Name _________________ Test 3 April 16, 2008
advertisement
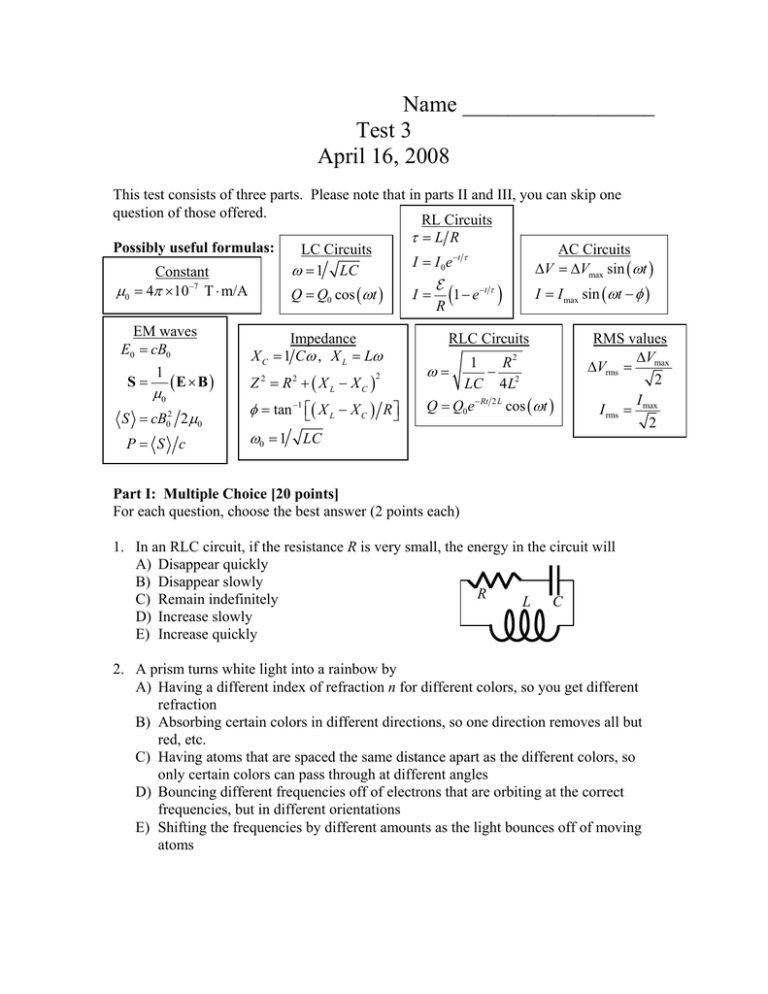
Name _________________ Test 3 April 16, 2008 This test consists of three parts. Please note that in parts II and III, you can skip one question of those offered. RL Circuits Possibly useful formulas: Constant μ0 = 4π ×10−7 T ⋅ m/A τ =L R LC Circuits ω = 1 LC Q = Q0 cos (ωt ) EM waves E0 = cB0 Impedance X C = 1 Cω , X L = Lω 1 Z = R + ( X L − XC ) S= μ0 (E × B) S = cB02 2μ0 P= S c 2 2 AC Circuits ΔV = ΔVmax sin (ωt ) I = I 0 e −t τ 2 φ = tan −1 ⎡⎣( X L − X C ) R ⎤⎦ ω0 = 1 LC I= E 1 − e −t τ ) ( R I = I max sin (ωt − φ ) RLC Circuits 2 1 R − 2 LC 4 L Q = Q0 e − Rt 2 L cos (ωt ) ω= RMS values ΔV ΔVrms = max 2 I I rms = max 2 Part I: Multiple Choice [20 points] For each question, choose the best answer (2 points each) 1. In an RLC circuit, if the resistance R is very small, the energy in the circuit will A) Disappear quickly B) Disappear slowly R C) Remain indefinitely L C D) Increase slowly E) Increase quickly 2. A prism turns white light into a rainbow by A) Having a different index of refraction n for different colors, so you get different refraction B) Absorbing certain colors in different directions, so one direction removes all but red, etc. C) Having atoms that are spaced the same distance apart as the different colors, so only certain colors can pass through at different angles D) Bouncing different frequencies off of electrons that are orbiting at the correct frequencies, but in different orientations E) Shifting the frequencies by different amounts as the light bounces off of moving atoms 3. The Poynting vector points in the direction of A) Motion of the EM wave B) Electric field C) Magnetic field D) Frequency E) None of the above 4. Inductors resist changes in A) Resistance B) Voltage C) Current D) Frequency E) Charge 5. For an ideal transformer, if the voltage is stepped up from 120 V to 240 V, what will happen to the current I? A) It will double B) It will quadruple C) It will cut in half D) It will be cut by ¼ E) It will remain the same 6. If a wave has a wavelength of 2 m, the wave number k must be B) 1/π m-1 C) 4π m-1 D) π m-1 A) 4/π m-1 E) 2π m-1 7. The ray approximation, or geometric optics, should only be applied when A) The frequency of light is much higher than any other frequency in the problem B) The frequency of light is much lower than any other frequency in the problem C) The wavelength is much longer than any other distance in the problem D) The wavelength is much shorter than any other distance in the problem E) None of the above 8. What does a diode do in a power supply? A) It stores charge from cycle to cycle, so the voltage can be kept uniform B) It blocks sudden changes in current caused by external power surges C) It converts the high voltage AC from the outlet into low voltage AC for a device D) It reduces the resistance in subsequent components by increasing the voltage E) It only allows current to flow one way, helping to turn AC into DC 9. To make a circuit where there is a lot of power fed to a resistor at low frequencies, but very little at high frequencies, you should put the resistor in series with A) a capacitor B) an inductor ? C) a capacitor and an inductor D) another resistor E) none of these will work 10. If a light beam is moving at 1.00×108 m/s, the index of refraction n must be about A) 1/3 B) 1/2 C) 1 D) 2 E) 3 Part II: Short answer [20 points] Choose two of the following questions and give a short answer (1-3 sentences). 