interests of men and against the interests of women.
While semiology stressses the role of popular culture in obscuring the interests of the powerful – in Barthe’s view the bourgeoisie – some structuralist theories see popular culture as an expression of universal and unchanging social and mental structures.
Those writers who advocate cultural populism define popular culture as a form of consumer subversion which is precisely how they wish to evaluate and explain it.
… according to postmodernist theory, popular culture embodies radical changes in the role of the mass media which wear away the distinction between image and reality.
(Strinati, Dominic. 2004 An Introduction to Theories of Popular Culture . London:
Routledge. Second edition)
Continued …
Five factors that popular culture is serious business
- Popular culture is basically fun but insubstantial, distracting people from the ordeal of workaday existence yet not bearing closer scrutiny except by quotidian television and movie critics;
- … that popular culture betrays traditional cultural values and should be edified;
- … that popular culture is simply a big business that can be understood in the strict terms of Marx’s economic analysis of capitalism;
- … that popular culture is imposed from the top down and has a certain totalizing impermeable quality that cannot be dislodged;
- … popular culture as a relevant arena of cultural politics and hence political theory.
(Agger, Ben. 1992. Cultural Studies as Cultural Theory . London: The Falmer Press)