11. Place the following in order from shortest wavelength to longest: gamma rays, infrared, microwaves, radio waves, ultraviolet, visible light, X-rays. C 12. At t = 0, the capacitor at right has a charge on it, and there is no current flowing. Explain qualitatively the behavior of the circuit. You should include at least one equation. L 13. As a light wave moves from air to glass, which of the following quantities will increase, decrease, or stay the same: velocity, frequency, angular frequency, wavelength, wave number. Part III: Calculation: [60 points] Choose three of the following four questions and perform the indicated calculations (20 points each) 1.5 mH 150 Ω 8Ω 4H 2Ω 14. In the circuit sketched at right, the switch is initially left closed for a long time (a) Describe the steady state circuit. In particular, find the current in the inductor in the steady state, and explain where else, if anywhere the current is flowing. (b) At t = 0, the switch is suddenly opened. At this moment, explain which way the current flows, if any. At t = 0, find the voltage across the 8 Ω resistor, if any. (c) Find an expression for the current at all subsequent + times t > 0. (d) At what time t will the current through the inductor 12 V have dropped to 1 A? 1.00 nF 15. An AC source with ΔVmax = 90 V operating at 120 kHz is fed through a 1.5 mH inductor, a 1 nF (= 10-9 F) capacitor, and a 150 Ω resistor. (a) What is the angular frequency ω? (b) What is the impedance for the inductor alone? For the capacitor alone? (c) What is the impedance for the whole circuit? ΔVmax = 90 V (d) Find the maximum current Imax and the average power f = 120 kHz dissipated in the resistor 16. In the year 2100, the Space Ship Carlson will be launched. It will have mass of 1000 kg and will also have a 300 kg solar sail in the shape of a square of size 20.0 km × 20.0 km. It will be pushed by advanced lasers that can illuminate its entire surface with an intensity of 10 kW/m2, which will impact perpendicular to the solar sail. The solar sail blocks 1/3 of the light, reflects 1/3 of it back, and the remaining 1/3 passes directly through it. (a) Calculate the magnitude of the electric and magnetic fields from the oscillating fields at this power. (b) Calculate the pressure on the solar sail due to the light that is absorbed and reflected. (c) Calculate the total force and the acceleration of the rocket/solar sail. 17. A light beam enters a rectangular aquarium from the side filled with water (n = 1.333) at an angle of θ = 27° below level, as sketched below. At the back of the tank is a mirror, which will reflect the light back into the water. (a) Most of the light will refract and enter the water, as sketched below. At what angle α will it enter the water? (b) After it reflects off the back wall, it will reflect with an angle β compared to normal. Find β (c) When the light reaches the top of the water, will it reflect, refract, or do a combination of both? Sketch which direction(s) it goes, and calculate any relevant angles. water α 27° mirror β